Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, C15H23NO5, contains two independent molecules. Phaeosphaeride A contains two primary sections, an alkyl chain consisting of five C atoms and a cyclic system consisting of fused five- and six-membered rings with attached substituents. In the crystal, the molecules form layered structures. Nearly planar sheets, parallel to the (001) plane, form bilayers of two-dimensional hydrogen-bonded networks with the hydroxy groups located on the interior of the bilayer sheets. The network is constructed primarily of four O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, which form a zigzag pattern in the (001) plane. The butyl chains interdigitate with the butyl chains on adjacent sheets. The crystal was twinned by a twofold rotation about the c axis, with refined major–minor occupancy fractions of 0.718 (6):0.282 (6).
Keywords: crystal structure, natural phaeosphaeride A
Related literature
For details of the extraction of natural phaeosphaeride A and a discussion of its biological activities, see: Maloney et al. (2006 ▸). For details of trials of the synthesis of natural phaeosphaeride A, see: Kobayashi et al. (2011 ▸); Chatzimpaloglou et al. (2012 ▸, 2014 ▸); Kobayashi et al. (2015 ▸). Ring-puckering parameters are as defined by Cremer & Pople (1975 ▸). Hydrogen bonding is described in detail by Desiraju & Steiner (1999 ▸) and by Arunan et al. (2011 ▸). The twin law was identified using TwinRotMat in PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▸). Criteria for absolute configuration determination are described by Flack (1983 ▸) and Parsons et al. (2013 ▸).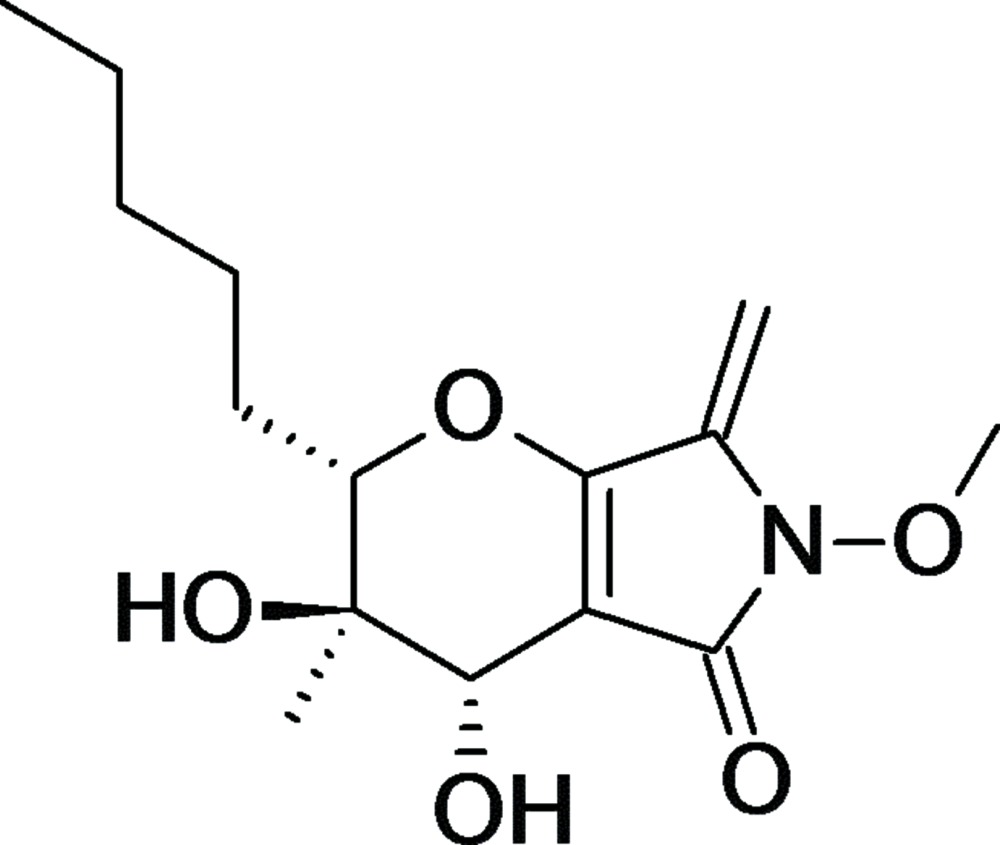
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H23NO5
M r = 297.34
Monoclinic,
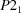
a = 10.14078 (18) Å
b = 9.10361 (14) Å
c = 17.5991 (3) Å
β = 100.1847 (16)°
V = 1599.11 (5) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 0.77 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.35 × 0.35 × 0.05 mm
Data collection
Agilent SuperNova Dual Source diffractometer with an Atlas detector
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012 ▸) T min = 0.824, T max = 1.000
6054 measured reflections
6054 independent reflections
5940 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.058
wR(F 2) = 0.150
S = 1.10
6054 reflections
389 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.36 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 2632 quotients [(I +) − (I −)]/[(I +) + (I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸)
Absolute structure parameter: 0.05 (8)
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2012 ▸); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015 ▸); molecular graphics: OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: OLEX2.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501395X/pk2560sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501395X/pk2560Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501395X/pk2560Isup3.cml
et al. . DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501395X/pk2560fig1.tif
A view of molecules I (left) and II (right) of phaeosphaeride A. The atom numbering scheme is that of Maloney et al. (2006). Displacement ellipsoids are shown at the 50% probability level.
. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501395X/pk2560fig2.tif
Projection of the layered crystal structure of phaeosphaeride A on the (100) plane. The dashed lines indicate the short contacts between molecules of phaeosphaeride A (only hydrogen atoms forming hydrogen bonds are shown).
CCDC reference: 1412515
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2H2O2A | 0.82 | 2.04 | 2.818(5) | 158 |
| O3H3O4i | 0.82 | 2.03 | 2.836(5) | 168 |
| O2AH2AO4i | 0.82 | 2.00 | 2.685(5) | 141 |
| O3AH3AO4A ii | 0.82 | 2.10 | 2.829(5) | 149 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 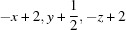 ; (ii)
; (ii) 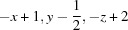 .
.
Acknowledgments
XRD study was completed at the X-ray Diffraction Centre of St Petersburg State University. The research was financially supported by Russian Scientific Fund (project No. 14-26-00067).
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Comment
In 2006, Clardy and colleagues isolated phaeosphaeride A from an endophytic fungus FA39 (Maloney et al., 2006). Phaeosphaeride A turned out to be an inhibitor of signal transduction and an activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)-dependent signaling. It was reported to selectively inhibit STAT3/DNA binding with an IC50 of 0.61 mM and to exhibit promising cell growth inhibition in STAT3-dependent U266 multiple myeloma cells with an IC50 of 6.7 µM.
While the relative stereochemistry of phaeosphaeride A was deduced on the basis of NOE experiments, its absolute configuration remained undetermined (Maloney et al., 2006). Moreover, the attempts of total synthesis of phaeosphaeride A showed considerable differences in 1H and 13C NMR data between the synthetic and natural phaeosphaeride A (Kobayashi et al., 2011; Chatzimpaloglou et al., 2012, 2014). In 2015, Kobayashi and colleagues established the relative and absolute configurations of natural phaeosphaeride A by completing the first total synthesis of ent-phaeosphaeride A (Kobayashi et al., 2015).
Our research group isolated phaeosphaeride A from a fungal strain belonging to the genus Phoma. Phaeosphaeride A was obtained as an optically active (-108.33 (c 0.06, CH2Cl2)) yellow glass. 1H and 13C NMR data as well as mass spectra of our phaeosphaeride A match with the data reported for Clardy's natural phaeosphaeride A (Maloney et al., 2006). Optical rotation of Clardy's product (-93.6 (c 2.0, CH2Cl2)) and our phaeosphaeride A have the same sign. In this work we describe the crystal structure of natural phaeosphaeride A.
S2. Experimental
NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker AVANCE III 400 MHz spectrometer in DMSO-d6. The same solvent was used as an internal standard. High-resolution mass spectra (HRMS) were recorded on a LTQ Orbitrap Velos spectrometer. Optical rotations were determined on an Optical Activity AA-55 polarimeter using a 20 cm cell with a Na 589 nm filter.
Phaeosphaeride A was isolated from solid culture of the fungus Phoma sp. N 19. The microorganism was obtained from leaves of Cirsium arvense (L.) Scop. and deposited in the culture collection of the All-Russian Institute of Plant Protection (Saint-Petersburg, Russian Federation). The metabolite was purified from the fungal extract with a combination of preparative column chromatography and TLC on silica gel to give phaeosphaeride A as a yellow precipitate. (-108.33 (c 0.06, CH2Cl2); 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 5.44 (d, J = 5.8 Hz, 1H), 4.97 (s, 2H), 4.92 (s, 1H), 4.07 (d, J = 11.3 Hz, 1H), 3.86 (d, J = 5.8 Hz, 1H), 3.79 (s, 3H), 1.82 (m, 1H), 1.58-1.22 (m, 7H), 1.19 (s, 3H), 0.86 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100.6 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 166.53, 155.30, 137.12, 104.80, 90.80, 86.25, 70.96, 64.36, 63.76, 30.90, 27.60, 26.11, 21.96, 20.40, 13.85; HRMS [M + H]+ calcd for C15H24NO5 298.16490, found 298.16493. Recrystallization from heptane yielded yellow crystals (-116.66; -108.33 (c 0.06, CH2Cl2).
S3. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 1.
H atoms bonded to C atoms were included in calculated positions and refined using a riding model, with Uiso(H) set to 1.2Ueq(C) and C–H = 0.97 Å for CH2 groups, Uiso(H) set to 1.5Ueq(N) and C–H = 0.96 Å for CH3 groups and Uiso(H) set to 1.2Ueq(N) and C–H = 0.93 Å for CH groups. All H atoms bonded to O atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and were refined with distance restraints and constrained displacement parameters OH 0.82 Å and Uiso(H) set to 1.2Ueq(O). The large thermal ellipsoid on C13 is characteristic for the distal end of long alkyl chains.
The structure of phaeosphaeride A (Fig.1) was refined as rotational twin [by a two-fold rotation about (001)] with twin fractions of 0.718 (6) and 0.282 (6). The 'HKLF 5' format file for the final refinement was generated by the TwinRotMat facility in Platon (Spek, 2009). The ratio (Fc2-Fo2)/esd for the reflections with the highest error in final refinement model (as a rotational twin) has lower residuals than in the initial solution. We have used Bayesian Statistics for verifying absolute structure. Supplementary crystallographic data for this paper have been deposited at Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC 1412515) and can be obtained free of charge via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif.
S4. Geometry
The asymmetric unit contains two independent molecules of phaeosphaeride A (I and II) (fig. 1). Each molecule of phaeosphaeride A (numbering of atoms of phaeosphaeride A is given according to Clardy (Maloney et al., 2006)) contains two primary sections; an alkyl chain consisting of C(13)—C(12)—C(11)—C(10)—C(9) atoms and a cyclic system consisting of five and six membered rings with adjacent atoms.
For the five-membered ring C(1)—N(2)—C(3)—C(4)—C(5) of molecule I the Cremer-Pople (Cremer & Pople, 1975) parameters are Q=0.0714 Å, φ=197.99°, revealing a slightly distorted half-chair (2T1) conformation. Cremer-Pople parameters of Q=0.501 Å, θ=128.71°, φ=88.01° for the six-membered heterocycle of molecule I are consistent with a half-chair conformation (5H4). The geometric parameters of the six-membered rings for both molecules are similar, but the five-membered rings have different conformations. The five-membered ring in molecule II exhibits an envelope (1E) conformation.
Torsion angles O(1)—C(4)—C(5)—C(1) and C(3)—C(4)—C(5)—C(6) are -178.2 (4)° and -177.1 (4)° respectively, corresponding to co-planar conformation between the five and six-membered rings. The geometry of the heterocyclic ring system of the molecule (base of the half chair and the five-membered ring) is close to planar.
The exocyclic alkyl chain of I and the back of the half-chair lie approximately in the same plane. The deviation between the plane of alkyl atoms C(8)—C(9)—C(10)—C(11)—C(12)—C(13) and the back of the chair is 9.7 (4)°.
The geometric parameters are similar for both molecules I and II forming the weak hydrogen-bonded dimer through O2—H2···O2A. But angles characterizing the methoxy groups N(2)—O(5)—C(16) are slightly different (109.9 (3)° for I and 110.4 (4)° for II). The difference between angles O(4)—C(1)—C(5) is much greater with values of 129.4 (4)° and 123.2 (4)° for I and II respectively.
The molecules form layered structures. Nearly planar sheets, parallel with the (001) plane, form primary layers of two-dimensional hydrogen-bonded networks with the hydroxyl moieties located on the interior of the sheets. The network (Fig. 2) is dependent primarily on four hydrogen bonds (Table 1) O2—H2···O2A, O3—H3···O4, O2A—H2A···O4, O3A—H3A···O4A (Desiraju et al., 1999; Arunan et al., 2011). In the (001) plane, two-dimensional hydrogen-bonded networks form a zig-zag pattern. The aliphatic butyl chains interdigitate with the butyl chains on the adjacent sheets.
Figures
Fig. 1.
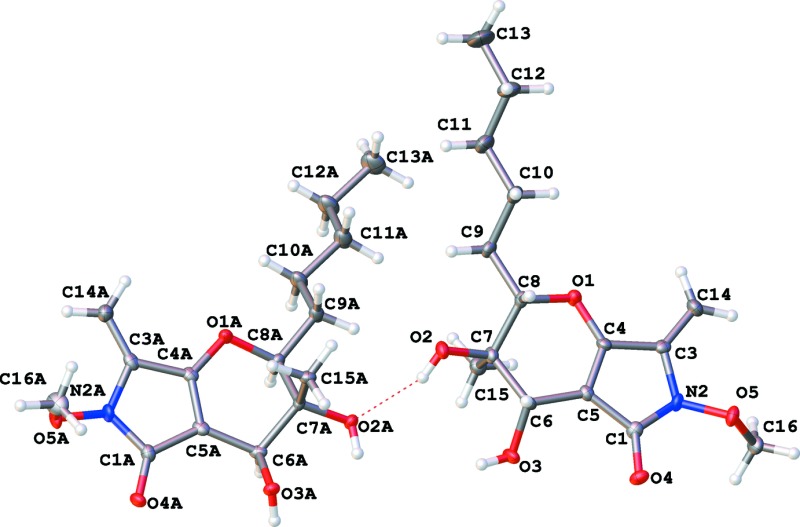
A view of molecules I (left) and II (right) of phaeosphaeride A. The atom numbering scheme is that of Maloney et al. (2006). Displacement ellipsoids are shown at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
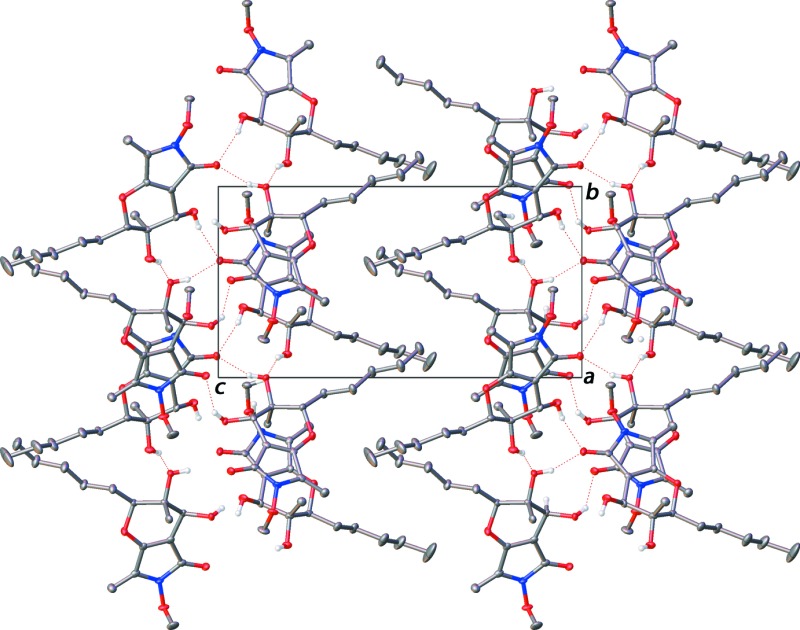
Projection of the layered crystal structure of phaeosphaeride A on the (100) plane. The dashed lines indicate the short contacts between molecules of phaeosphaeride A (only hydrogen atoms forming hydrogen bonds are shown).
Crystal data
| C15H23NO5 | F(000) = 640 |
| Mr = 297.34 | Dx = 1.235 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| a = 10.14078 (18) Å | Cell parameters from 14376 reflections |
| b = 9.10361 (14) Å | θ = 4.4–75.9° |
| c = 17.5991 (3) Å | µ = 0.77 mm−1 |
| β = 100.1847 (16)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 1599.11 (5) Å3 | Tabular, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.35 × 0.35 × 0.05 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova Dual Source diffractometer with an Atlas detector | 6054 measured reflections |
| Radiation source: SuperNova (Cu) X-ray Source | 6054 independent reflections |
| Mirror monochromator | 5940 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.3829 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 70.0°, θmin = 4.4° |
| ω scans | h = −12→12 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012) | k = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.824, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −4→21 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.058 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0289P)2 + 2.9758P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.150 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.10 | Δρmax = 0.36 e Å−3 |
| 6054 reflections | Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3 |
| 389 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 2632 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure parameter: 0.05 (8) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refined as a 2-component twin. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 1.1431 (5) | 0.8972 (6) | 0.9253 (3) | 0.0153 (10) | |
| N2 | 1.1842 (4) | 0.7850 (5) | 0.8817 (2) | 0.0163 (9) | |
| C3 | 1.1862 (5) | 0.8314 (6) | 0.8053 (3) | 0.0149 (10) | |
| C4 | 1.1266 (5) | 0.9782 (6) | 0.8025 (3) | 0.0143 (10) | |
| C5 | 1.0975 (5) | 1.0166 (5) | 0.8717 (3) | 0.0135 (9) | |
| C6 | 1.0311 (5) | 1.1589 (6) | 0.8845 (3) | 0.0159 (10) | |
| H6 | 1.0984 | 1.2269 | 0.9115 | 0.019* | |
| C7 | 0.9703 (5) | 1.2250 (6) | 0.8039 (3) | 0.0167 (10) | |
| C8 | 1.0752 (5) | 1.2122 (5) | 0.7508 (3) | 0.0144 (10) | |
| H8 | 1.1580 | 1.2596 | 0.7765 | 0.017* | |
| C9 | 1.0343 (5) | 1.2809 (6) | 0.6718 (3) | 0.0194 (11) | |
| H9A | 1.0006 | 1.3791 | 0.6779 | 0.023* | |
| H9B | 0.9620 | 1.2237 | 0.6426 | 0.023* | |
| C10 | 1.1482 (5) | 1.2899 (7) | 0.6264 (3) | 0.0231 (11) | |
| H10A | 1.1855 | 1.1924 | 0.6231 | 0.028* | |
| H10B | 1.2183 | 1.3519 | 0.6543 | 0.028* | |
| C11 | 1.1059 (7) | 1.3504 (8) | 0.5454 (4) | 0.0349 (15) | |
| H11A | 1.0380 | 1.2864 | 0.5171 | 0.042* | |
| H11B | 1.0657 | 1.4463 | 0.5487 | 0.042* | |
| C12 | 1.2195 (8) | 1.3646 (9) | 0.5007 (4) | 0.0433 (19) | |
| H12A | 1.2627 | 1.2697 | 0.4998 | 0.052* | |
| H12B | 1.2852 | 1.4326 | 0.5278 | 0.052* | |
| C13 | 1.1771 (12) | 1.4175 (13) | 0.4187 (5) | 0.080 (4) | |
| H13A | 1.1119 | 1.3511 | 0.3913 | 0.120* | |
| H13B | 1.2538 | 1.4211 | 0.3936 | 0.120* | |
| H13C | 1.1387 | 1.5138 | 0.4189 | 0.120* | |
| C14 | 1.2311 (5) | 0.7567 (6) | 0.7508 (3) | 0.0213 (11) | |
| H14A | 1.2660 | 0.6629 | 0.7611 | 0.026* | |
| H14B | 1.2277 | 0.7979 | 0.7021 | 0.026* | |
| C15 | 0.8381 (5) | 1.1508 (6) | 0.7705 (3) | 0.0193 (10) | |
| H15A | 0.8540 | 1.0495 | 0.7600 | 0.029* | |
| H15B | 0.7986 | 1.1992 | 0.7235 | 0.029* | |
| H15C | 0.7782 | 1.1570 | 0.8070 | 0.029* | |
| C16 | 1.2068 (6) | 0.5407 (6) | 0.9208 (3) | 0.0203 (11) | |
| H16A | 1.1648 | 0.5103 | 0.8701 | 0.031* | |
| H16B | 1.1400 | 0.5521 | 0.9528 | 0.031* | |
| H16C | 1.2706 | 0.4678 | 0.9429 | 0.031* | |
| O1 | 1.1050 (4) | 1.0568 (4) | 0.73717 (19) | 0.0172 (7) | |
| O2 | 0.9541 (4) | 1.3789 (4) | 0.8112 (2) | 0.0183 (8) | |
| H2 | 0.8942 | 1.3951 | 0.8359 | 0.027* | |
| O3 | 0.9324 (4) | 1.1327 (4) | 0.9312 (2) | 0.0213 (8) | |
| H3 | 0.9060 | 1.2114 | 0.9456 | 0.032* | |
| O4 | 1.1447 (4) | 0.8881 (4) | 0.99543 (19) | 0.0183 (8) | |
| O5 | 1.2747 (4) | 0.6794 (4) | 0.9159 (2) | 0.0194 (8) | |
| C1A | 0.4815 (5) | 1.9716 (6) | 0.8996 (3) | 0.0156 (10) | |
| N2A | 0.4361 (4) | 2.0638 (5) | 0.8379 (2) | 0.0174 (9) | |
| C3A | 0.4890 (5) | 2.0271 (6) | 0.7717 (3) | 0.0159 (10) | |
| C4A | 0.5564 (5) | 1.8865 (6) | 0.7938 (3) | 0.0136 (9) | |
| C5A | 0.5529 (5) | 1.8520 (5) | 0.8678 (3) | 0.0147 (10) | |
| C6A | 0.6116 (5) | 1.7116 (5) | 0.9032 (3) | 0.0140 (10) | |
| H6A | 0.5393 | 1.6398 | 0.9020 | 0.017* | |
| C7A | 0.7097 (5) | 1.6545 (5) | 0.8525 (3) | 0.0126 (9) | |
| C8A | 0.6355 (5) | 1.6563 (5) | 0.7676 (3) | 0.0140 (10) | |
| H8A | 0.5498 | 1.6055 | 0.7656 | 0.017* | |
| C9A | 0.7086 (5) | 1.5840 (6) | 0.7096 (3) | 0.0191 (11) | |
| H9AA | 0.7419 | 1.4891 | 0.7296 | 0.023* | |
| H9AB | 0.7853 | 1.6439 | 0.7038 | 0.023* | |
| C10A | 0.6212 (6) | 1.5621 (7) | 0.6302 (3) | 0.0223 (11) | |
| H10C | 0.5384 | 1.5139 | 0.6364 | 0.027* | |
| H10D | 0.5986 | 1.6572 | 0.6066 | 0.027* | |
| C11A | 0.6921 (6) | 1.4697 (7) | 0.5771 (3) | 0.0270 (13) | |
| H11C | 0.7732 | 1.5202 | 0.5699 | 0.032* | |
| H11D | 0.7183 | 1.3768 | 0.6023 | 0.032* | |
| C12A | 0.6074 (6) | 1.4392 (8) | 0.4983 (3) | 0.0295 (14) | |
| H12C | 0.5805 | 1.5318 | 0.4730 | 0.035* | |
| H12D | 0.5269 | 1.3871 | 0.5051 | 0.035* | |
| C13A | 0.6823 (7) | 1.3483 (8) | 0.4466 (3) | 0.0344 (15) | |
| H13D | 0.6244 | 1.3297 | 0.3982 | 0.052* | |
| H13E | 0.7096 | 1.2566 | 0.4715 | 0.052* | |
| H13F | 0.7599 | 1.4013 | 0.4377 | 0.052* | |
| C14A | 0.4806 (5) | 2.1038 (6) | 0.7075 (3) | 0.0210 (11) | |
| H14C | 0.4356 | 2.1932 | 0.7026 | 0.025* | |
| H14D | 0.5198 | 2.0685 | 0.6671 | 0.025* | |
| C15A | 0.8399 (5) | 1.7422 (6) | 0.8646 (3) | 0.0160 (10) | |
| H15D | 0.8201 | 1.8444 | 0.8550 | 0.024* | |
| H15E | 0.8958 | 1.7077 | 0.8296 | 0.024* | |
| H15F | 0.8858 | 1.7298 | 0.9168 | 0.024* | |
| C16A | 0.5035 (6) | 2.3002 (6) | 0.8752 (4) | 0.0273 (12) | |
| H16D | 0.5616 | 2.2998 | 0.8376 | 0.041* | |
| H16E | 0.5520 | 2.2663 | 0.9238 | 0.041* | |
| H16F | 0.4719 | 2.3983 | 0.8809 | 0.041* | |
| O1A | 0.6069 (4) | 1.8064 (4) | 0.74144 (18) | 0.0166 (7) | |
| O2A | 0.7369 (3) | 1.5024 (4) | 0.86892 (19) | 0.0145 (7) | |
| H2A | 0.7410 | 1.4877 | 0.9152 | 0.022* | |
| O3A | 0.6775 (3) | 1.7297 (4) | 0.98091 (18) | 0.0145 (7) | |
| H3A | 0.6363 | 1.6850 | 1.0097 | 0.022* | |
| O4A | 0.4586 (4) | 1.9909 (4) | 0.9650 (2) | 0.0179 (7) | |
| O5A | 0.3911 (4) | 2.2045 (4) | 0.8499 (2) | 0.0186 (8) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.015 (2) | 0.013 (2) | 0.017 (2) | −0.004 (2) | −0.0009 (19) | −0.0023 (19) |
| N2 | 0.016 (2) | 0.013 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.0036 (17) | −0.0009 (16) | 0.0025 (17) |
| C3 | 0.011 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.016 (2) | −0.0028 (19) | 0.0039 (18) | 0.0019 (19) |
| C4 | 0.014 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.015 (2) | −0.0008 (19) | 0.0064 (18) | −0.0002 (19) |
| C5 | 0.010 (2) | 0.014 (2) | 0.017 (2) | −0.0018 (19) | 0.0024 (17) | −0.0027 (19) |
| C6 | 0.017 (2) | 0.017 (2) | 0.014 (2) | 0.001 (2) | 0.0063 (19) | −0.0035 (19) |
| C7 | 0.017 (2) | 0.012 (2) | 0.022 (3) | 0.001 (2) | 0.006 (2) | −0.0002 (19) |
| C8 | 0.013 (2) | 0.012 (2) | 0.017 (2) | 0.0003 (18) | −0.0002 (18) | 0.0007 (19) |
| C9 | 0.018 (2) | 0.021 (3) | 0.018 (2) | 0.005 (2) | 0.0005 (19) | 0.006 (2) |
| C10 | 0.022 (3) | 0.027 (3) | 0.020 (3) | 0.009 (2) | 0.003 (2) | 0.008 (2) |
| C11 | 0.037 (4) | 0.041 (4) | 0.027 (3) | 0.016 (3) | 0.009 (3) | 0.017 (3) |
| C12 | 0.055 (5) | 0.047 (4) | 0.035 (3) | 0.015 (4) | 0.027 (3) | 0.021 (3) |
| C13 | 0.113 (9) | 0.095 (8) | 0.046 (5) | 0.054 (7) | 0.049 (5) | 0.046 (5) |
| C14 | 0.021 (3) | 0.022 (3) | 0.022 (3) | 0.005 (2) | 0.009 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C15 | 0.016 (2) | 0.020 (3) | 0.021 (2) | 0.000 (2) | 0.003 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C16 | 0.024 (3) | 0.012 (2) | 0.026 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.007 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0200 (18) | 0.0170 (18) | 0.0144 (16) | 0.0042 (15) | 0.0022 (13) | −0.0008 (14) |
| O2 | 0.0174 (18) | 0.0135 (17) | 0.0253 (19) | 0.0032 (14) | 0.0075 (15) | 0.0004 (14) |
| O3 | 0.030 (2) | 0.0158 (18) | 0.0222 (18) | 0.0035 (16) | 0.0158 (16) | −0.0017 (15) |
| O4 | 0.0252 (19) | 0.0170 (17) | 0.0123 (16) | −0.0038 (15) | 0.0022 (14) | 0.0014 (14) |
| O5 | 0.0177 (18) | 0.0127 (18) | 0.0263 (19) | 0.0023 (14) | −0.0006 (15) | 0.0034 (14) |
| C1A | 0.013 (2) | 0.013 (2) | 0.021 (2) | −0.0010 (19) | 0.0022 (19) | −0.0025 (19) |
| N2A | 0.021 (2) | 0.011 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.0053 (18) | 0.0049 (17) | −0.0022 (17) |
| C3A | 0.010 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.023 (2) | −0.0024 (19) | 0.0038 (18) | −0.005 (2) |
| C4A | 0.010 (2) | 0.014 (2) | 0.017 (2) | −0.0044 (19) | 0.0032 (18) | −0.0027 (19) |
| C5A | 0.013 (2) | 0.014 (2) | 0.019 (2) | −0.0059 (19) | 0.0059 (19) | −0.0034 (19) |
| C6A | 0.016 (2) | 0.014 (2) | 0.012 (2) | −0.0061 (19) | 0.0038 (18) | −0.0016 (18) |
| C7A | 0.012 (2) | 0.011 (2) | 0.015 (2) | 0.0008 (19) | 0.0008 (18) | 0.0019 (18) |
| C8A | 0.014 (2) | 0.014 (2) | 0.013 (2) | 0.0007 (19) | −0.0007 (18) | 0.0015 (18) |
| C9A | 0.018 (3) | 0.024 (3) | 0.015 (2) | 0.006 (2) | 0.002 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C10A | 0.023 (3) | 0.028 (3) | 0.016 (2) | 0.006 (2) | 0.004 (2) | −0.005 (2) |
| C11A | 0.031 (3) | 0.032 (3) | 0.018 (3) | 0.010 (3) | 0.003 (2) | −0.004 (2) |
| C12A | 0.029 (3) | 0.041 (4) | 0.019 (3) | 0.006 (3) | 0.003 (2) | −0.008 (2) |
| C13A | 0.040 (4) | 0.043 (4) | 0.020 (3) | 0.003 (3) | 0.005 (3) | −0.010 (3) |
| C14A | 0.021 (3) | 0.021 (3) | 0.021 (3) | 0.005 (2) | 0.005 (2) | 0.003 (2) |
| C15A | 0.017 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.014 (2) | −0.002 (2) | 0.0056 (18) | 0.0015 (19) |
| C16A | 0.029 (3) | 0.017 (3) | 0.036 (3) | −0.011 (2) | 0.006 (2) | −0.008 (2) |
| O1A | 0.0188 (17) | 0.0195 (18) | 0.0120 (15) | 0.0060 (15) | 0.0039 (13) | 0.0011 (14) |
| O2A | 0.0181 (17) | 0.0128 (17) | 0.0122 (15) | 0.0024 (14) | 0.0016 (13) | 0.0016 (13) |
| O3A | 0.0175 (17) | 0.0154 (17) | 0.0104 (15) | −0.0013 (14) | 0.0022 (13) | 0.0008 (13) |
| O4A | 0.0234 (19) | 0.0152 (18) | 0.0175 (17) | 0.0020 (15) | 0.0105 (14) | −0.0016 (14) |
| O5A | 0.0157 (18) | 0.0102 (17) | 0.0301 (19) | 0.0022 (14) | 0.0044 (15) | −0.0040 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—N2 | 1.385 (7) | C1A—N2A | 1.386 (7) |
| C1—C5 | 1.460 (7) | C1A—C5A | 1.472 (7) |
| C1—O4 | 1.234 (6) | C1A—O4A | 1.226 (6) |
| N2—C3 | 1.412 (6) | N2A—C3A | 1.406 (7) |
| N2—O5 | 1.391 (5) | N2A—O5A | 1.389 (5) |
| C3—C4 | 1.463 (7) | C3A—C4A | 1.471 (7) |
| C3—C14 | 1.320 (7) | C3A—C14A | 1.318 (7) |
| C4—C5 | 1.349 (7) | C4A—C5A | 1.347 (7) |
| C4—O1 | 1.339 (6) | C4A—O1A | 1.345 (6) |
| C5—C6 | 1.495 (7) | C5A—C6A | 1.498 (7) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9800 | C6A—H6A | 0.9800 |
| C6—C7 | 1.563 (7) | C6A—C7A | 1.540 (7) |
| C6—O3 | 1.423 (6) | C6A—O3A | 1.422 (6) |
| C7—C8 | 1.540 (7) | C7A—C8A | 1.549 (6) |
| C7—C15 | 1.523 (7) | C7A—C15A | 1.526 (7) |
| C7—O2 | 1.419 (6) | C7A—O2A | 1.431 (6) |
| C8—H8 | 0.9800 | C8A—H8A | 0.9800 |
| C8—C9 | 1.514 (7) | C8A—C9A | 1.515 (7) |
| C8—O1 | 1.475 (6) | C8A—O1A | 1.455 (6) |
| C9—H9A | 0.9700 | C9A—H9AA | 0.9700 |
| C9—H9B | 0.9700 | C9A—H9AB | 0.9700 |
| C9—C10 | 1.518 (7) | C9A—C10A | 1.529 (7) |
| C10—H10A | 0.9700 | C10A—H10C | 0.9700 |
| C10—H10B | 0.9700 | C10A—H10D | 0.9700 |
| C10—C11 | 1.519 (7) | C10A—C11A | 1.528 (7) |
| C11—H11A | 0.9700 | C11A—H11C | 0.9700 |
| C11—H11B | 0.9700 | C11A—H11D | 0.9700 |
| C11—C12 | 1.510 (9) | C11A—C12A | 1.523 (8) |
| C12—H12A | 0.9700 | C12A—H12C | 0.9700 |
| C12—H12B | 0.9700 | C12A—H12D | 0.9700 |
| C12—C13 | 1.511 (10) | C12A—C13A | 1.527 (8) |
| C13—H13A | 0.9600 | C13A—H13D | 0.9600 |
| C13—H13B | 0.9600 | C13A—H13E | 0.9600 |
| C13—H13C | 0.9600 | C13A—H13F | 0.9600 |
| C14—H14A | 0.9300 | C14A—H14C | 0.9300 |
| C14—H14B | 0.9300 | C14A—H14D | 0.9300 |
| C15—H15A | 0.9600 | C15A—H15D | 0.9600 |
| C15—H15B | 0.9600 | C15A—H15E | 0.9600 |
| C15—H15C | 0.9600 | C15A—H15F | 0.9600 |
| C16—H16A | 0.9600 | C16A—H16D | 0.9600 |
| C16—H16B | 0.9600 | C16A—H16E | 0.9600 |
| C16—H16C | 0.9600 | C16A—H16F | 0.9600 |
| C16—O5 | 1.448 (6) | C16A—O5A | 1.442 (6) |
| O2—H2 | 0.8200 | O2A—H2A | 0.8200 |
| O3—H3 | 0.8200 | O3A—H3A | 0.8200 |
| N2—C1—C5 | 106.4 (4) | N2A—C1A—C5A | 105.5 (4) |
| O4—C1—N2 | 123.6 (5) | O4A—C1A—N2A | 123.9 (5) |
| O4—C1—C5 | 129.9 (5) | O4A—C1A—C5A | 130.6 (5) |
| C1—N2—C3 | 111.3 (4) | C1A—N2A—C3A | 112.5 (4) |
| C1—N2—O5 | 120.6 (4) | C1A—N2A—O5A | 120.8 (4) |
| O5—N2—C3 | 120.0 (4) | O5A—N2A—C3A | 122.0 (4) |
| N2—C3—C4 | 103.3 (4) | N2A—C3A—C4A | 102.4 (4) |
| C14—C3—N2 | 127.0 (5) | C14A—C3A—N2A | 127.4 (5) |
| C14—C3—C4 | 129.7 (5) | C14A—C3A—C4A | 130.1 (5) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 111.2 (4) | C5A—C4A—C3A | 111.6 (4) |
| O1—C4—C3 | 121.4 (4) | O1A—C4A—C3A | 120.4 (4) |
| O1—C4—C5 | 127.4 (5) | O1A—C4A—C5A | 127.9 (5) |
| C1—C5—C6 | 130.4 (4) | C1A—C5A—C6A | 131.2 (4) |
| C4—C5—C1 | 107.1 (4) | C4A—C5A—C1A | 107.1 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 122.5 (5) | C4A—C5A—C6A | 121.6 (4) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 109.0 | C5A—C6A—H6A | 108.7 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 108.3 (4) | C5A—C6A—C7A | 107.3 (4) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 109.0 | C7A—C6A—H6A | 108.7 |
| O3—C6—C5 | 108.9 (4) | O3A—C6A—C5A | 112.7 (4) |
| O3—C6—H6 | 109.0 | O3A—C6A—H6A | 108.7 |
| O3—C6—C7 | 112.6 (4) | O3A—C6A—C7A | 110.8 (4) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 108.5 (4) | C6A—C7A—C8A | 107.6 (4) |
| C15—C7—C6 | 111.0 (4) | C15A—C7A—C6A | 112.0 (4) |
| C15—C7—C8 | 112.8 (4) | C15A—C7A—C8A | 113.0 (4) |
| O2—C7—C6 | 109.4 (4) | O2A—C7A—C6A | 109.3 (4) |
| O2—C7—C8 | 103.5 (4) | O2A—C7A—C8A | 104.4 (4) |
| O2—C7—C15 | 111.4 (4) | O2A—C7A—C15A | 110.3 (4) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 108.3 | C7A—C8A—H8A | 107.8 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 114.8 (4) | C9A—C8A—C7A | 115.7 (4) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 108.3 | C9A—C8A—H8A | 107.8 |
| O1—C8—C7 | 110.8 (4) | O1A—C8A—C7A | 110.5 (4) |
| O1—C8—H8 | 108.3 | O1A—C8A—H8A | 107.8 |
| O1—C8—C9 | 106.1 (4) | O1A—C8A—C9A | 106.8 (4) |
| C8—C9—H9A | 108.9 | C8A—C9A—H9AA | 108.9 |
| C8—C9—H9B | 108.9 | C8A—C9A—H9AB | 108.9 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 113.3 (4) | C8A—C9A—C10A | 113.5 (4) |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 107.7 | H9AA—C9A—H9AB | 107.7 |
| C10—C9—H9A | 108.9 | C10A—C9A—H9AA | 108.9 |
| C10—C9—H9B | 108.9 | C10A—C9A—H9AB | 108.9 |
| C9—C10—H10A | 108.9 | C9A—C10A—H10C | 109.3 |
| C9—C10—H10B | 108.9 | C9A—C10A—H10D | 109.3 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 113.5 (4) | H10C—C10A—H10D | 107.9 |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 107.7 | C11A—C10A—C9A | 111.7 (5) |
| C11—C10—H10A | 108.9 | C11A—C10A—H10C | 109.3 |
| C11—C10—H10B | 108.9 | C11A—C10A—H10D | 109.3 |
| C10—C11—H11A | 108.8 | C10A—C11A—H11C | 108.7 |
| C10—C11—H11B | 108.8 | C10A—C11A—H11D | 108.7 |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 107.7 | H11C—C11A—H11D | 107.6 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 113.9 (5) | C12A—C11A—C10A | 114.0 (5) |
| C12—C11—H11A | 108.8 | C12A—C11A—H11C | 108.7 |
| C12—C11—H11B | 108.8 | C12A—C11A—H11D | 108.7 |
| C11—C12—H12A | 108.7 | C11A—C12A—H12C | 109.1 |
| C11—C12—H12B | 108.7 | C11A—C12A—H12D | 109.1 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 114.2 (7) | C11A—C12A—C13A | 112.4 (5) |
| H12A—C12—H12B | 107.6 | H12C—C12A—H12D | 107.8 |
| C13—C12—H12A | 108.7 | C13A—C12A—H12C | 109.1 |
| C13—C12—H12B | 108.7 | C13A—C12A—H12D | 109.1 |
| C12—C13—H13A | 109.5 | C12A—C13A—H13D | 109.5 |
| C12—C13—H13B | 109.5 | C12A—C13A—H13E | 109.5 |
| C12—C13—H13C | 109.5 | C12A—C13A—H13F | 109.5 |
| H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 | H13D—C13A—H13E | 109.5 |
| H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 | H13D—C13A—H13F | 109.5 |
| H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 | H13E—C13A—H13F | 109.5 |
| C3—C14—H14A | 120.0 | C3A—C14A—H14C | 120.0 |
| C3—C14—H14B | 120.0 | C3A—C14A—H14D | 120.0 |
| H14A—C14—H14B | 120.0 | H14C—C14A—H14D | 120.0 |
| C7—C15—H15A | 109.5 | C7A—C15A—H15D | 109.5 |
| C7—C15—H15B | 109.5 | C7A—C15A—H15E | 109.5 |
| C7—C15—H15C | 109.5 | C7A—C15A—H15F | 109.5 |
| H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 | H15D—C15A—H15E | 109.5 |
| H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 | H15D—C15A—H15F | 109.5 |
| H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 | H15E—C15A—H15F | 109.5 |
| H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 | H16D—C16A—H16E | 109.5 |
| H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 | H16D—C16A—H16F | 109.5 |
| H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 | H16E—C16A—H16F | 109.5 |
| O5—C16—H16A | 109.5 | O5A—C16A—H16D | 109.5 |
| O5—C16—H16B | 109.5 | O5A—C16A—H16E | 109.5 |
| O5—C16—H16C | 109.5 | O5A—C16A—H16F | 109.5 |
| C4—O1—C8 | 112.3 (4) | C4A—O1A—C8A | 111.8 (4) |
| C7—O2—H2 | 109.5 | C7A—O2A—H2A | 109.5 |
| C6—O3—H3 | 109.5 | C6A—O3A—H3A | 109.5 |
| N2—O5—C16 | 110.1 (4) | N2A—O5A—C16A | 109.9 (4) |
| C1—N2—C3—C4 | −6.7 (5) | C1A—N2A—C3A—C4A | 8.7 (5) |
| C1—N2—C3—C14 | 173.8 (5) | C1A—N2A—C3A—C14A | −170.0 (5) |
| C1—N2—O5—C16 | 107.4 (5) | C1A—N2A—O5A—C16A | 76.8 (6) |
| C1—C5—C6—C7 | −165.0 (5) | C1A—C5A—C6A—C7A | −162.9 (5) |
| C1—C5—C6—O3 | −42.4 (7) | C1A—C5A—C6A—O3A | −40.7 (7) |
| N2—C1—C5—C4 | −6.6 (5) | N2A—C1A—C5A—C4A | 5.5 (5) |
| N2—C1—C5—C6 | 173.7 (5) | N2A—C1A—C5A—C6A | −172.8 (5) |
| N2—C3—C4—C5 | 2.4 (5) | N2A—C3A—C4A—C5A | −5.0 (5) |
| N2—C3—C4—O1 | −176.8 (4) | N2A—C3A—C4A—O1A | 172.2 (4) |
| C3—N2—O5—C16 | −106.7 (5) | C3A—N2A—O5A—C16A | −77.1 (6) |
| C3—C4—C5—C1 | 2.5 (6) | C3A—C4A—C5A—C1A | −0.2 (6) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −177.7 (4) | C3A—C4A—C5A—C6A | 178.2 (4) |
| C3—C4—O1—C8 | −166.3 (4) | C3A—C4A—O1A—C8A | −164.3 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 15.3 (7) | C4A—C5A—C6A—C7A | 19.1 (6) |
| C4—C5—C6—O3 | 137.9 (5) | C4A—C5A—C6A—O3A | 141.3 (4) |
| C5—C1—N2—C3 | 8.4 (6) | C5A—C1A—N2A—C3A | −9.1 (6) |
| C5—C1—N2—O5 | 157.1 (4) | C5A—C1A—N2A—O5A | −165.3 (4) |
| C5—C4—O1—C8 | 14.7 (7) | C5A—C4A—O1A—C8A | 12.4 (7) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −45.3 (5) | C5A—C6A—C7A—C8A | −49.7 (5) |
| C5—C6—C7—C15 | 79.3 (5) | C5A—C6A—C7A—C15A | 75.0 (5) |
| C5—C6—C7—O2 | −157.4 (4) | C5A—C6A—C7A—O2A | −162.5 (4) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −176.2 (4) | C6A—C7A—C8A—C9A | −171.8 (4) |
| C6—C7—C8—O1 | 63.7 (5) | C6A—C7A—C8A—O1A | 66.7 (5) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 170.0 (5) | C7A—C8A—C9A—C10A | 168.8 (4) |
| C7—C8—O1—C4 | −47.0 (5) | C7A—C8A—O1A—C4A | −45.8 (5) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 176.6 (5) | C8A—C9A—C10A—C11A | −171.9 (5) |
| C9—C8—O1—C4 | −172.2 (4) | C9A—C8A—O1A—C4A | −172.5 (4) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 178.0 (6) | C9A—C10A—C11A—C12A | 177.7 (5) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 177.0 (8) | C10A—C11A—C12A—C13A | 179.3 (6) |
| C14—C3—C4—C5 | −178.1 (5) | C14A—C3A—C4A—C5A | 173.7 (5) |
| C14—C3—C4—O1 | 2.7 (8) | C14A—C3A—C4A—O1A | −9.1 (8) |
| C15—C7—C8—C9 | 60.4 (6) | C15A—C7A—C8A—C9A | 64.2 (6) |
| C15—C7—C8—O1 | −59.7 (5) | C15A—C7A—C8A—O1A | −57.4 (5) |
| O1—C4—C5—C1 | −178.4 (5) | O1A—C4A—C5A—C1A | −177.1 (5) |
| O1—C4—C5—C6 | 1.4 (8) | O1A—C4A—C5A—C6A | 1.3 (8) |
| O1—C8—C9—C10 | −67.3 (6) | O1A—C8A—C9A—C10A | −67.7 (6) |
| O2—C7—C8—C9 | −60.1 (5) | O2A—C7A—C8A—C9A | −55.7 (5) |
| O2—C7—C8—O1 | 179.8 (4) | O2A—C7A—C8A—O1A | −177.2 (4) |
| O3—C6—C7—C8 | −165.6 (4) | O3A—C6A—C7A—C8A | −173.1 (4) |
| O3—C6—C7—C15 | −41.1 (6) | O3A—C6A—C7A—C15A | −48.4 (5) |
| O3—C6—C7—O2 | 82.2 (5) | O3A—C6A—C7A—O2A | 74.1 (5) |
| O4—C1—N2—C3 | −173.2 (5) | O4A—C1A—N2A—C3A | 173.0 (5) |
| O4—C1—N2—O5 | −24.5 (7) | O4A—C1A—N2A—O5A | 16.8 (8) |
| O4—C1—C5—C4 | 175.2 (5) | O4A—C1A—C5A—C4A | −176.8 (5) |
| O4—C1—C5—C6 | −4.6 (9) | O4A—C1A—C5A—C6A | 5.0 (9) |
| O5—N2—C3—C4 | −155.6 (4) | O5A—N2A—C3A—C4A | 164.6 (4) |
| O5—N2—C3—C14 | 24.9 (8) | O5A—N2A—C3A—C14A | −14.2 (8) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2···O2A | 0.82 | 2.04 | 2.818 (5) | 158 |
| O3—H3···O4i | 0.82 | 2.03 | 2.836 (5) | 168 |
| O2A—H2A···O4i | 0.82 | 2.00 | 2.685 (5) | 141 |
| O3A—H3A···O4Aii | 0.82 | 2.10 | 2.829 (5) | 149 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+2; (ii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+2.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: PK2560).
References
- Agilent (2012). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England.
- Arunan, E., Desiraju, G. R., Klein, R. A., Sadley, J., Scheiner, S., Alcorta, I., Clary, D. C., Crabtree, R. H., Dannenberg, J. J., Hobza, P., Kjaergaard, H. G., Legon, A. C., Menucci, B. & Nesbitt, D. J. (2011). Pure Appl. Chem. 83, 1637–1641.
- Chatzimpaloglou, A., Kolosov, M., Eckols, T. K., Tweardy, D. J. & Sarli, V. (2014). J. Org. Chem. 79, 4043–4054. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chatzimpaloglou, A., Yavropoulou, M. P., Rooij, K. E., Biedermann, R., Mueller, U., Kaskel, S. & Sarli, V. (2012). J. Org. Chem. 77, 9659–9667. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Desiraju, G. R. & Steiner, T. (1999). In The Weak Hydrogen Bond in Structural Chemistry and Biology. New York: Oxford University Press Inc.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Kobayashi, K., Kobayashi, Y., Nakamura, M., Tamura, O. & Kogen, H. (2015). J. Org. Chem. 80, 1243–1248. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K., Okamoto, I., Morita, N., Kiyotani, T. & Tamura, O. (2011). Org. Biomol. Chem. 9, 5825–5832. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Maloney, K. N., Hao, W., Xu, J., Gibbons, J., Hucul, J., Roll, D., Brady, S. F., Schroeder, F. C. & Clardy, J. (2006). Org. Lett. 8, 4067–4070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501395X/pk2560sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501395X/pk2560Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501395X/pk2560Isup3.cml
et al. . DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501395X/pk2560fig1.tif
A view of molecules I (left) and II (right) of phaeosphaeride A. The atom numbering scheme is that of Maloney et al. (2006). Displacement ellipsoids are shown at the 50% probability level.
. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501395X/pk2560fig2.tif
Projection of the layered crystal structure of phaeosphaeride A on the (100) plane. The dashed lines indicate the short contacts between molecules of phaeosphaeride A (only hydrogen atoms forming hydrogen bonds are shown).
CCDC reference: 1412515
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


