Abstract
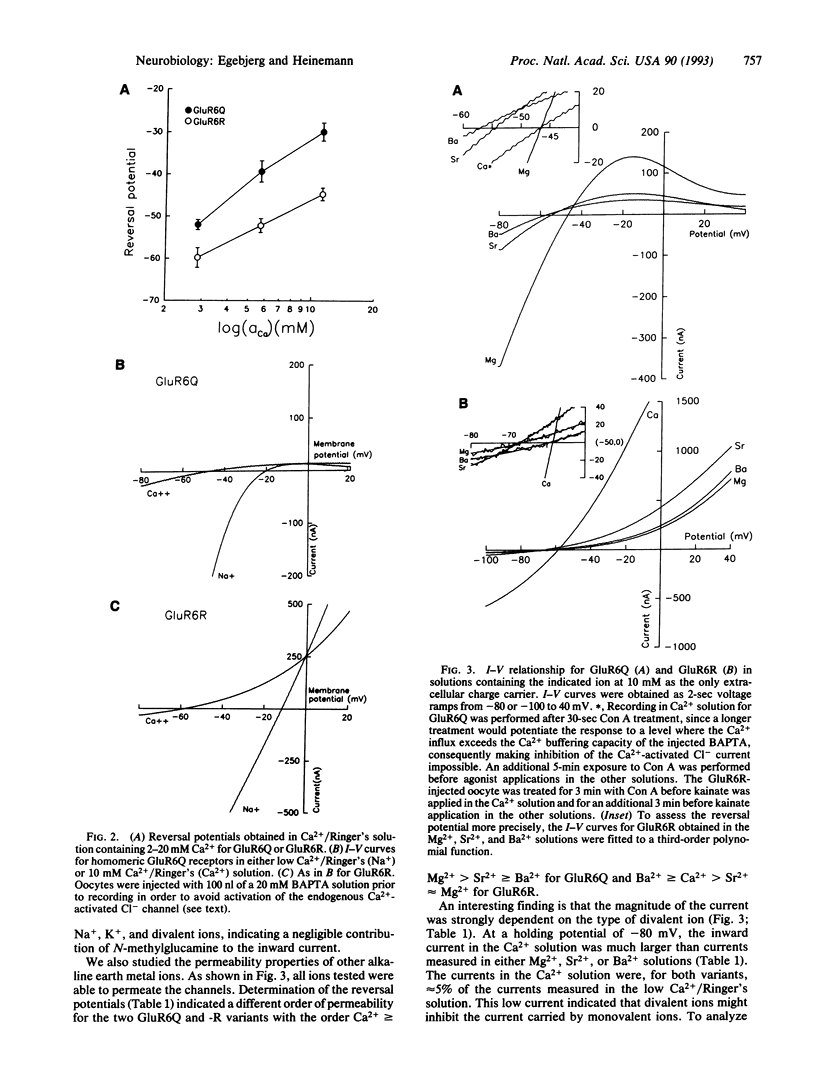
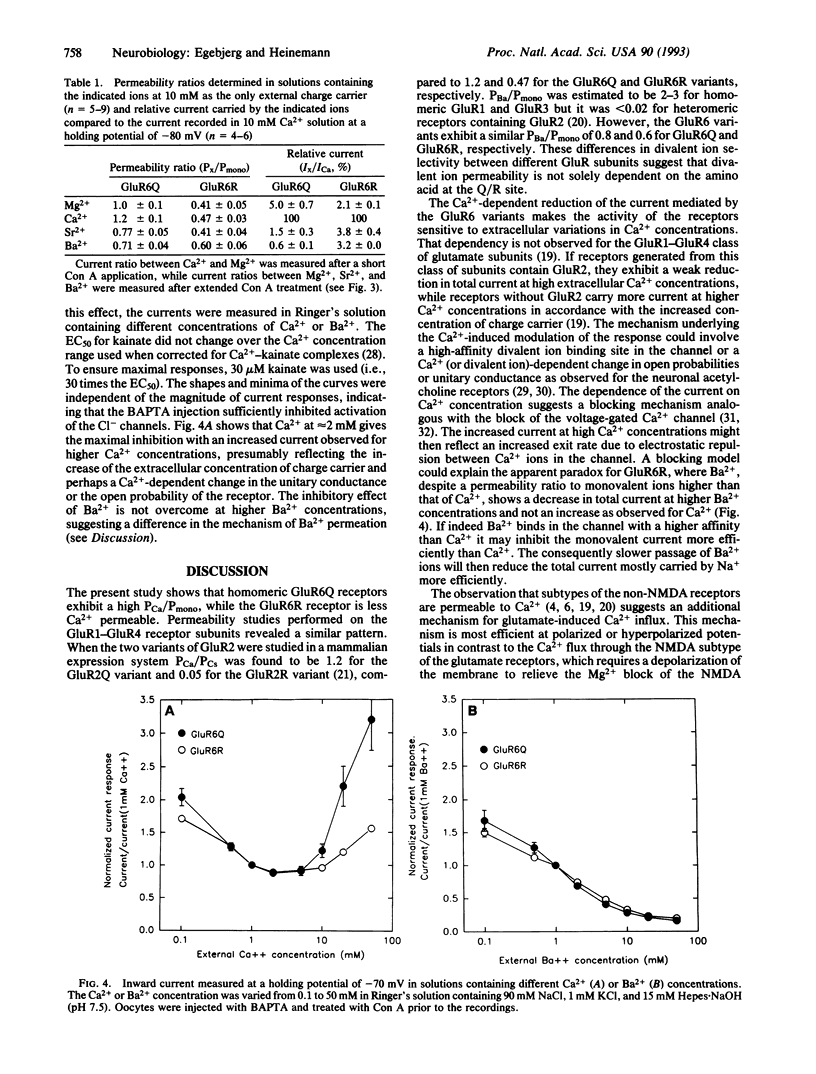
The Ca2+ permeability of the kainate selective glutamate receptor GluR6 depends on the editing of the RNA (or DNA). The unedited version of GluR6, GluR6Q, encodes a glutamine at position 621 (Q/R site) and exhibits a Ca2+/monovalent ion permeability ratio of 1.2, while the edited version of GluR6, GluR6R, encodes an arginine at position 621 and exhibits a permeability ratio of 0.47. Kainate activation of the GluR6 receptor results in currents that are modulated by extracellular calcium ions. Permeability ratios of other divalent ions indicate that the Q/R site is not the only determinant for divalent ion permeability. The level of editing of the receptor will determine the Ca2+ influx through the GluR6 receptor channels and, consequently, may modulate the synaptic activity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bettler B., Boulter J., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Deneris E. S., Moll C., Borgmeyer U., Hollmann M., Heinemann S. Cloning of a novel glutamate receptor subunit, GluR5: expression in the nervous system during development. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):583–595. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90213-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettler B., Egebjerg J., Sharma G., Pecht G., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Moll C., Stevens C. F., Heinemann S. Cloning of a putative glutamate receptor: a low affinity kainate-binding subunit. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90292-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Hollmann M., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Hartley M., Deneris E., Maron C., Heinemann S. Molecular cloning and functional expression of glutamate receptor subunit genes. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1033–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.2168579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Khodorova A., Jonas P., Helm P. J., Wisden W., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Calcium-permeable AMPA-kainate receptors in fusiform cerebellar glial cells. Science. 1992 Jun 12;256(5063):1566–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.1317970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Divalent ion permeability of AMPA receptor channels is dominated by the edited form of a single subunit. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Hume R. I., Heinemann S. F. Structural determinants of barium permeation and rectification in non-NMDA glutamate receptor channels. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):4080–4087. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-04080.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Bettler B., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Heinemann S. Cloning of a cDNA for a glutamate receptor subunit activated by kainate but not AMPA. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):745–748. doi: 10.1038/351745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbertson T. A., Scobey R., Wilson M. Permeation of calcium ions through non-NMDA glutamate channels in retinal bipolar cells. Science. 1991 Mar 29;251(5001):1613–1615. doi: 10.1126/science.1849316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaum S. R., Holzwarth J. A., Miller R. J. Glutamate receptors activate Ca2+ mobilization and Ca2+ influx into astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3454–3458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y. P., Huang L. Y. Block of kainate receptor channels by Ca2+ in isolated spinal trigeminal neurons of rat. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):777–784. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90174-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herb A., Burnashev N., Werner P., Sakmann B., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. The KA-2 subunit of excitatory amino acid receptors shows widespread expression in brain and forms ion channels with distantly related subunits. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Calcium channel selectivity for divalent and monovalent cations. Voltage and concentration dependence of single channel current in ventricular heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):293–319. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Hartley M., Heinemann S. Ca2+ permeability of KA-AMPA--gated glutamate receptor channels depends on subunit composition. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):851–853. doi: 10.1126/science.1709304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Rogers S. W., Heinemann S. Cloning by functional expression of a member of the glutamate receptor family. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):643–648. doi: 10.1038/342643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume R. I., Dingledine R., Heinemann S. F. Identification of a site in glutamate receptor subunits that controls calcium permeability. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1028–1031. doi: 10.1126/science.1653450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M., Ozawa S., Tsuzuki K. Permeation of calcium through excitatory amino acid receptor channels in cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:151–165. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keinänen K., Wisden W., Sommer B., Werner P., Herb A., Verdoorn T. A., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. A family of AMPA-selective glutamate receptors. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):556–560. doi: 10.1126/science.2166337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. Permeation and block of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor channels by divalent cations in mouse cultured central neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:501–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. A calcium-dependent transient outward current in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Jul 22;215(1201):491–497. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I. Chloride current induced by injection of calcium into Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:173–183. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulle C., Choquet D., Korn H., Changeux J. P. Calcium influx through nicotinic receptor in rat central neurons: its relevance to cellular regulation. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90115-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S. N., Thayer S. A., Miller R. J. The effects of excitatory amino acids on intracellular calcium in single mouse striatal neurons in vitro. J Neurosci. 1987 Dec;7(12):4145–4158. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-12-04145.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi N., Shneider N. A., Axel R. A family of glutamate receptor genes: evidence for the formation of heteromultimeric receptors with distinct channel properties. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):569–581. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90212-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakimura K., Bujo H., Kushiya E., Araki K., Yamazaki M., Yamazaki M., Meguro H., Warashina A., Numa S., Mishina M. Functional expression from cloned cDNAs of glutamate receptor species responsive to kainate and quisqualate. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 15;272(1-2):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80452-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakimura K., Morita T., Kushiya E., Mishina M. Primary structure and expression of the gamma 2 subunit of the glutamate receptor channel selective for kainate. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90293-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Burnashev N., Verdoorn T. A., Keinänen K., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. A glutamate receptor channel with high affinity for domoate and kainate. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1651–1656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Köhler M., Sprengel R., Seeburg P. H. RNA editing in brain controls a determinant of ion flow in glutamate-gated channels. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90568-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A., Burnashev N., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Structural determinants of ion flow through recombinant glutamate receptor channels. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1715–1718. doi: 10.1126/science.1710829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernino S., Amador M., Luetje C. W., Patrick J., Dani J. A. Calcium modulation and high calcium permeability of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90114-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner P., Voigt M., Keinänen K., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. Cloning of a putative high-affinity kainate receptor expressed predominantly in hippocampal CA3 cells. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):742–744. doi: 10.1038/351742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



