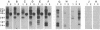Abstract
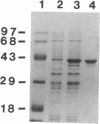
We report the cloning of a Leishmania chagasi antigen gene and an evaluation of leishmaniasis patient antibody responses to the recombinant protein, rK39. rK39 contains a 39-amino acid repeat that is part of a 230-kDa protein predominant in L. chagasi tissue amastigotes. Sequence analyses showed this protein, LcKin, to be related to the kinesin superfamily of motor proteins. Southern blot analyses demonstrated LcKin-related sequences in seven species of Leishmania, with conservation of the repeat between L. chagasi and Leishmania donovani. Serological evaluation revealed that 98% (56 of 57) of Brazilian and 100% (52 of 52) of Sudanese visceral leishmaniasis patients have high antibody levels to the rK39 repeat. Detectable anti-K39 antibody was virtually absent in cutaneous and mucosal leishmaniasis patients and in individuals infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. The data show that rK39 may replace crude parasite antigens as a basis for serological diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badaro R., Jones T. C., Carvalho E. M., Sampaio D., Reed S. G., Barral A., Teixeira R., Johnson W. D., Jr New perspectives on a subclinical form of visceral leishmaniasis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Dec;154(6):1003–1011. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.6.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badaró R., Reed S. G., Barral A., Orge G., Jones T. C. Evaluation of the micro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for antibodies in American visceral leishmaniasis: antigen selection for detection of infection-specific responses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Jan;35(1):72–78. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley S. M., Ismach R. B., Pratt D. M. Evolution of the genus Leishmania as revealed by comparisons of nuclear DNA restriction fragment patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):484–488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaxter M. L., Miles M. A., Kelly J. M. Specific serodiagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis using a Leishmania donovani antigen identified by expression cloning. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Sep;30(3):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S. Motor proteins for cytoplasmic microtubules. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):66–73. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90060-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. M., Jr, Scott J. M., Carvalho E. M., Russo D. M., March C. J., Van Ness K. P., Reed S. G. Characterization of a membrane antigen of Leishmania amazonensis that stimulates human immune responses. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):742–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. M., Jr, Shreffler W. G., Rosman D. E., Sleath P. R., March C. J., Reed S. G. Identification and synthesis of a major conserved antigenic epitope of Trypanosoma cruzi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1239–1243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghose A. C., Haldar J. P., Pal S. C., Mishra B. P., Mishra K. K. Serological investigations on Indian kala-azar. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 May;40(2):318–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoft D. F., Kim K. S., Otsu K., Moser D. R., Yost W. J., Blumin J. H., Donelson J. E., Kirchhoff L. V. Trypanosoma cruzi expresses diverse repetitive protein antigens. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1959–1967. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1959-1967.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommel M., Peters W., Ranque J., Quilici M., Lanotte G. The micro-ELISA technique in the serodiagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1978 Jun;72(3):213–218. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1978.11719308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibañez C. F., Affranchino J. L., Macina R. A., Reyes M. B., Leguizamon S., Camargo M. E., Aslund L., Pettersson U., Frasch A. C. Multiple Trypanosoma cruzi antigens containing tandemly repeated amino acid sequence motifs. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jul;30(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90129-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe C. L., Zalis M. Use of purified parasite proteins from Leishmania donovani for the rapid serodiagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;157(6):1212–1220. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.6.1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Coppel R. L., Anders R. F. Repetitive proteins and genes of malaria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:181–208. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.001145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafaille J. J., Linss J., Krieger M. A., Souto-Padrón T., de Souza W., Goldenberg S. Structure and expression of two Trypanosoma cruzi genes encoding antigenic proteins bearing repetitive epitopes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jun 15;35(2):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90115-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T. F., de la Cruz V. F., Good M. F., Wellems T. E. Antigenic diversity in Plasmodium falciparum. Prog Allergy. 1988;41:173–192. doi: 10.1159/000415223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka A. J., Jeyaprakash A., García-Añoveros J., Tang L. Z., Fisk G., Hartshorne T., Franco R., Born T. The C. elegans unc-104 gene encodes a putative kinesin heavy chain-like protein. Neuron. 1991 Jan;6(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90126-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. G., Badaro R., Lloyd R. M. Identification of specific and cross-reactive antigens of Leishmania donovani chagasi by human infection sera. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1596–1601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. G., Shreffler W. G., Burns J. M., Jr, Scott J. M., Orge M. da G., Ghalib H. W., Siddig M., Badaro R. An improved serodiagnostic procedure for visceral leishmaniasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Dec;43(6):632–639. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.43.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholler J. K., Reed S. G., Stuart K. Molecular karyotype of species and subspecies of Leishmania. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Sep;20(3):279–293. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard H. W., Dwyer D. M. Cloning of Leishmania donovani genes encoding antigens recognized during human visceral leishmaniasis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Apr;19(1):35–43. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeiky Y. A., Benson D. R., Parsons M., Elkon K. B., Reed S. G. Cloning and expression of Trypanosoma cruzi ribosomal protein P0 and epitope analysis of anti-P0 autoantibodies in Chagas' disease patients. J Exp Med. 1992 Jul 1;176(1):201–211. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D. Microtubule motors: many new models off the assembly line. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Aug;17(8):300–304. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90440-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis A. E., McMaster W. R. Identification of Leishmania genes encoding proteins containing tandemly repeating peptides. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1814–1824. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Laymon R. A., Goldstein L. S. A three-domain structure of kinesin heavy chain revealed by DNA sequence and microtubule binding analyses. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):879–889. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90692-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Safi S. H., Evans D. A. A comparison of the direct agglutination test and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the sero-diagnosis of leishmaniasis in the Sudan. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1989 May-Jun;83(3):334–337. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(89)90493-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]