Abstract
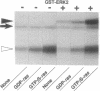
To identify the direct target molecule of ras p21 in higher eukaryotes, we have recently developed the cell-free system in which ras p21 activates mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). In this cell-free system, the guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate- bound form of Ki-ras p21, but not the GDP-bound form, activates endogenous Xenopus MAP kinase as well as recombinant ERK2 in the presence of the cytosol fraction of Xenopus oocytes. We separated two protein factors from the cytosol fraction of Xenopus oocytes by column chromatography: one was the inactive form of MAP kinase kinase and the other was a factor tentatively named ras p21-dependent ERK-kinase stimulator (REKS). The former and latter showed M(r) values of approximately 45,000 and 150,000-200,000, respectively, as estimated by gel filtration. Both factors were necessary for Ki-ras p21-dependent activation of MAP kinase/ERK2. These results indicate that an additional protein factor (REKS) is essential for Ki-ras p21 to activate MAP kinase through MAP kinase kinase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Seger R., Bratlien R. L., Diltz C. D., Tonks N. K., Krebs E. G. Multiple components in an epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase cascade. In vitro activation of a myelin basic protein/microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4220–4227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgering B. M., Medema R. H., Maassen J. A., van de Wetering M. L., van der Eb A. J., McCormick F., Bos J. L. Insulin stimulation of gene expression mediated by p21ras activation. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1103–1109. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Graves J. D., Warne P. H., Rayter S., Cantrell D. A. Stimulation of p21ras upon T-cell activation. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):719–723. doi: 10.1038/346719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Cooper G. M. Inhibition of NIH 3T3 cell proliferation by a mutant ras protein with preferential affinity for GDP. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3235–3243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Dixon R. A., Vogel U. S. Modulation of guanine nucleotides bound to Ras in NIH3T3 cells by oncogenes, growth factors, and the GTPase activating protein (GAP). J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20437–20442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Moriyama K., Matsuda S., Okumura E., Kishimoto T., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K., Yahara I., Sakai H., Nishida E. Xenopus M phase MAP kinase: isolation of its cDNA and activation by MPF. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2661–2668. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Matsuda S., Shiina N., Kosako H., Shiokawa K., Akiyama T., Ohta K., Sakai H. In vitro effects on microtubule dynamics of purified Xenopus M phase-activated MAP kinase. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):251–254. doi: 10.1038/349251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Yamashita T., Hoshi M., Kawakami M., Sakai H. Microtubule-associated-protein (MAP) kinase activated by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in PC12 cells. Identity with the mitogen-activated MAP kinase of fibroblastic cells. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):661–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez N., Cohen P. Dissection of the protein kinase cascade by which nerve growth factor activates MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):170–173. doi: 10.1038/353170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi M., Nishida E., Sakai H. Activation of a Ca2+-inhibitable protein kinase that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro by growth factors, phorbol esters, and serum in quiescent cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5396–5401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., App H., Zhang X. F., Banerjee P., Brautigan D. L., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ERK2, by p21ras oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):569–574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda S., Kosako H., Takenaka K., Moriyama K., Sakai H., Akiyama T., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Xenopus MAP kinase activator: identification and function as a key intermediate in the phosphorylation cascade. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):973–982. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05136.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. ras GTPase activating protein: signal transmitter and signal terminator. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90976-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Kaibuchi K., Yamamoto T., Kawamura M., Sakoda T., Fujioka H., Matsuura Y., Takai Y. A stimulatory GDP/GTP exchange protein for smg p21 is active on the post-translationally processed form of c-Ki-ras p21 and rhoA p21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6442–6446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakielny S., Cohen P., Wu J., Sturgill T. MAP kinase activator from insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle is a protein threonine/tyrosine kinase. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2123–2129. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05271.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nori M., L'Allemain G., Weber M. J. Regulation of tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate-induced responses in NIH 3T3 cells by GAP, the GTPase-activating protein associated with p21c-ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):936–945. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerance M., Schweighoffer F., Tocque B., Pierre M. Stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by oncogenic Ras p21 in Xenopus oocytes. Requirement for Ras p21-GTPase-activating protein interaction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16155–16160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Rapid stimulation by insulin of a serine/threonine kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Endo M., Nakafuku M., Nakamura S., Kaziro Y. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates formation of active p21ras.GTP complex in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5993–5997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Ahn N. G., Boulton T. G., Yancopoulos G. D., Panayotatos N., Radziejewska E., Ericsson L., Bratlien R. L., Cobb M. H., Krebs E. G. Microtubule-associated protein 2 kinases, ERK1 and ERK2, undergo autophosphorylation on both tyrosine and threonine residues: implications for their mechanism of activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6142–6146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Ahn N. G., Posada J., Munar E. S., Jensen A. M., Cooper J. A., Cobb M. H., Krebs E. G. Purification and characterization of mitogen-activated protein kinase activator(s) from epidermal growth factor-stimulated A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14373–14381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeberényi J., Cai H., Cooper G. M. Effect of a dominant inhibitory Ha-ras mutation on neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5324–5332. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Kikuchi A., Kawata M. Small GTP-binding proteins. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;133:187–230. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61861-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., D'Arcangelo G., Halegoua S., Brugge J. S. Ras is essential for nerve growth factor- and phorbol ester-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of MAP kinases. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1031–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90075-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usui H., Kinohara N., Yoshikawa K., Imazu M., Imaoka T., Takeda M. Phosphoprotein phosphatases in human erythrocyte cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10455–10463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries-Smits A. M., Burgering B. M., Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J., Bos J. L. Involvement of p21ras in activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2. Nature. 1992 Jun 18;357(6379):602–604. doi: 10.1038/357602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]