Abstract
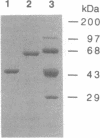
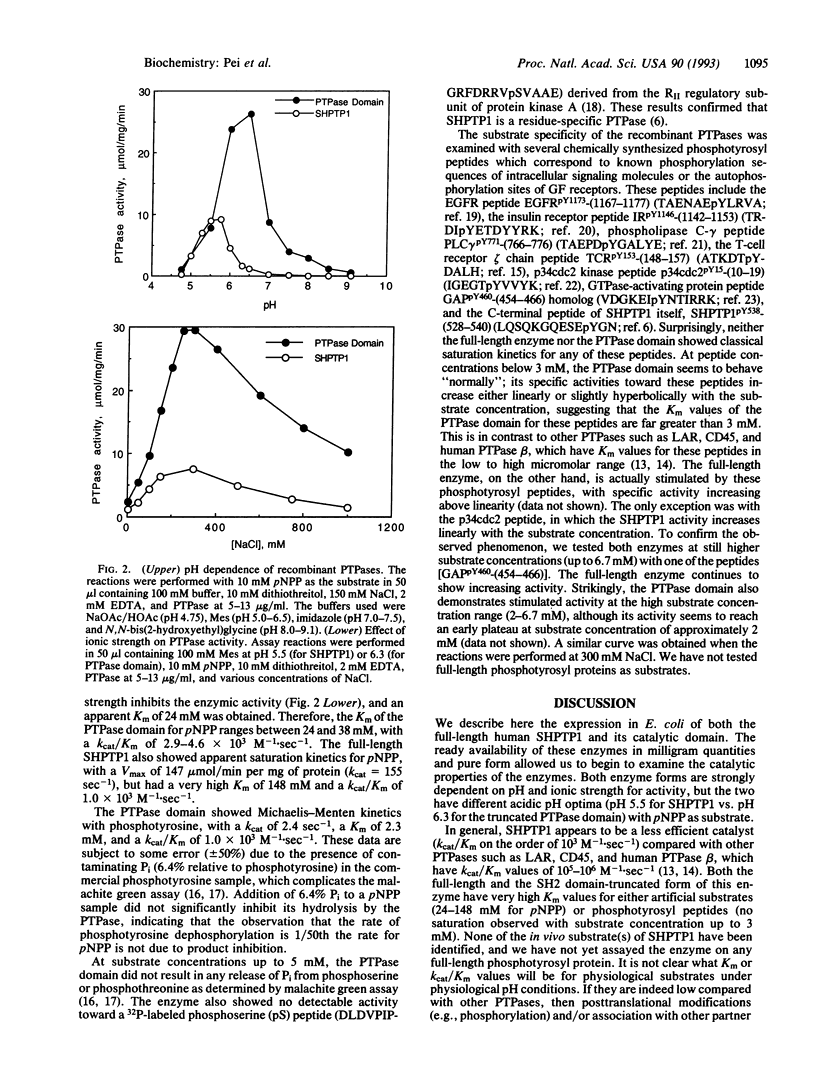
A protein-tyrosine-phosphatase (PTPase; EC 3.1.3.48) containing two Src homology 2 (SH2) domains, SHPTP1, was previously identified in hematopoietic and epithelial cells. By placing the coding sequence of the PTPase behind a bacteriophage T7 promoter, we have overexpressed both the full-length enzyme and a truncated PTPase domain in Escherichia coli. In each case, the soluble enzyme was expressed at levels of 3-4% of total soluble E. coli protein. The recombinant proteins had molecular weights of 63,000 and 45,000 for the full-length protein and the truncated PTPase domain, respectively, as determined by SDS/PAGE. The recombinant enzymes dephosphorylated p-nitrophenyl phosphate, phosphotyrosine, and phosphotyrosyl peptides but not phosphoserine, phosphothreonine, or phosphoseryl peptides. The enzymes showed a strong dependence on pH and ionic strength for their activity, with pH optima of 5.5 and 6.3 for the full-length enzyme and the catalytic domain, respectively, and an optimal NaCl concentration of 250-300 mM. The recombinant PTPases had high Km values for p-nitrophenyl phosphate and exhibited non-Michaelis-Menten kinetics for phosphotyrosyl peptides.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrein K. E., Flint N., Panholzer B., Burn P. Ras GTPase-activating protein: a substrate and a potential binding protein of the protein-tyrosine kinase p56lck. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3343–3346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Molecular themes in oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90636-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal D. K., Takio K., Hansen R. S., Krebs E. G. Dephosphorylation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulatory subunit (type II) by calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase. Determinants of substrate specificity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8140–8145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H. The leukocyte common antigen (CD45): a putative receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7182–7186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J., Ramer S. E., Itoh M., Winkler D. G., Kitas E., Bannwarth W., Burn P., Saito H., Walsh C. T. Purification and characterization of a soluble catalytic fragment of the human transmembrane leukocyte antigen related (LAR) protein tyrosine phosphatase from an Escherichia coli expression system. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 25;30(25):6210–6216. doi: 10.1021/bi00239a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H., Ramer S. E., Itoh M., Kitas E., Bannwarth W., Burn P., Saito H., Walsh C. T. Catalytic domains of the LAR and CD45 protein tyrosine phosphatases from Escherichia coli expression systems: purification and characterization for specificity and mechanism. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):133–138. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer E. H., Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: a diverse family of intracellular and transmembrane enzymes. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):401–406. doi: 10.1126/science.1650499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. M., Jr, Plutzky J., Neel B. G. Identification of a human src homology 2-containing protein-tyrosine-phosphatase: a putative homolog of Drosophila corkscrew. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11239–11243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Perrino B. A., Soderling T. R. Identification of an autoinhibitory domain in calcineurin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1924–1927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennelly P. J., Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Rabbit skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase. The calmodulin binding domain as a potential active site-directed inhibitory domain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):11958–11963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. W., Sim S. S., Kim U. H., Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Carpenter G., Rhee S. G. Tyrosine residues in bovine phospholipase C-gamma phosphorylated by the epidermal growth factor receptor in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3940–3943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyasu S., McConkey D. J., Clayton L. K., Abraham S., Yandava B., Katagiri T., Moingeon P., Yamamoto T., Reinherz E. L. Phosphorylation of multiple CD3 zeta tyrosine residues leads to formation of pp21 in vitro and in vivo. Structural changes upon T cell receptor stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3375–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzetta P. A., Alvarez L. J., Reinach P. S., Candia O. A. An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B., Pallen C. J., Wang J. H., Graves D. J. Use of fluorinated tyrosine phosphates to probe the substrate specificity of the low molecular weight phosphatase activity of calcineurin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):14932–14937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. J., Bowne D. B., Flores E., Thomas M. L. Characterization of hematopoietic intracellular protein tyrosine phosphatases: description of a phosphatase containing an SH2 domain and another enriched in proline-, glutamic acid-, serine-, and threonine-rich sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2396–2405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr J. W., Keranen L. M., Newton A. C. Reversible exposure of the pseudosubstrate domain of protein kinase C by phosphatidylserine and diacylglycerol. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15263–15266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins L. A., Larsen I., Perrimon N. corkscrew encodes a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase that functions to transduce the terminal signal from the receptor tyrosine kinase torso. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90098-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plutzky J., Neel B. G., Rosenberg R. D. Isolation of a src homology 2-containing tyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1123–1127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. H., Bastien L., Posner B. I., Chrétien P. A protein-tyrosine phosphatase with sequence similarity to the SH2 domain of the protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):736–739. doi: 10.1038/352736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Krueger N. X., Hall L. R., Schlossman S. F., Saito H. A new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that has a cytoplasmic region homologous to the leukocyte common antigen. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1523–1530. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Takayama S., Kahn C. R. Differences in the sites of phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9470–9478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi T. L., Cleveland J. L., Ihle J. N. Protein tyrosine phosphatase containing SH2 domains: characterization, preferential expression in hematopoietic cells, and localization to human chromosome 12p12-p13. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):836–846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zander N. F., Lorenzen J. A., Cool D. E., Tonks N. K., Daum G., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H. Purification and characterization of a human recombinant T-cell protein-tyrosine-phosphatase from a baculovirus expression system. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 16;30(28):6964–6970. doi: 10.1021/bi00242a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]