Abstract
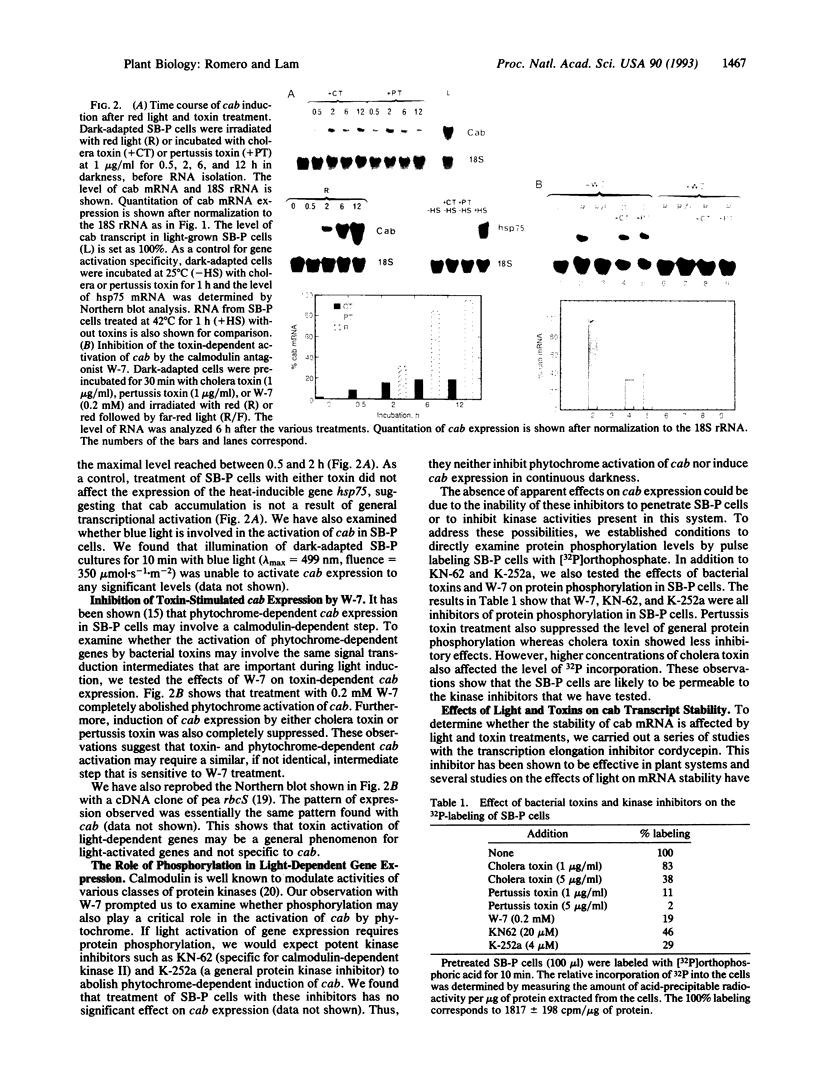
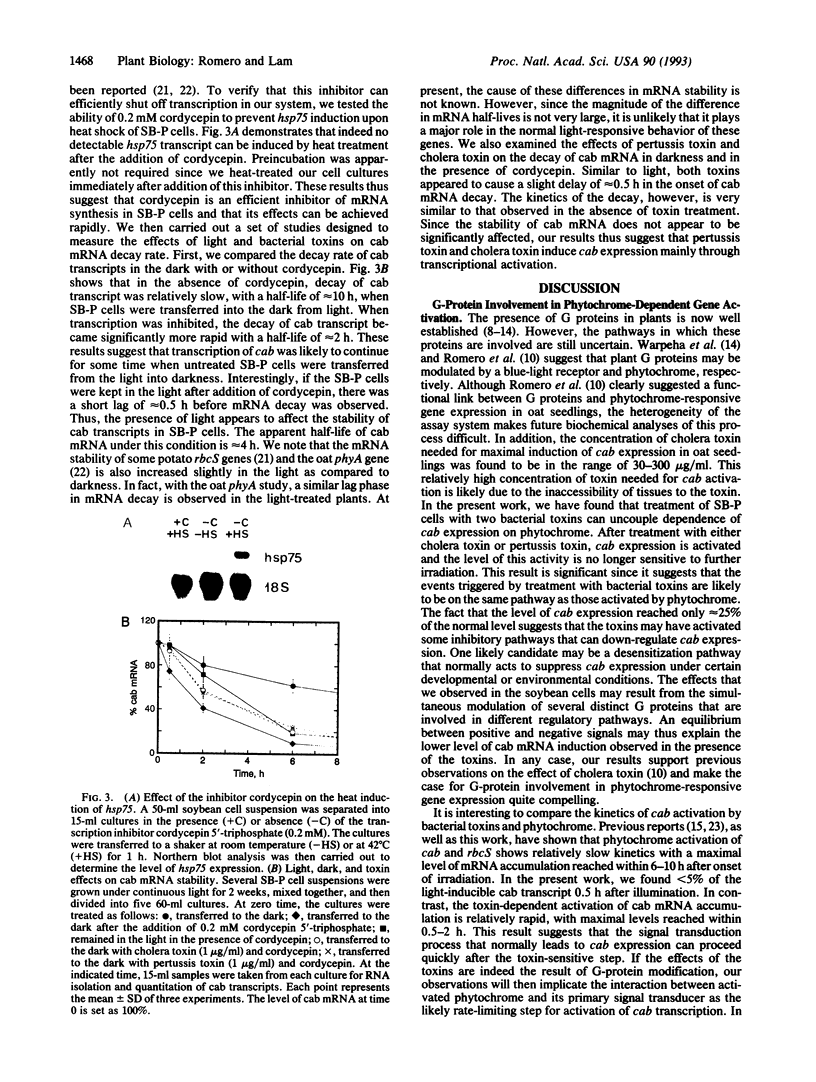
The transmission process of light signals from plant photoreceptors to target cellular events is largely unknown. In the present work, we show that treatment of dark-adapted soybean cells (SB-P) with cholera toxin or pertussis toxin uncouples phytochrome-dependent gene expression. Addition of as little as 10 ng of toxin per ml is sufficient to activate expression of genes encoding the major chlorophyll a/b-binding protein (cab) in the dark. Significant levels of cab transcript accumulation are detected within 0.5 h after addition of the toxins and expression of these genes is desensitized to further light treatments. Treatment of SB-P cells with the calmodulin antagonist N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphtha-lenesulfonamide hydrochloride (W-7) prevents induction of the photoregulated gene by phytochrome or bacterial toxins. These results indicate the involvement of guanine nucleotide binding protein(s) in phytochrome-mediated cab gene activation. A likely site of action for this step is between the photoreceptor and a downstream W-7-sensitive effector.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blum W., Hinsch K. D., Schultz G., Weiler E. W. Identification of GTP-binding proteins in the plasma membrane of higher plants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 31;156(2):954–959. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chory J. Light signals in leaf and chloroplast development: photoreceptors and downstream responses in search of a transduction pathway. New Biol. 1991 Jun;3(6):538–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coruzzi G., Broglie R., Cashmore A., Chua N. H. Nucleotide sequences of two pea cDNA clones encoding the small subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and the major chlorophyll a/b-binding thylakoid polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1399–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Caspar T., Quail P. H. cop1: a regulatory locus involved in light-controlled development and gene expression in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1172–1182. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairley-Grenot K., Assmann S. M. Evidence for G-Protein Regulation of Inward K+ Channel Current in Guard Cells of Fava Bean. Plant Cell. 1991 Sep;3(9):1037–1044. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.9.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz C. C., Herget T., Wolter F. P., Schell J., Schreier P. H. Reduced steady-state levels of rbcS mRNA in plants kept in the dark are due to differential degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4458–4462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin P. M., Sarokin L., Memelink J., Chua N. H. Molecular light switches for plant genes. Plant Cell. 1990 May;2(5):369–378. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.5.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nakafuku M., Satoh T. Structure and function of signal-transducing GTP-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:349–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Benedyk M., Chua N. H. Characterization of phytochrome-regulated gene expression in a photoautotrophic cell suspension: possible role for calmodulin. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4819–4823. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Green P. J., Wong M., Chua N. H. Phytochrome activation of two nuclear genes requires cytoplasmic protein synthesis. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2777–2783. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma H., Yanofsky M. F., Meyerowitz E. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of GPA1, a G protein alpha subunit gene from Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3821–3825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCurdy D. W., Pratt L. H. Immunogold electron microscopy of phytochrome in Avena: identification of intracellular sites responsible for phytochrome sequestering and enhanced pelletability. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2541–2550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Carlson J., Hagen G., Rubenstein I., Oleson A. Cloning and sequencing of the ribosomal RNA genes in maize: the 17S region. DNA. 1984;3(1):31–40. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quail P. H. Phytochrome: a light-activated molecular switch that regulates plant gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:389–409. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero L. C., Sommer D., Gotor C., Song P. S. G-proteins in etiolated Avena seedlings. Possible phytochrome regulation. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 6;282(2):341–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80509-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman H., Lou L. L. Multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase: domain structure and regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):62–66. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeley K. A., Byrne D. H., Colbert J. T. Red Light-Independent Instability of Oat Phytochrome mRNA in Vivo. Plant Cell. 1992 Jan;4(1):29–38. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dop C., Yamanaka G., Steinberg F., Sekura R. D., Manclark C. R., Stryer L., Bourne H. R. ADP-ribosylation of transducin by pertussis toxin blocks the light-stimulated hydrolysis of GTP and cGMP in retinal photoreceptors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):23–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walling L. L., Chang Y. C., Demmin D. S., Holzer F. M. Isolation, characterization and evolutionary relatedness of three members from the soybean multigene family encoding chlorophyll a/b binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10477–10492. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warpeha K. M., Hamm H. E., Rasenick M. M., Kaufman L. S. A blue-light-activated GTP-binding protein in the plasma membranes of etiolated peas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8925–8929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]