Abstract
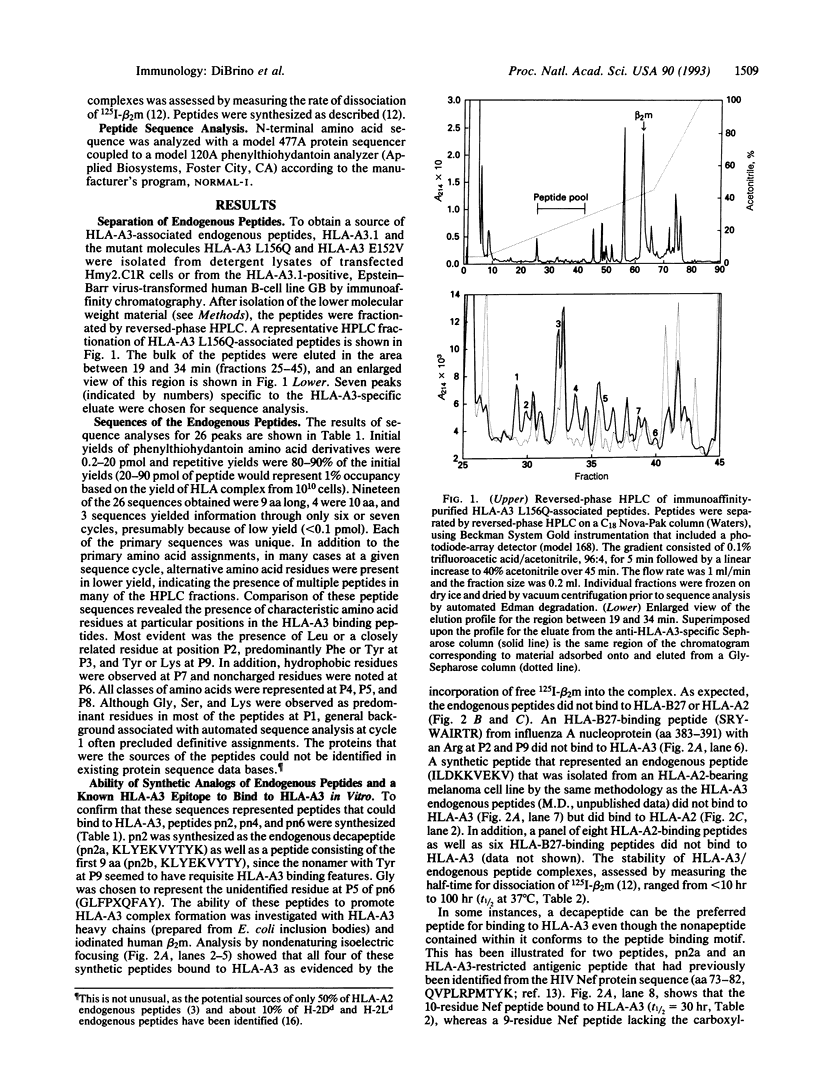
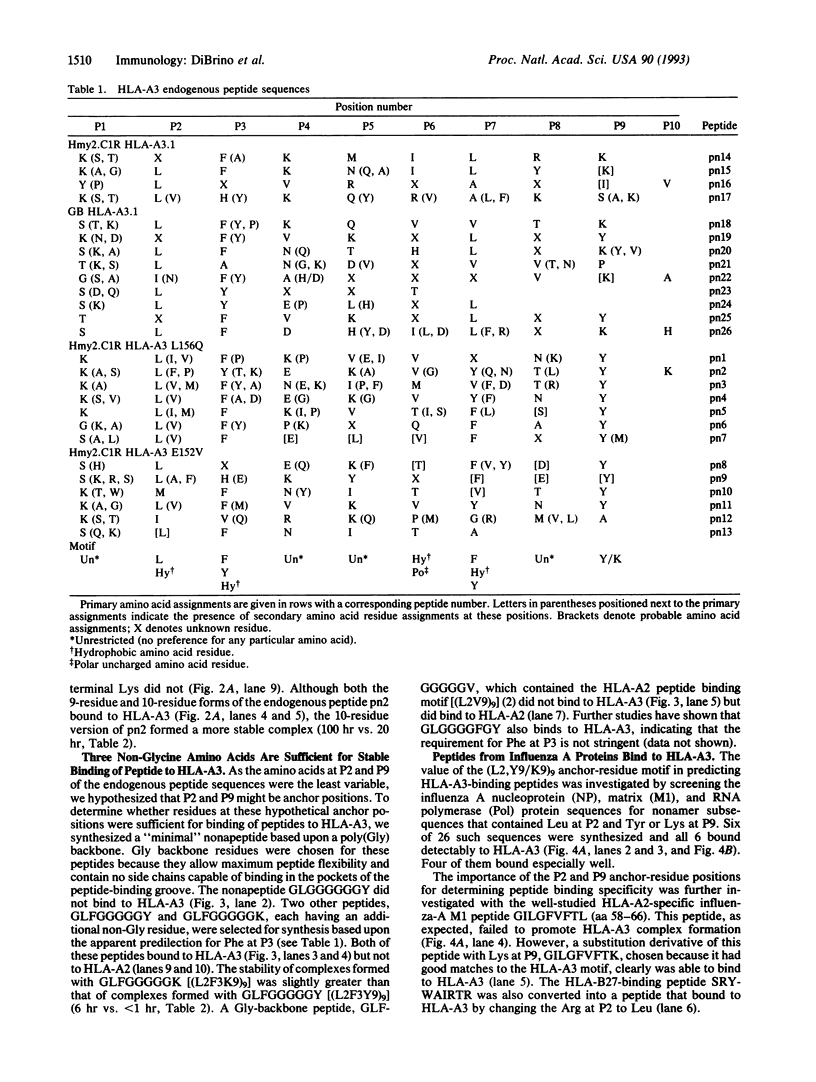
A motif specific to peptides that bind to the human class I major histocompatibility complex molecule HLA-A3 was identified by sequence analysis of HPLC fractions containing endogenous peptides. Twenty-six different sequences were obtained, 19 of which were nonamers. The majority of these endogenous peptide sequences contained Leu at position (P)2, while most sequences contained Tyr or Lys at P9. In addition, Phe was shared by 16 sequences at P3. Synthetic peptides corresponding to endogenous peptide sequences were shown to bind to HLA-A3. The importance of Leu at P2 and Tyr or Lys at P9 ("anchor" residues) for peptide binding to HLA-A3 was demonstrated by the following results: (i) peptides GLFGGGGGY, GLFGGGGGK, and GLGGGGFGY, but not GLFGGGGGV, specifically bound to HLA-A3 and (ii) six nonapeptides from within the influenza A nucleoprotein, matrix, and polymerase proteins, selected for synthesis based upon their possession of P2 and P9 anchor residues, were shown to bind HLA-A3. In contrast, none of a set of eight peptides that bound to HLA-A2, or six that bound to HLA-B27, bound detectably to HLA-A3. These findings provide a rationale for the design and selection of peptides that can be recognized by HLA-A3-restricted T cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger A. E., Davis J. E., Cresswell P. Monoclonal antibody to HLA-A3. Hybridoma. 1982;1(2):87–90. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1.1982.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corr M., Boyd L. F., Frankel S. R., Kozlowski S., Padlan E. A., Margulies D. H. Endogenous peptides of a soluble major histocompatibility complex class I molecule, H-2Lds: sequence motif, quantitative binding, and molecular modeling of the complex. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1681–1692. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K., Rötzschke O., Stevanović S., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. Allele-specific motifs revealed by sequencing of self-peptides eluted from MHC molecules. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):290–296. doi: 10.1038/351290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. F., Henderson R. A., Shabanowitz J., Sakaguchi K., Michel H., Sevilir N., Cox A. L., Appella E., Engelhard V. H. Characterization of peptides bound to the class I MHC molecule HLA-A2.1 by mass spectrometry. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1261–1263. doi: 10.1126/science.1546328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky T. S., Lane W. S., Robinson R. A., Madden D. R., Wiley D. C. Identification of self peptides bound to purified HLA-B27. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):326–329. doi: 10.1038/353326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelachich M. L., Cowan E. P., Turner R. V., Coligan J. E., Biddison W. E. Analysis of the molecular basis of HLA-A3 recognition by cytotoxic T cells using defined mutants of the HLA-A3 molecule. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1108–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Fuerst T. R., Wood L. V., Woods R. M., Suzich J. A., Jones G. M., de la Cruz V. F., Davey R. T., Jr, Venkatesan S., Moss B. Mapping the fine specificity of a cytolytic T cell response to HIV-1 nef protein. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):127–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latron F., Moots R., Rothbard J. B., Garrett T. P., Strominger J. L., McMichael A. Positioning of a peptide in the cleft of HLA-A2 by complementing amino acid changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11325–11329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden D. R., Gorga J. C., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The structure of HLA-B27 reveals nonamer self-peptides bound in an extended conformation. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):321–325. doi: 10.1038/353321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes: specificity, surveillance, and escape. Adv Cancer Res. 1992;59:227–244. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60307-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. C., Carreno B. M., Sestak L., Utz U., Biddison W. E., Coligan J. E. Peptide binding to HLA-A2 and HLA-B27 isolated from Escherichia coli. Reconstitution of HLA-A2 and HLA-B27 heavy chain/beta 2-microglobulin complexes requires specific peptides. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5451–5459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. C., DiBrino M., Hull L., Coligan J. E. The beta 2-microglobulin dissociation rate is an accurate measure of the stability of MHC class I heterotrimers and depends on which peptide is bound. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):1896–1904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saper M. A., Bjorkman P. J., Wiley D. C. Refined structure of the human histocompatibility antigen HLA-A2 at 2.6 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):277–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90567-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Dai L. C., Fuerst T. R., Biddison W. E., Earl P. L., Moss B., Ennis F. A. Specific lysis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected cells by a HLA-A3.1-restricted CD8+ cytotoxic T-lymphocyte clone that recognizes a conserved peptide sequence within the gp41 subunit of the envelope protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10277–10281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A. R., Rothbard J., Gotch F. M., Bahadur G., Wraith D., McMichael A. J. The epitopes of influenza nucleoprotein recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be defined with short synthetic peptides. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]