Abstract
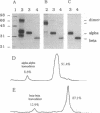
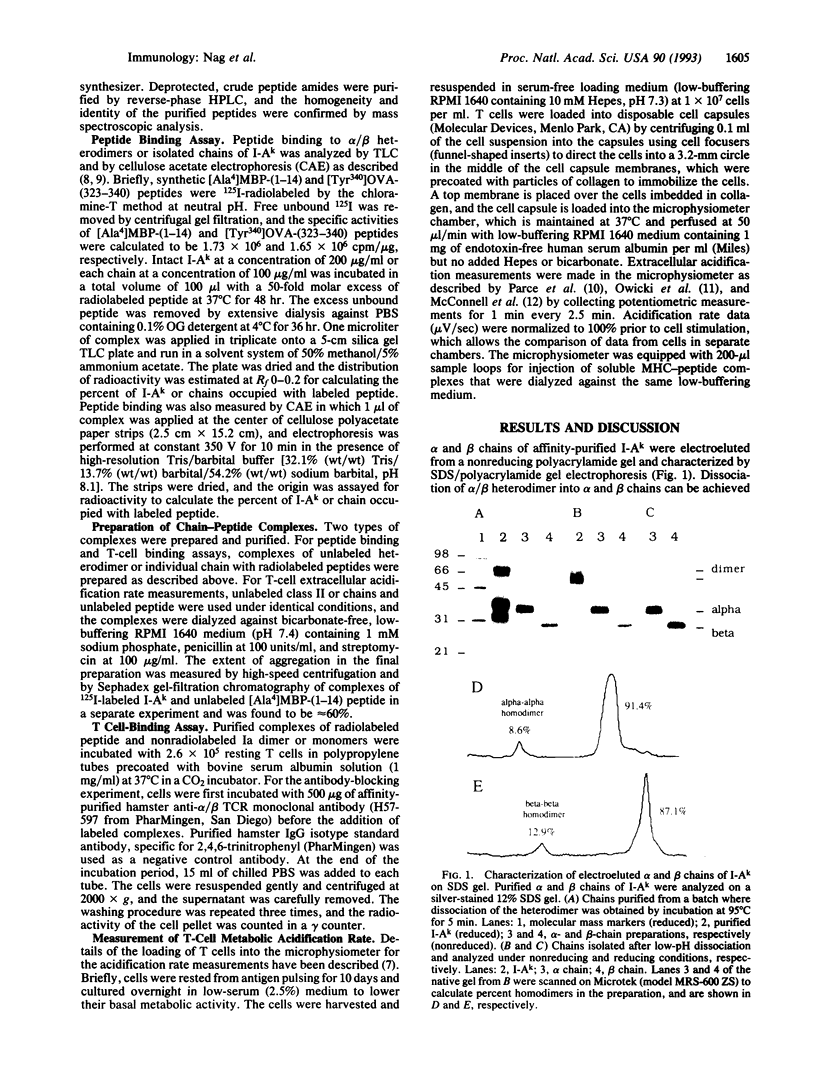
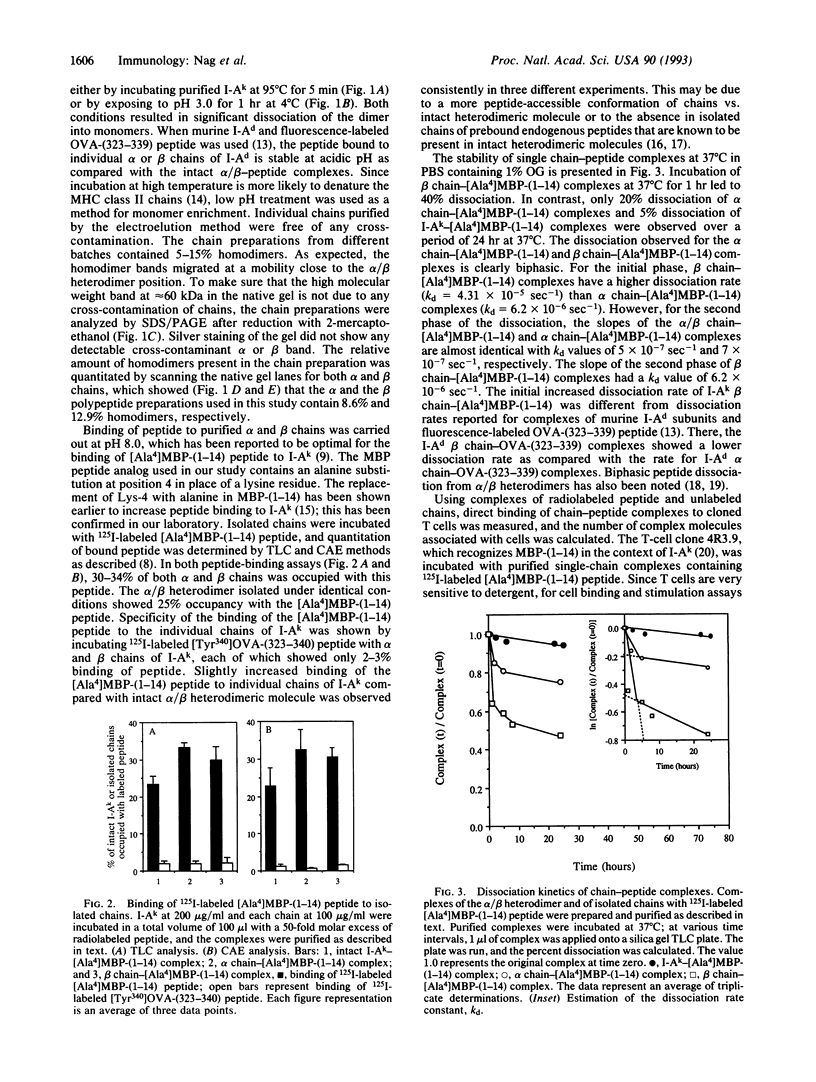
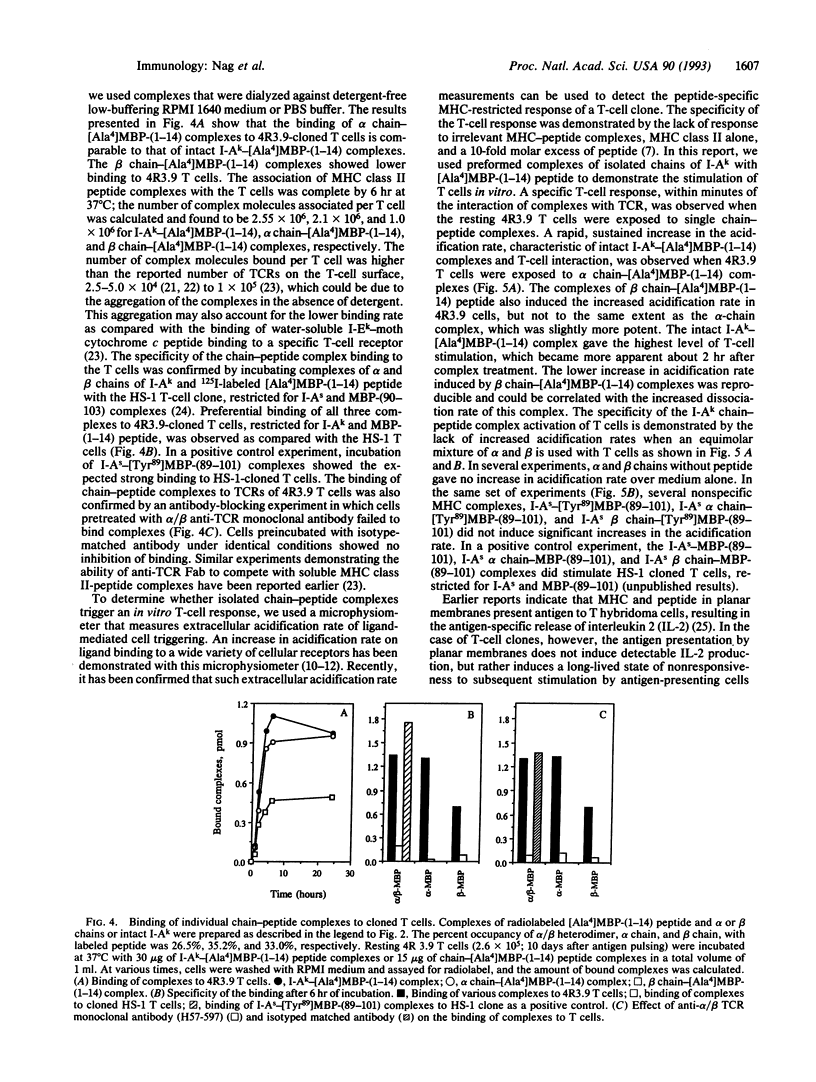
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules are heterodimeric glycoproteins with one alpha and one beta polypeptide chain of similar molecular size. In this report, we describe the binding of an acetylated N-terminal peptide of myelin basic protein, [Ala4]MBP-(1-14), to purified individual alpha and beta chains of murine I-Ak molecules. Purified complexes of isolated single chains and antigenic peptide bind to cloned T cells restricted by I-Ak and [Ala4]MBP-(1-14) tetradecapeptide. The binding is blocked by alpha/beta anti-T-cell receptor (TCR) monoclonal antibody. Cell triggering as measured by an increase in extracellular acidification rate is observed when cloned T cells are exposed to purified complexes of isolated chains and antigenic peptide. This increase in the extracellular acidification rate is antigen specific and MHC-restricted, as chains alone or irrelevant chain-peptide complexes do not trigger an increase in the metabolic acidification rate. These results together demonstrate that in vitro cloned T cells are triggered by complexes of specific antigenic peptides and isolated individual chains of their cognate MHC proteins.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acha-Orbea H., Mitchell D. J., Timmermann L., Wraith D. C., Tausch G. S., Waldor M. K., Zamvil S. S., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L. Limited heterogeneity of T cell receptors from lymphocytes mediating autoimmune encephalomyelitis allows specific immune intervention. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90558-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babbitt B. P., Allen P. M., Matsueda G., Haber E., Unanue E. R. Binding of immunogenic peptides to Ia histocompatibility molecules. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):359–361. doi: 10.1038/317359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Colon S., Smith C., Freed J. H., Miles C., Grey H. M. Interaction between a "processed" ovalbumin peptide and Ia molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3968–3971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Grey H. M. The interaction between protein-derived immunogenic peptides and Ia. Immunol Rev. 1987 Aug;98:115–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicz R. M., Urban R. G., Lane W. S., Gorga J. C., Stern L. J., Vignali D. A., Strominger J. L. Predominant naturally processed peptides bound to HLA-DR1 are derived from MHC-related molecules and are heterogeneous in size. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):764–768. doi: 10.1038/358764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. B., Moxley M., Crichton D., Deane D. L., Steel C. M. A mild procedure for separating polypeptide chains prior to immunoprecipitation and western blotting analysis. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Dec 14;75(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. B., Mitchell D. J., Wraith D. C., Todd J. A., Zamvil S. S., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L., Jones P. P. Polymorphic residues on the I-A beta chain modulate the stimulation of T cell clones specific for the N-terminal peptide of the autoantigen myelin basic protein. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2083–2093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding H., McCluskey J., Munitz T. I., Germain R. N., Margulies D. H., Singer A. T-cell recognition of a chimaeric class II/class I MHC molecule and the role of L3T4. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):425–427. doi: 10.1038/317425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui K., Boniface J. J., Reay P. A., Schild H., Fazekas de St Groth B., Davis M. M. Low affinity interaction of peptide-MHC complexes with T cell receptors. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1788–1791. doi: 10.1126/science.1763329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCluskey J., Munitz T., Boyd L., Germain R. N., Coligan J. E., Singer A., Margulies D. H. Cell surface expression of the amino-terminal domain of A kappa alpha. Recognition of an isolated MHC antigenic structure by allospecific T cells but not alloantibodies. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):2081–2089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell H. M., Owicki J. C., Parce J. W., Miller D. L., Baxter G. T., Wada H. G., Pitchford S. The cytosensor microphysiometer: biological applications of silicon technology. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1906–1912. doi: 10.1126/science.1329199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Acuto O., Hussey R. E., Hodgdon J. C., Fitzgerald K. A., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Evidence for the T3-associated 90K heterodimer as the T-cell antigen receptor. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):808–810. doi: 10.1038/303808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag B., Deshpande S. V., Clark B. R. Novel methods to rapidly and sensitively analyze antigenic peptide binding to MHC class II molecules. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Aug 28;142(1):105–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90297-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag B., Passmore D., Deshpande S. V., Clark B. R. In vitro maximum binding of antigenic peptides to murine MHC class II molecules does not always take place at the acidic pH of the in vivo endosomal compartment. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):369–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag B., Wada H. G., Fok K. S., Green D. J., Sharma S. D., Clark B. R., Parce J. W., McConnell H. M. Antigen-specific stimulation of T cell extracellular acidification by MHC class II-peptide complexes. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2040–2044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton S. D., Hovinen D. E., Jenkins M. K. IL-2 secretion and T cell clonal anergy are induced by distinct biochemical pathways. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1125–1129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owicki J. C., Parce J. W., Kercso K. M., Sigal G. B., Muir V. C., Venter J. C., Fraser C. M., McConnell H. M. Continuous monitoring of receptor-mediated changes in the metabolic rates of living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):4007–4011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.4007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parce J. W., Owicki J. C., Kercso K. M., Sigal G. B., Wada H. G., Muir V. C., Bousse L. J., Ross K. L., Sikic B. I., McConnell H. M. Detection of cell-affecting agents with a silicon biosensor. Science. 1989 Oct 13;246(4927):243–247. doi: 10.1126/science.2799384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quill H., Schwartz R. H. Stimulation of normal inducer T cell clones with antigen presented by purified Ia molecules in planar lipid membranes: specific induction of a long-lived state of proliferative nonresponsiveness. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3704–3712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenhäusler B., Dornmair K., McConnell H. M. Specific binding of antigenic peptides to separate alpha and beta chains of class II molecules of the major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):352–354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadegh-Nasseri S., McConnell H. M. A kinetic intermediate in the reaction of an antigenic peptide and I-Ek. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):274–276. doi: 10.1038/337274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Germain R. N., Schwartz R. H. Monoclonal antibodies against the antigen receptor on a cloned T-cell hybrid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6972–6976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su X. M., Sriram S. Analysis of TCR V beta gene usage and encephalitogenicity of myelin basic protein peptide p91-103 reactive T cell clones in SJL mice: lack of evidence for V gene hypothesis. Cell Immunol. 1992 May;141(2):485–495. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90165-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tampé R., Tyvoll D., McConnell H. M. Reactions of the subunits of the class II major histocompatibility complex molecule IAd. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10667–10670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts T. H., Brian A. A., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., McConnell H. M. Antigen presentation by supported planar membranes containing affinity-purified I-Ad. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7564–7568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts T. H., McConnell H. M. High-affinity fluorescent peptide binding to I-Ad in lipid membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9660–9664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]