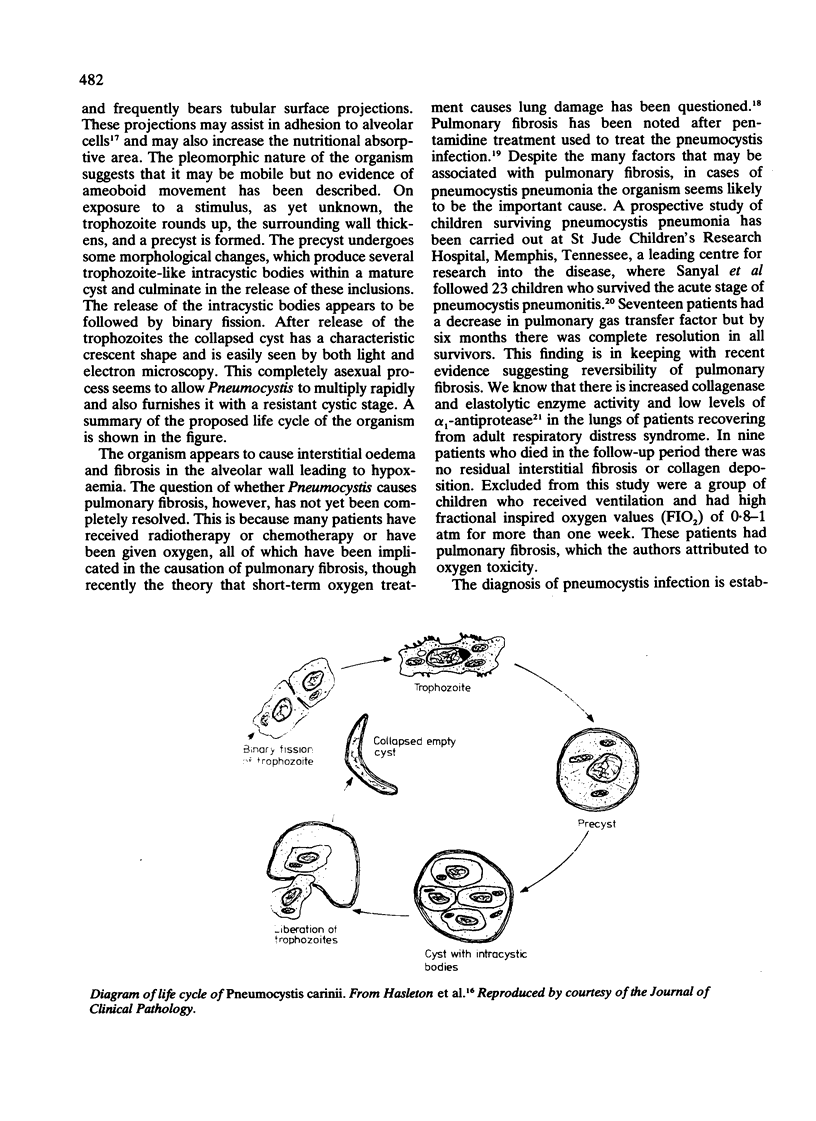
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAAR H. S. Interstitial plasmacellular pneumonia due to Pneumocystis carinii. J Clin Pathol. 1955 Feb;8(1):19–24. doi: 10.1136/jcp.8.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden D. H. Alveolar response to injury. Thorax. 1981 Nov;36(11):801–804. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.11.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. O., Durack D. T. Gay compromise syndrome. Lancet. 1981 Dec 12;2(8259):1338–1339. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91352-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. M., Stimmel B., Taub R. N., Kochwa S., Rosenfield R. E. Immunologic dysfunction in heroin addicts. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Dec;134(6):1001–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B. A., Good R. A. Pneumocystis carinii infection. Medicine (Baltimore) 1973 Jan;52(1):23–51. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197301000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew W. L., Mintz L., Miner R. C., Sands M., Ketterer B. Prevalence of cytomegalovirus infection in homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):188–192. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T. Opportunistic infections and Kaposi's sarcoma in homosexual men. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1465–1467. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOETZ O. SEROLOGISCHE BEFUNDEINTERSTITIELLER PNEUMONIEN AUS DEN VEREINIGTEN STAATEN. Arch Kinderheilkd. 1964 Feb;170:60–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. S., Schroff R., Schanker H. M., Weisman J. D., Fan P. T., Wolf R. A., Saxon A. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and mucosal candidiasis in previously healthy homosexual men: evidence of a new acquired cellular immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1425–1431. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. Differential diagnosis of spindle cell tumours by electron microscopy--personal experience and a review. Histopathology. 1981 Jan;5(1):81–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1981.tb01769.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasleton P. S., Curry A., Rankin E. M. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: a light microscopical and ultrastructural study. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Oct;34(10):1138–1146. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.10.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasleton P. S., Penna P., Torry J. Effect of oxygen on the lungs after blast injury and burns. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Oct;34(10):1147–1154. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.10.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T. Current status of laboratory diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1975 Sep;6(2):145–170. doi: 10.3109/10408367509151568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Feldman S., Aur R. J., Verzosa M. S., Hustu H. O., Simone J. V. Intensity of immunosuppressive therapy and the incidence of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Cancer. 1975 Dec;36(6):2004–2009. doi: 10.1002/cncr.2820360912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Price R. A., Kim H. K., Coburn T. P., Grigsby D., Feldman S. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in children with malignancies. J Pediatr. 1973 Mar;82(3):404–415. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klepp O., Dahl O., Stenwig J. T. Association of Kaposi's sarcoma and prior immunosuppressive therapy: a 5-year material of Kaposi's sarcoma in Norway. Cancer. 1978 Dec;42(6):2626–2630. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197812)42:6<2626::aid-cncr2820420618>3.0.co;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Michelis M. A., Greene J. B., Onorato I., Stouwe R. A., Holzman R. S., Wormser G., Brettman L., Lange M., Murray H. W. An outbreak of community-acquired Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: initial manifestation of cellular immune dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1431–1438. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesanti E. L. In vitro effects of antiprotozoan drugs and immune serum on Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):775–780. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Murphy M. J., Jr Propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in vitro. Pediatr Res. 1977 Apr;11(4):305–316. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197704000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Woods D., Hughes W. T. Propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in Vero cell culture. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):66–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.66-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi S. A. Disseminated Pneumocystis carinii in thymic alymphoplasia. Arch Pathol. 1974 Mar;97(3):162–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowden G., Lewis M. G. Experience with a three-hour electron microscopy biopsy service. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jun;27(6):505–510. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.6.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal S. K., Mariencheck W. C., Hughes W. T., Parvey L. S., Tsiatis A. A., Mackert P. W. Course of pulmonary dysfunction in children surviving Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. A prospective study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Aug;124(2):161–166. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd V., Jameson B., Knowles G. K. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis: a serological study. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Aug;32(8):773–777. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.8.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P., Lopez C., Hammer G. S., Brown A. E., Kornfeld S. J., Gold J., Hassett J., Hirschman S. Z., Cunningham-Rundles C., Adelsberg B. R. Severe acquired immunodeficiency in male homosexuals, manifested by chronic perianal ulcerative herpes simplex lesions. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1439–1444. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavra J., Kucera K. Pneumocystis carinii delanoë, its ultrastructure and ultrastructural affinities. J Protozool. 1970 Aug;17(3):463–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1970.tb04715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickerman K. On the surface coat and flagellar adhesion in trypanosomes. J Cell Sci. 1969 Jul;5(1):163–193. doi: 10.1242/jcs.5.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Perl D. P., Krogstad D. J., Rawson P. G., Schultz M. G. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the United States. Epidemiologic, diagnostic, and clinical features. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jan;80(1):83–93. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Powell R. D., Jr, Yoneda K. Experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in different strains of cortisonized mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):939–947. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.939-947.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E. Comparison of rat, mouse, and human Pneumocystis carinii by immunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):449–449. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. O., Young J. R., Majiwa P. A. Genomic rearrangements correlated with antigenic variation in Trypanosoma brucei. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):847–849. doi: 10.1038/282847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- du Bois R. M., Branthwaite M. A., Mikhail J. R., Batten J. C. Primary Pneumocystis carinii and cytomegalovirus infections. Lancet. 1981 Dec 12;2(8259):1339–1339. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91353-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]