Abstract
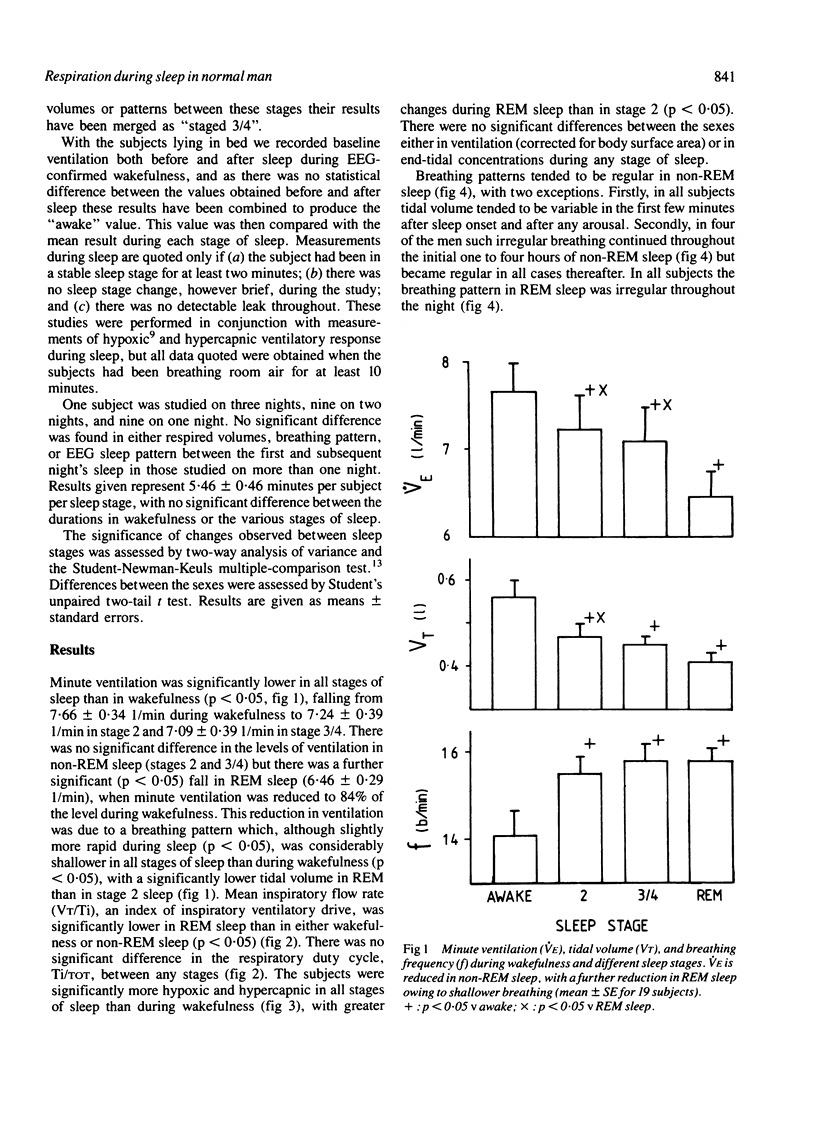
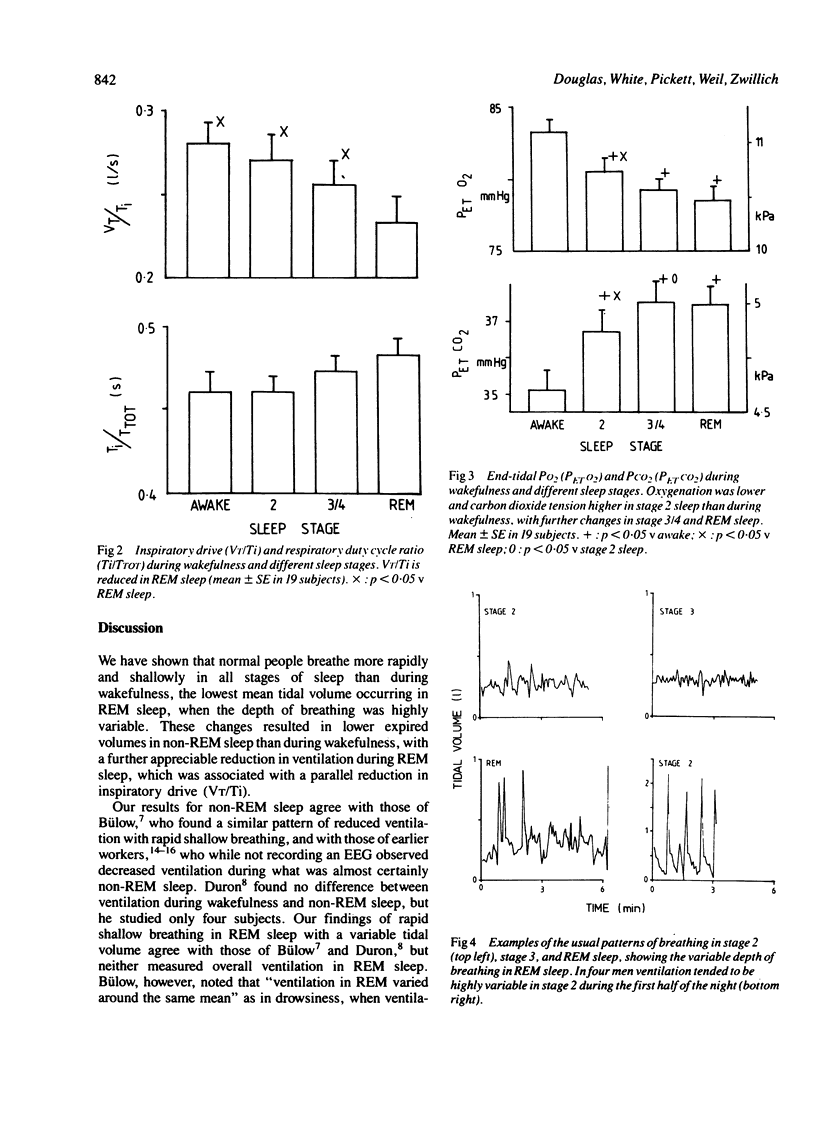
Respiratory volumes and timing have been measured in 19 healthy adults during wakefulness and sleep. Minute ventilation was significantly less (p less than 0.05) in all stages of sleep than when the subject was awake (7.66 +/- 0.34(SEM) 1/min), the level in rapid-eye-movement (REM) sleep (6.46 +/- 0.29 1/min) being significantly lower than in non-REM sleep (7.18 +/- 0.39 1/min). The breathing pattern during all stages of sleep was significantly more rapid and shallow than during wakefulness, tidal volume in REM sleep being reduced to 73% of the level during wakefulness. Mean inspiratory flow rate (VT/Ti), an index of inspiratory drive, was significantly lower in REM sleep than during wakefulness or non-REM sleep. Thus ventilation falls during sleep, the greatest reduction occurring during REM sleep, when there is a parallel reduction in inspiratory drive. Similar changes in ventilation may contribute to the REM-associated hypoxaemia observed in normal subjects and in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Block A. J., Boysen P. G., Wynne J. W., Hunt L. A. Sleep apnea, hypopnea and oxygen desaturation in normal subjects. A strong male predominance. N Engl J Med. 1979 Mar 8;300(10):513–517. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197903083001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. P., Herman S. Ventilation and sleep state in the new-born. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(1):67–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark F. J., von Euler C. On the regulation of depth and rate of breathing. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):267–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas N. J., Calverley P. M., Leggett R. J., Brash H. M., Flenley D. C., Brezinova V. Transient hypoxaemia during sleep in chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Lancet. 1979 Jan 6;1(8106):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas N. J., White D. P., Weil J. V., Pickett C. K., Martin R. J., Hudgel D. W., Zwillich C. W. Hypoxic ventilatory response decreases during sleep in normal men. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Mar;125(3):286–289. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.3.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagenholz S. A., O'Connell K., Shannon D. C. Chemoreceptor function and sleep state in apnea. Pediatrics. 1976 Jul;58(1):31–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer N. N., Abroms I. F., Taeusch H. W., Jr Ventilation and sleep states in newborn infants. J Pediatr. 1976 Jul;89(1):100–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80941-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleetham J. A., Mezon B., West P., Bradley C. A., Anthonisen N. R., Kryger M. H. Chemical control of ventilation and sleep arterial oxygen desaturation in patients with COPD. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Oct;122(4):583–589. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.4.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick M. R., Block A. J. Continuous in-vivo monitoring of arterial oxygenation in chronic obstructive lung disease. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):725–730. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Tilkian A., Dement W. C. The sleep apnea syndromes. Annu Rev Med. 1976;27:465–484. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.27.020176.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. A., Hunter M. E., Seelye E. R., Vedder M., Whitlock R. M. Prediction of the physiological dead-space in resting normal subjects. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Sep;45(3):375–386. doi: 10.1042/cs0450375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathorn M. K. The rate and depth of breathing in new-born infants in different sleep states. J Physiol. 1974 Nov;243(1):101–113. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo K. W., Sax D. S., Snider G. L. Arterial blood gases and pH during sleep in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Med. 1975 May;58(5):663–670. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90502-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milic-Emili J., Grunstein M. M. Drive and timing components of ventilation. Chest. 1976 Jul;70(1 Suppl):131–133. doi: 10.1378/chest.70.1_supplement.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller N. L., Francis P. W., Gurwitz D., Levison H., Bryan A. C. Mechanism of hemoglobin desaturation during rapid-eye-movement sleep in normal subjects and in patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Mar;121(3):463–469. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.3.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orem J., Netick A., Dement W. C. Breathing during sleep and wakefulness in the cat. Respir Physiol. 1977 Aug;30(3):265–289. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(77)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillipson E. A., Murphy E., Kozar L. F. Regulation of respiration in sleeping dogs. J Appl Physiol. 1976 May;40(5):688–693. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.40.5.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell M. Response in the newborn to raised upper airway resistance. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Aug;51(8):602–607. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.8.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REED D. J., KELLOGG R. H. Effect of sleep on hypoxic stimulation of breathing at sea level and altitude. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Nov;15:1130–1134. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.6.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBIN E. D., WHALEY R. D., CRUMP C. H., TRAVIS D. M. Alveolar gas tensions, pulmonary ventilation and blood pH during physiologic sleep in normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1958 Jul;37(7):981–989. doi: 10.1172/JCI103694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remmers J. E., Bartlett D., Jr, Putnam M. D. Changes in the respiratory cycle associated with sleep. Respir Physiol. 1976 Nov;28(2):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(76)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skatrud J. B., Dempsey J. A., Iber C., Berssenbrugge A. Correction of CO2 retention during sleep in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Sep;124(3):260–268. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.3.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodal I. E., Bowman R. R., Filley G. F. A fast-response oxygen analyzer with high accuracy for respiratory gas measurement. J Appl Physiol. 1968 Aug;25(2):181–183. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1968.25.2.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabachnik E., Muller N. L., Bryan A. C., Levison H. Changes in ventilation and chest wall mechanics during sleep in normal adolescents. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Sep;51(3):557–564. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.3.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Euler C., Trippenbach T. Excitability changes of the inspiratory "off-switch" mechanism tested by electrical stimulation in nucleus parabrachialis in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1976 Jun;97(2):175–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1976.tb10250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


