Abstract
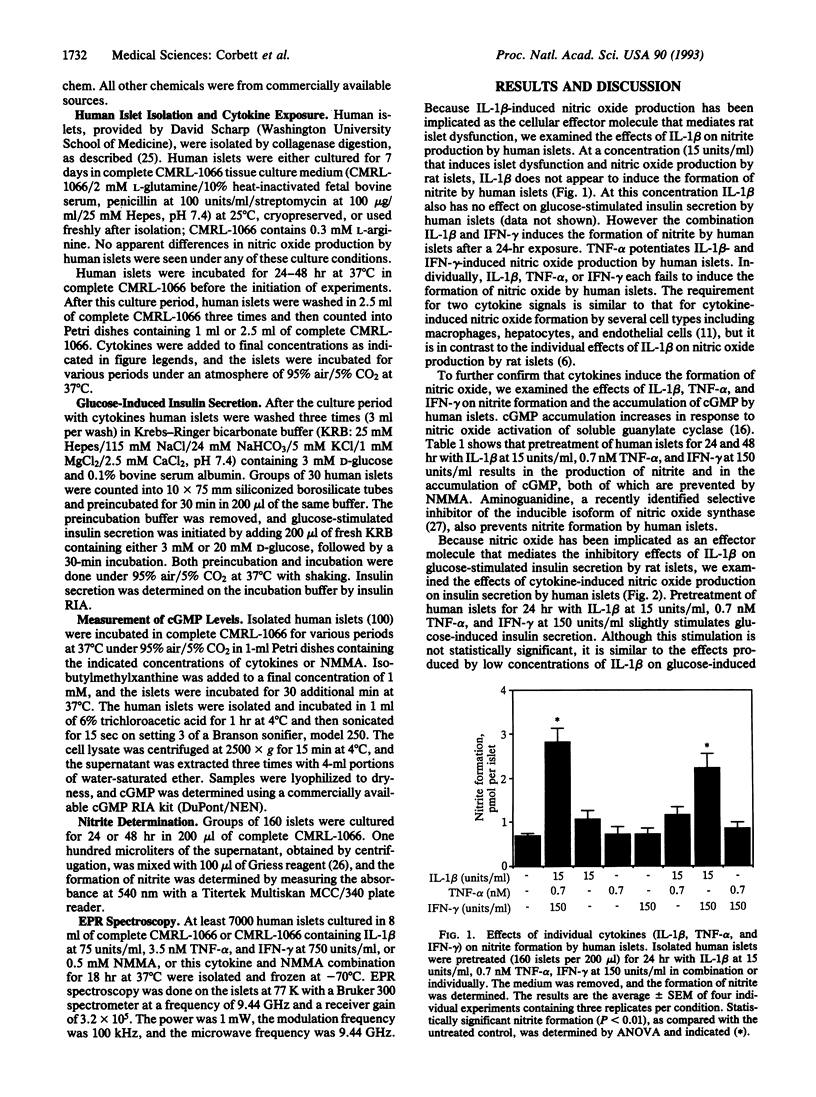
Cytokines have been implicated as immunological effector molecules that mediate beta cell destruction associated with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. In this report we demonstrate that the cytokine combination of human recombinant interleukin 1 beta (IL-1 beta), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), and interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) induces the formation of nitric oxide by human islets. This combination of cytokines stimulates both the formation of the nitric oxide derivative, nitrite, and the accumulation of cGMP by human islets. The nitric oxide synthase inhibitor NG-monomethyl-L-arginine prevents formation of both cGMP and nitrite. IL-1 beta and IFN-gamma are sufficient to induce nitric oxide formation by human islets, whereas TNF-alpha potentiates nitrite production. This combination of cytokines (IL-1 beta, TNF-alpha, and IFN-gamma) also influences insulin secretion by human islets. Pretreatment of human islets with low concentrations of this cytokine combination (IL-1 beta at 15 units/ml, 0.7 nM TNF-alpha, and IFN-gamma at 150 units/ml) appears to slightly stimulate insulin secretion. Higher concentrations (IL-1 beta at 75 units/ml, 3.5 nM TNF-alpha, and IFN-gamma at 750 units/ml) inhibit insulin secretion from human islets, and the inhibitory effect is prevented by NG-monomethyl-L-arginine. This higher concentration of cytokines also induces the formation of an electron paramagnetic resonance-detectable g = 2.04 axial feature by human islets that is characteristic of the formation of an iron-dithio-dinitrosyl complex. The formation of this complex is prevented by NG-monomethyl-L-arginine, thus confirming that this cytokine combination induces the formation of nitric oxide by human islets. These results indicate that nitric oxide mediates the inhibitory effects of cytokines on glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by human islets and suggest that nitric oxide may participate in beta-cell dysfunction associated with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bendtzen K., Mandrup-Poulsen T., Nerup J., Nielsen J. H., Dinarello C. A., Svenson M. Cytotoxicity of human pI 7 interleukin-1 for pancreatic islets of Langerhans. Science. 1986 Jun 20;232(4757):1545–1547. doi: 10.1126/science.3086977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Isolation of nitric oxide synthetase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):682–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comens P. G., Wolf B. A., Unanue E. R., Lacy P. E., McDaniel M. L. Interleukin 1 is potent modulator of insulin secretion from isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Diabetes. 1987 Aug;36(8):963–970. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.8.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. A., Lancaster J. R., Jr, Sweetland M. A., McDaniel M. L. Interleukin-1 beta-induced formation of EPR-detectable iron-nitrosyl complexes in islets of Langerhans. Role of nitric oxide in interleukin-1 beta-induced inhibition of insulin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21351–21354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. A., McDaniel M. L. Does nitric oxide mediate autoimmune destruction of beta-cells? Possible therapeutic interventions in IDDM. Diabetes. 1992 Aug;41(8):897–903. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.8.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. A., Tilton R. G., Chang K., Hasan K. S., Ido Y., Wang J. L., Sweetland M. A., Lancaster J. R., Jr, Williamson J. R., McDaniel M. L. Aminoguanidine, a novel inhibitor of nitric oxide formation, prevents diabetic vascular dysfunction. Diabetes. 1992 Apr;41(4):552–556. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.4.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. A., Wang J. L., Hughes J. H., Wolf B. A., Sweetland M. A., Lancaster J. R., Jr, McDaniel M. L. Nitric oxide and cyclic GMP formation induced by interleukin 1 beta in islets of Langerhans. Evidence for an effector role of nitric oxide in islet dysfunction. Biochem J. 1992 Oct 1;287(Pt 1):229–235. doi: 10.1042/bj2870229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. A., Wang J. L., Sweetland M. A., Lancaster J. R., Jr, McDaniel M. L. Interleukin 1 beta induces the formation of nitric oxide by beta-cells purified from rodent islets of Langerhans. Evidence for the beta-cell as a source and site of action of nitric oxide. J Clin Invest. 1992 Dec;90(6):2384–2391. doi: 10.1172/JCI116129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Pellat C., Henry Y. Generation of EPR-detectable nitrosyl-iron complexes in tumor target cells cocultured with activated macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10162–10167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gepts W. Pathologic anatomy of the pancreas in juvenile diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1965 Oct;14(10):619–633. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.10.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. C., Wagner D. A., Glogowski J., Skipper P. L., Wishnok J. S., Tannenbaum S. R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Westenfelder C., Taintor R., Vavrin Z., Kablitz C., Baranowski R. L., Ward J. H., Menlove R. L., McMurry M. P., Kushner J. P. Evidence for cytokine-inducible nitric oxide synthesis from L-arginine in patients receiving interleukin-2 therapy. J Clin Invest. 1992 Mar;89(3):867–877. doi: 10.1172/JCI115666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt N. C., Goldin R. D. Nitric oxide production by monocytes in alcoholic liver disease. J Hepatol. 1992 Mar;14(2-3):146–150. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(92)90150-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröncke K. D., Kolb-Bachofen V., Berschick B., Burkart V., Kolb H. Activated macrophages kill pancreatic syngeneic islet cells via arginine-dependent nitric oxide generation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 29;175(3):752–758. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91630-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster J. R., Jr, Hibbs J. B., Jr EPR demonstration of iron-nitrosyl complex formation by cytotoxic activated macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1223–1227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laychock S. G., Modica M. E., Cavanaugh C. T. L-arginine stimulates cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate formation in rat islets of Langerhans and RINm5F insulinoma cells: evidence for L-arginine:nitric oxide synthase. Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):3043–3052. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-3043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Weringer E. J., Holdash A., McGill P., Atkinson D., Rossini A. A. Adoptive transfer of autoimmune diabetes mellitus in biobreeding/Worcester (BB/W) inbred and hybrid rats. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1583–1587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukic M. L., Stosic-Grujicic S., Ostojic N., Chan W. L., Liew F. Y. Inhibition of nitric oxide generation affects the induction of diabetes by streptozocin in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):913–920. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90978-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussler A. K., Di Silvio M., Billiar T. R., Hoffman R. A., Geller D. A., Selby R., Madariaga J., Simmons R. L. Stimulation of the nitric oxide synthase pathway in human hepatocytes by cytokines and endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1992 Jul 1;176(1):261–264. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.1.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa J. B., Curti B., Peitzman A. B., Simmons R. L., Billiar T. R., Hoffman R., Rault R., Longo D. L., Urba W. J., Ochoa A. C. Increased circulating nitrogen oxides after human tumor immunotherapy: correlation with toxic hemodynamic changes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Jun 3;84(11):864–867. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.11.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa J. B., Udekwu A. O., Billiar T. R., Curran R. D., Cerra F. B., Simmons R. L., Peitzman A. B. Nitrogen oxide levels in patients after trauma and during sepsis. Ann Surg. 1991 Nov;214(5):621–626. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199111000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. P., Helqvist S., Spinas G. A., Mølvig J., Mandrup-Poulsen T., Andersen H. U., Nerup J. Interaction of beta-cell activity and IL-1 concentration and exposure time in isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Diabetes. 1989 Oct;38(10):1211–1216. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.10.1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellat C., Henry Y., Drapier J. C. IFN-gamma-activated macrophages: detection by electron paramagnetic resonance of complexes between L-arginine-derived nitric oxide and non-heme iron proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 15;166(1):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91919-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch A., Suarez W. L., Thomas P. D., Strynadka K., Simpson I. Cytotoxic effects of cytokines on rat islets: evidence for involvement of free radicals and lipid peroxidation. Diabetologia. 1992 May;35(5):409–413. doi: 10.1007/BF02342435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharp D. W., Lacy P. E., Finke E., Olack B. Low-temperature culture of human islets isolated by the distention method and purified with Ficoll or Percoll gradients. Surgery. 1987 Nov;102(5):869–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Murad F. Purification and characterization of a human NO synthase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 31;181(3):1372–1377. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Warner T. D., Ishii K., Sheng H., Murad F. Insulin secretion from pancreatic B cells caused by L-arginine-derived nitrogen oxides. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):721–723. doi: 10.1126/science.1371193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Bredt D. S. Biological roles of nitric oxide. Sci Am. 1992 May;266(5):68-71, 74-7. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0592-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern C., Schulster D., Green I. C. Inhibition of insulin secretion by interleukin-1 beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha via an L-arginine-dependent nitric oxide generating mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 10;276(1-2):42–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80502-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinas G. A., Hansen B. S., Linde S., Kastern W., Mølvig J., Mandrup-Poulsen T., Dinarello C. A., Nielsen J. H., Nerup J. Interleukin 1 dose-dependently affects the biosynthesis of (pro)insulin in isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Diabetologia. 1987 Jul;30(7):474–480. doi: 10.1007/BF00279615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Cho H. J., Kwon N. S., Weise M. F., Nathan C. F. Purification and characterization of the cytokine-induced macrophage nitric oxide synthase: an FAD- and FMN-containing flavoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7773–7777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh N., Eizirik D. L., Bendtzen K., Sandler S. Interleukin-1 beta-induced nitric oxide production in isolated rat pancreatic islets requires gene transcription and may lead to inhibition of the Krebs cycle enzyme aconitase. Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):3167–3173. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-3167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicker L. S., Miller B. J., Mullen Y. Transfer of autoimmune diabetes mellitus with splenocytes from nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. Diabetes. 1986 Aug;35(8):855–860. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.8.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


