Abstract
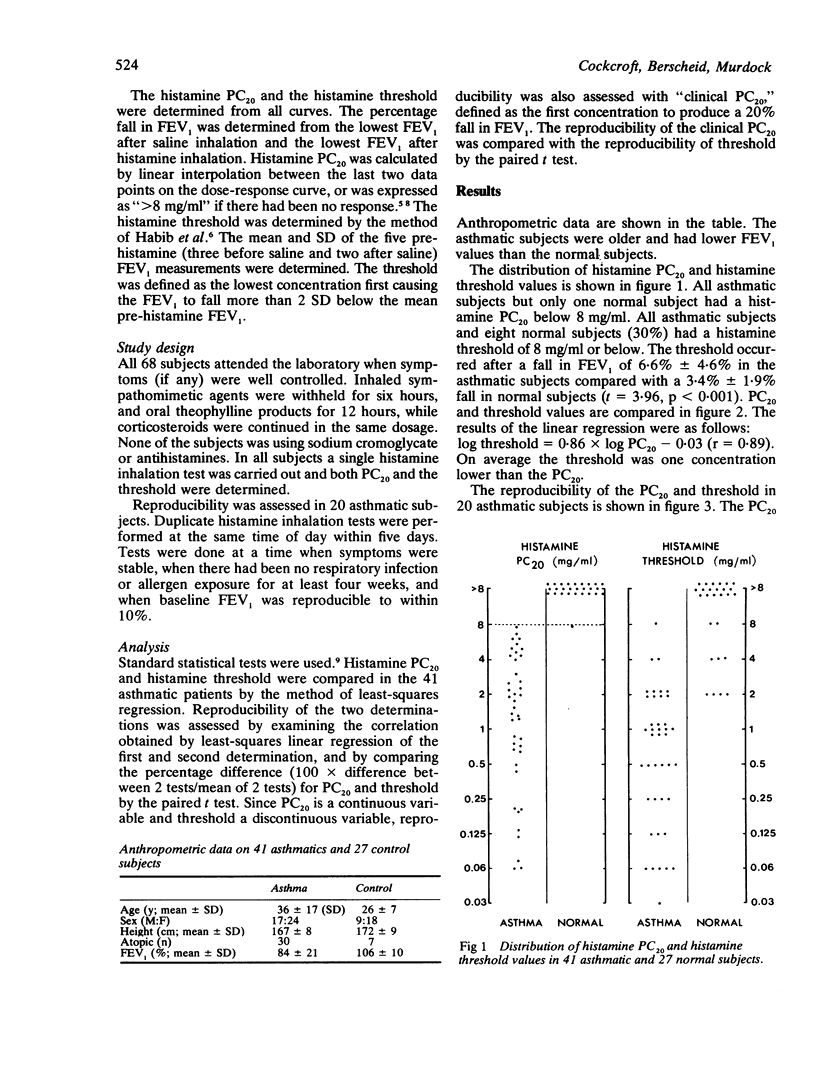
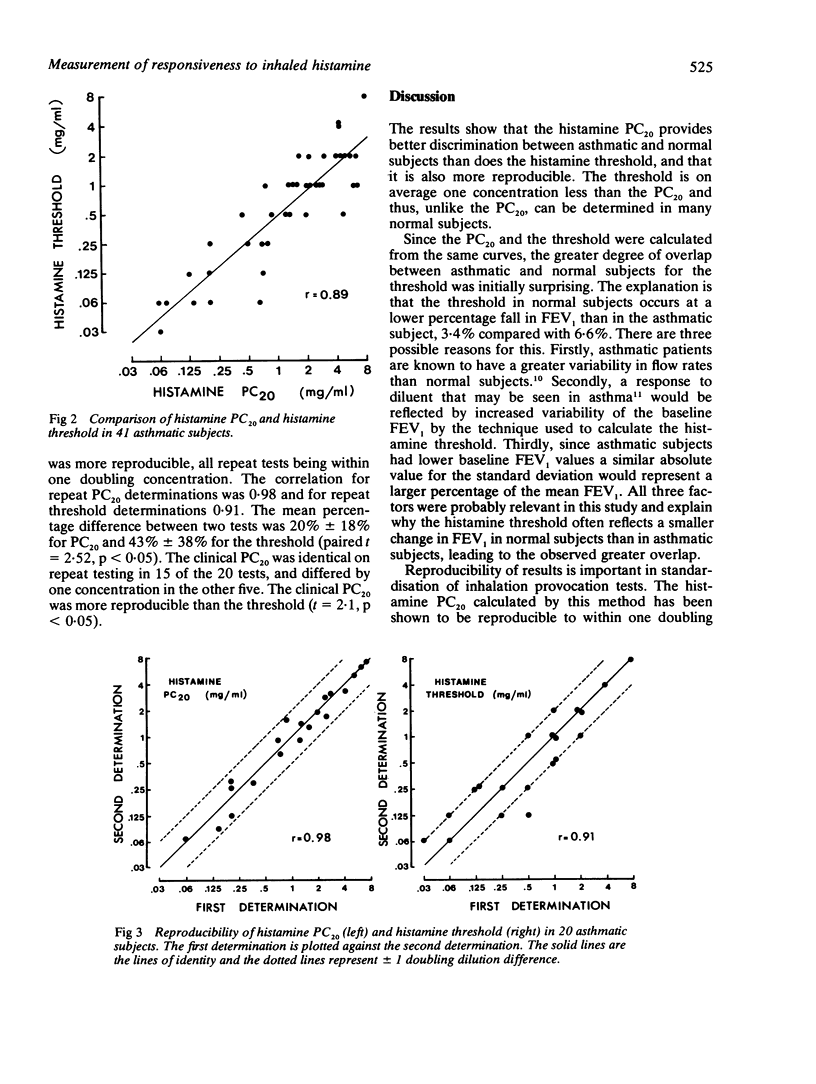
Two methods of interpreting histamine inhalation dose-response curves were compared in 27 normal and 41 asthmatic subjects. The histamine provocation concentration producing a 20% fall (PC20) in forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) was calculated on the basis of the lowest FEV1 after inhalation of saline and the lowest value after inhalation of histamine. The histamine threshold was determined as the first histamine concentration causing the FEV1 to fall more than 2 SD below the mean of five pre-histamine (three pre-saline, two post-saline) FEV1 determinations. The PC20 was on average one doubling concentration larger than the threshold. The PC20 provided better discrimination between asthmatic and normal subjects than did the histamine threshold and was significantly more reproducible. These findings suggest that the histamine threshold may prove useful for studies on populations, particularly those with a low degree of responsiveness to histamine, because of the possibility of measuring a response at a lower histamine concentration. On the other hand, the PC20 is preferable for clinical use in individuals because of its better discriminating power and better reproducibility.
Full text
PDF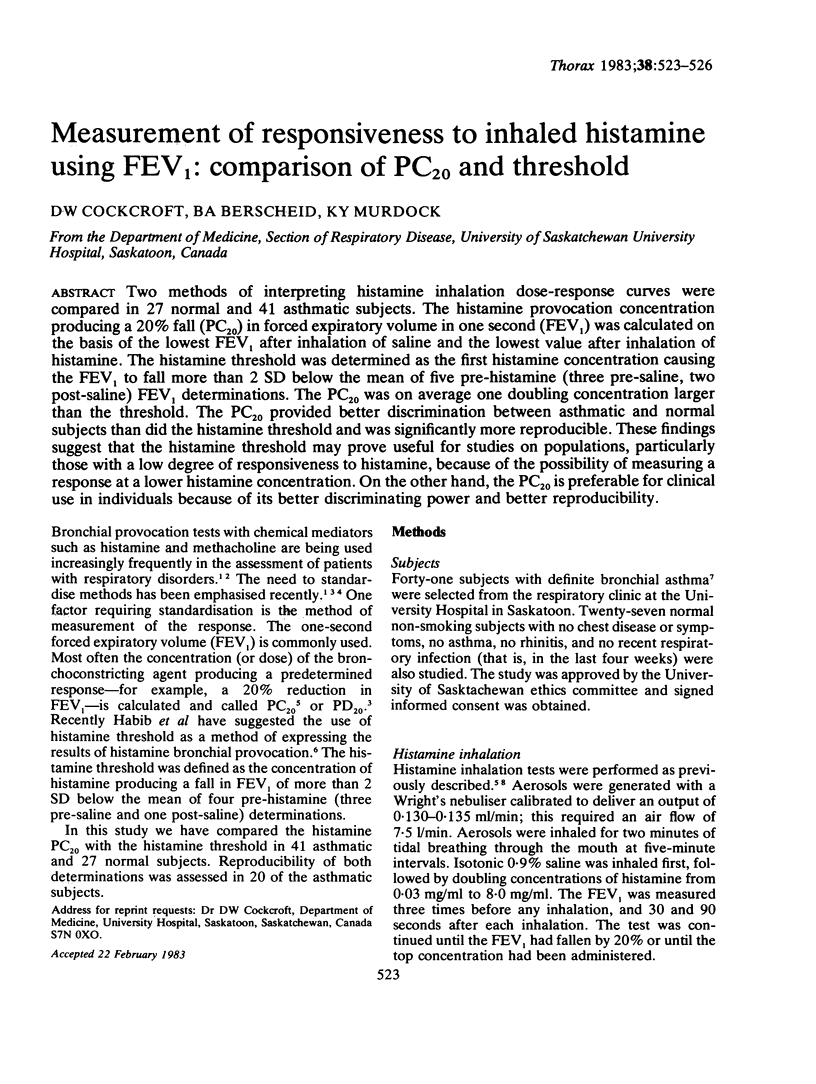

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boushey H. A., Holtzman M. J., Sheller J. R., Nadel J. A. Bronchial hyperreactivity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Feb;121(2):389–413. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.2.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai H., Farr R. S., Froehlich L. A., Mathison D. A., McLean J. A., Rosenthal R. R., Sheffer A. L., Spector S. L., Townley R. G. Standardization of bronchial inhalation challenge procedures. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Oct;56(4):323–327. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Berscheid B. A. Correlation of bronchial responsiveness to diluent and to histamine. Ann Allergy. 1982 Sep;49(3):139–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Berscheid B. A., Murdock K. Y. Bronchial response to inhaled histamine in asymptomatic young smokers. Eur J Respir Dis. 1983 Apr;64(3):207–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Killian D. N., Mellon J. J., Hargreave F. E. Bronchial reactivity to inhaled histamine: a method and clinical survey. Clin Allergy. 1977 May;7(3):235–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1977.tb01448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juniper E. F., Frith P. A., Dunnett C., Cockcroft D. W., Hargreave F. E. Reproducibility and comparison of responses to inhaled histamine and methacholine. Thorax. 1978 Dec;33(6):705–710. doi: 10.1136/thx.33.6.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orehek J., Gayrard P. Les tests de provocation bronchique non-spécifiques dans l'asthme. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1976 Jul-Aug;12(4):565–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan G., Latimer K. M., Dolovich J., Hargreave F. E. Bronchial responsiveness to histamine: relationship to diurnal variation of peak flow rate, improvement after bronchodilator, and airway calibre. Thorax. 1982 Jun;37(6):423–429. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.6.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


