Abstract
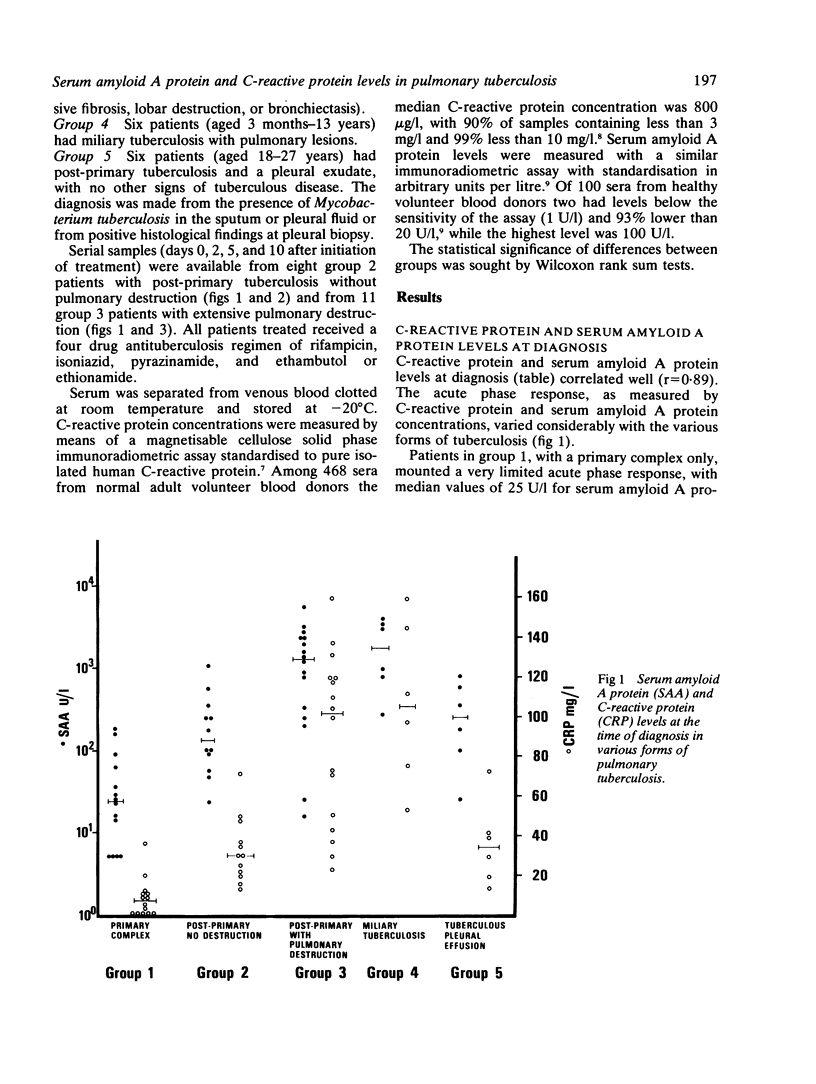
C-reactive protein and serum amyloid A protein levels were measured in 54 patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. The primary tuberculous complex was associated with an insignificant acute phase response, while post-primary tuberculosis without evidence of lung destruction caused modest increases in C-reactive protein and serum amyloid A protein. In most patients with post-primary pulmonary tuberculosis with significant pulmonary destruction there was a major acute phase response, with very high serum amyloid A protein and C-reactive protein levels. The response in these patients is most likely to be due to secondary bacterial infection in addition to infection by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Patients with miliary tuberculosis showed a major acute phase response. Serum amyloid A protein and C-reactive protein levels decreased rapidly after initiation of treatment in the patients with post-primary tuberculosis without significant pulmonary destruction.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benditt E. P., Eriksen N. Amyloid protein SAA is associated with high density lipoprotein from human serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4025–4028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Beer F. C., Mallya R. K., Fagan E. A., Lanham J. G., Hughes G. R., Pepys M. B. Serum amyloid-A protein concentration in inflammatory diseases and its relationship to the incidence of reactive systemic amyloidosis. Lancet. 1982 Jul 31;2(8292):231–234. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90321-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G. Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis: the beta-fibrilloses (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 12;302(24):1333–1343. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006123022403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie G., Zucker-Franklin D., Franklin E. C. Degradation of serum amyloid A protein by surface-associated enzymes of human blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1020–1031. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B. C-reactive protein fifty years on. Lancet. 1981 Mar 21;1(8221):653–657. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91565-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROANTREE R. J., RANTZ L. A. Clinical experience with the C-reactive protein test. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1955 Nov;96(5):674–682. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1955.00250160116009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine B., de Beer F. C., Pepys M. B. Solid phase radioimmunoassays for human C-reactive protein. Clin Chim Acta. 1981 Nov 25;117(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogen B., Natvig J. B., Bøorresen A. L., Berg K. Degradation of amyloid-related serum protein SAA by a component present in rabbit and human serum. Scand J Immunol. 1980;11(6):643–648. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


