Abstract
Hospital case notes and chest radiographs of 100 patients with Marfan syndrome were investigated for evidence of pulmonary disease. The criteria for inclusion of details of a given patient in the study were the occurrence of Marfan abnormalities in at least two separate body systems (skeletal, cardiovascular, ocular) or in one body system where there was a family history of a classically affected first degree relative. Selection of cases was biased towards those with cardiorespiratory problems by virtue of the hospitals from which the patients were drawn. Forty eight patients underwent cardiac surgery. Eleven patients had a history of spontaneous pneumothorax, which had been recurrent in 10 cases and bilateral in six. Eight had had pneumonia or excessively frequent respiratory infections and two had bronchiectasis. Chest radiographs showed emphysematous bullae in five, upper lobe fibrosis in four, and aspergilloma in two. The cases reviewed together with other published evidence suggest that spontaneous pneumothorax and bullae are causally related to Marfan syndrome. The presence of idiopathic upper lobe fibrosis in four Marfan patients is interesting but provides insufficient evidence to assess possible causality.
Full text
PDF
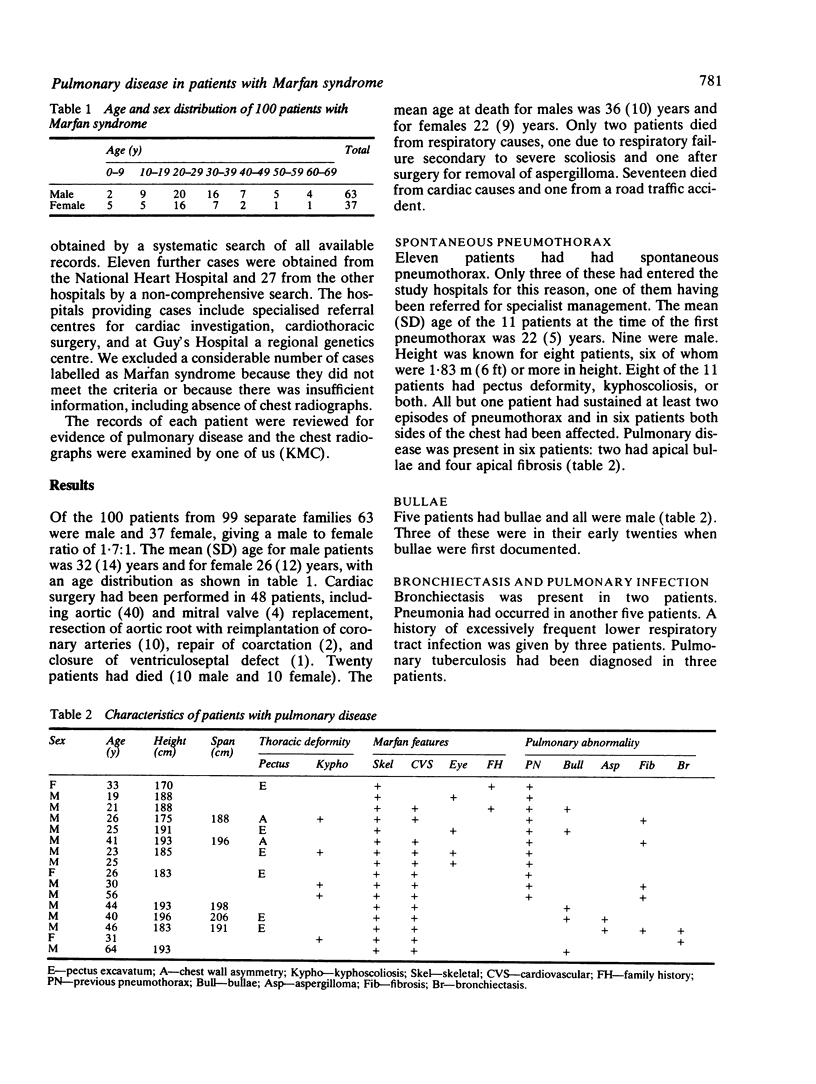
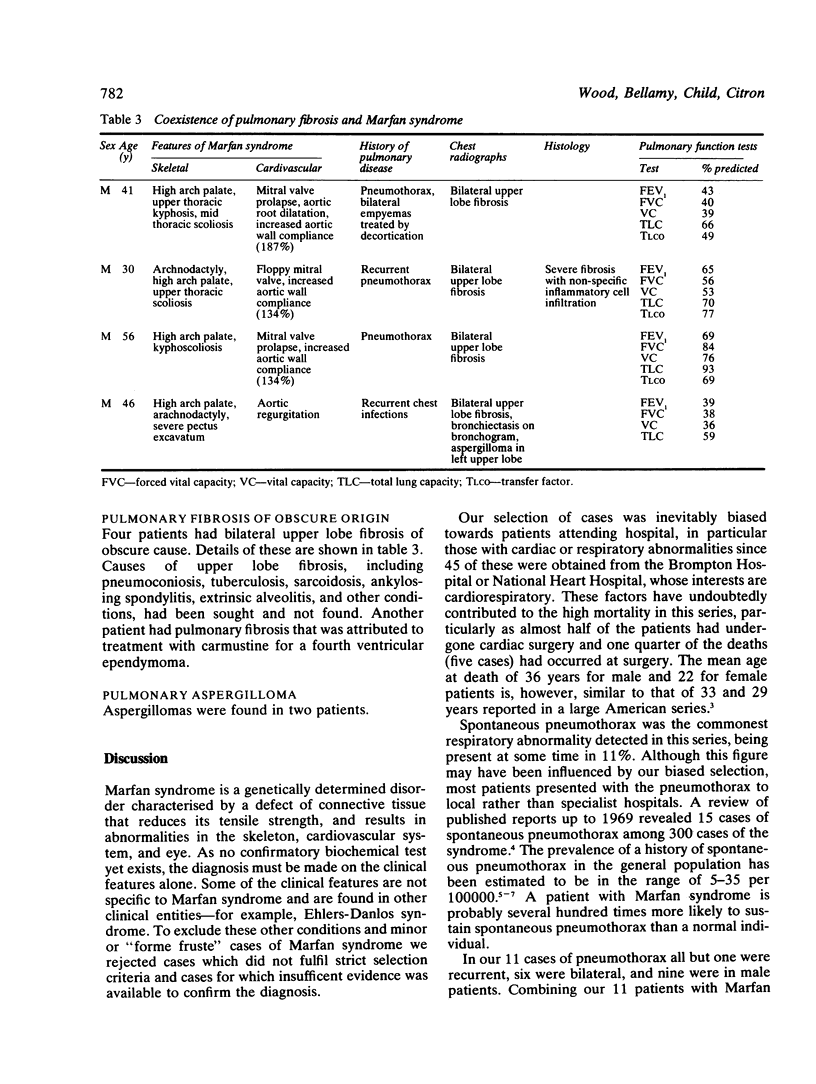


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boucek R. J., Noble N. L., Gunja-Smith Z., Butler W. T. The Marfan syndrome: a deficiency in chemically stable collagen cross-links. N Engl J Med. 1981 Oct 22;305(17):988–991. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198110223051705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. S., Cormack J., Zacks D. Metacarpal index and span-height difference in patients with spontaneous pneumothorax. Guys Hosp Rep. 1974;123(2):155–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Siegel R. C., Peterson K. E., Rowe D. W., Holbrook K. A., Smith L. T., Chang Y. H., Fu J. C. Marfan syndrome: abnormal alpha 2 chain in type I collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7745–7749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chyczewski L., Jodczyk K. J., Chyczewska E. Płuca w zespole Marfana z przedstawieniem przypadku własnego w oparciu o badania w mikroskopie świetlnym i skaningowym. Przegl Lek. 1978;35(3):377–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D., Crowther J. S., MacFarlane A. Idiopathic progressive pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax. 1975 Jun;30(3):316–325. doi: 10.1136/thx.30.3.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgacs P. Stature in simple pneumothorax. Guys Hosp Rep. 1969;118(1):199–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. B., Heaphy M. R., Perry H. O. Generalized elastolysis (cutis laxa). Am J Med. 1978 Nov;65(5):815–822. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90801-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ H. L. Thoracic manifestation in Marfan's syndrome (arachnodactyly). Q Bull Sea View Hosp. 1952 Apr;13(2):95–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landman S., Burgener F. A. Pneumothorax in Marfan's disease. N Y State J Med. 1976 Dec;76(13):2180–2181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motoyoshi K., Momoi H., Mikami R., Kosada K. [Pulmonary lesions seen in a family with Marfanoid hypermobility syndrome]. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1973 Mar;11(3):138–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch J. L., Walker B. A., Halpern B. L., Kuzma J. W., McKusick V. A. Life expectancy and causes of death in the Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1972 Apr 13;286(15):804–808. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197204132861502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neimann N., Rauber G., Marchal C., Vidailhet M., Fall M. Maladie de Marfan chez un nouveau-né avec atteintes polyviscérales. Etude anatomo-clinique. Ann Pediatr (Paris) 1968 Oct 2;15(10):619–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill S., Sweeney J., Walker F., O'Dwyer W. F. Pneumothorax in the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Ir J Med Sci. 1981 Feb;150(2):43–44. doi: 10.1007/BF02938195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reye R. D., Bale P. M. Elastic tissue in pulmonary emphysema in Marfan syndrome. Arch Pathol. 1973 Dec;96(6):427–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers C. P., Goltz R. W., Mottiaz J. Pulmonary elastic tissue in generalized elastolysis (cutis laxa) and Marfan's syndrome: a light and electron microscopic study. J Invest Dermatol. 1975 Nov;65(5):451–457. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12608193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheck M., Siegel R. C., Parker J., Chang Y. H., Fu J. C. Aortic aneurysm in Marfan's syndrome: changes in the ultrastructure and composition of collagen. J Anat. 1979 Oct;129(Pt 3):645–657. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


