Abstract
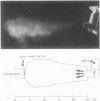
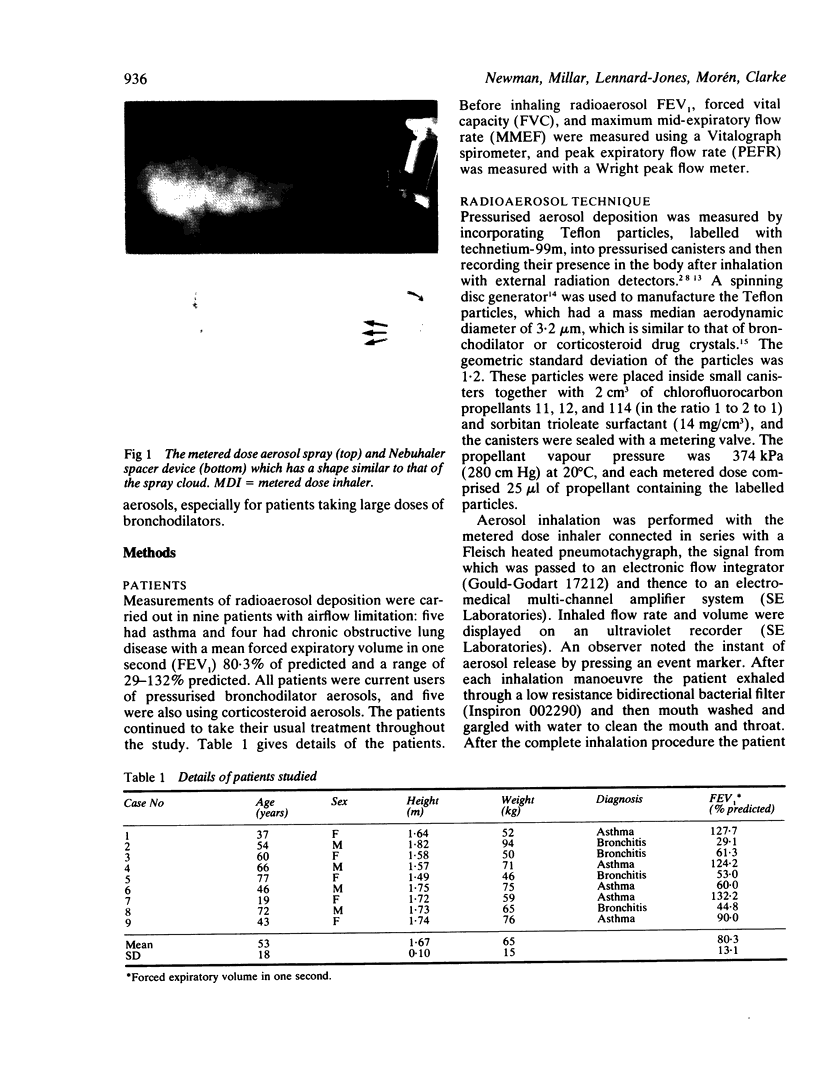
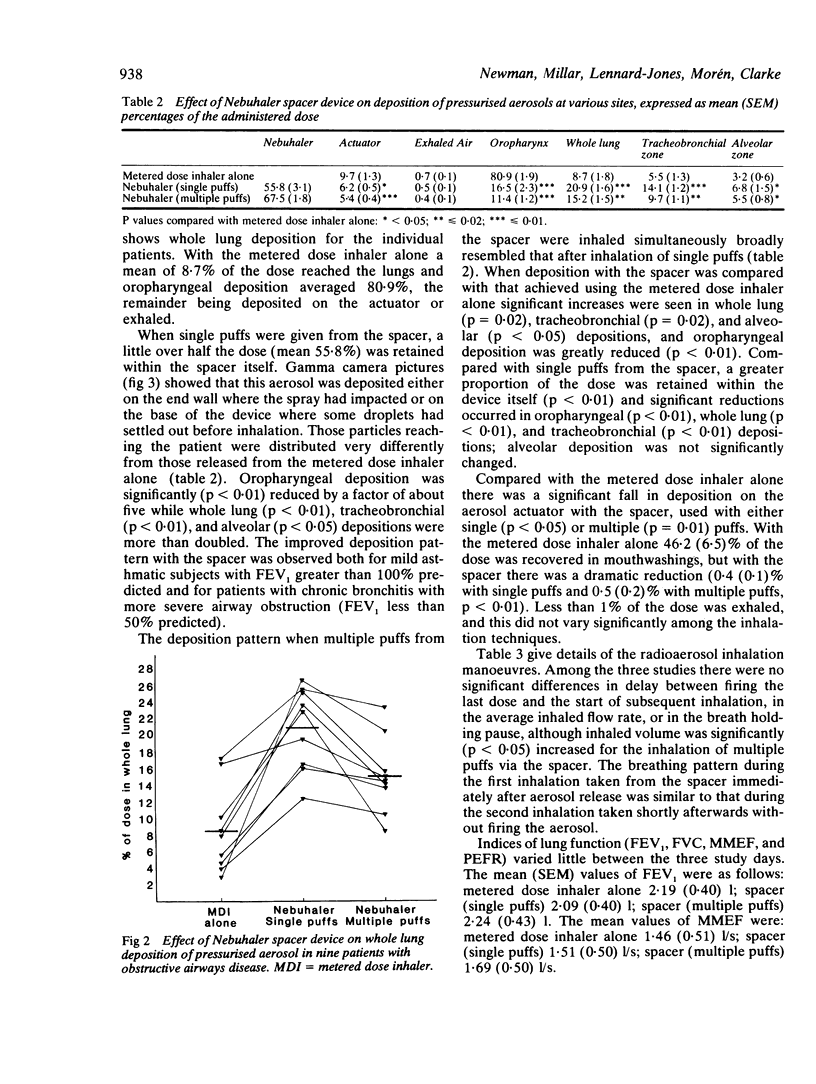
The effect on aerosol deposition from a pressurised metered dose inhaler of a 750 cm3 spacer device with a one way inhalation valve (Nebuhaler, Astra Pharmaceuticals) was assessed by means of an in vivo radiotracer technique. Nine patients with obstructive lung disease took part in the study. The pattern of deposition associated with use of a metered dose inhaler alone was compared with that achieved with the spacer used both for inhalation of single puffs of aerosol and for inhalation of four puffs actuated in rapid succession and then inhaled simultaneously. On each occasion there was a delay of 1 s between aerosol release and inhalation, simulating poor inhaler technique. With the metered dose inhaler alone, a mean (SEM) 8.7 (1.8)% of the dose reached the lungs and 80.9 (1.9)% was deposited in the oropharynx. With single puffs from the spacer 20.9 (1.6)% of the dose (p less than 0.01) reached the lungs, only 16.5 (2.3)% (p less than 0.01) was deposited in the oropharynx, and 55.8 (3.1)% was retained within the spacer itself. With four puffs from the spacer 15.2 (1.5)% reached the lungs (p = 0.02 compared with the metered dose inhaler alone, p less than 0.01 compared with single puffs from the spacer), 11.4 (1.2)% was deposited in the oropharynx, and 67.5 (1.8)% in the device itself. It is concluded that the spacer device gives lung deposition of metered dose aerosols comparable to or greater than a correctly used inhaler and oropharyngeal deposition is greatly reduced. The spacer should be used preferably for the inhalation of single puffs of aerosol but may also be used for the inhalation of up to four puffs actuated in rapid succession and then inhaled simultaneously.
Full text
PDF

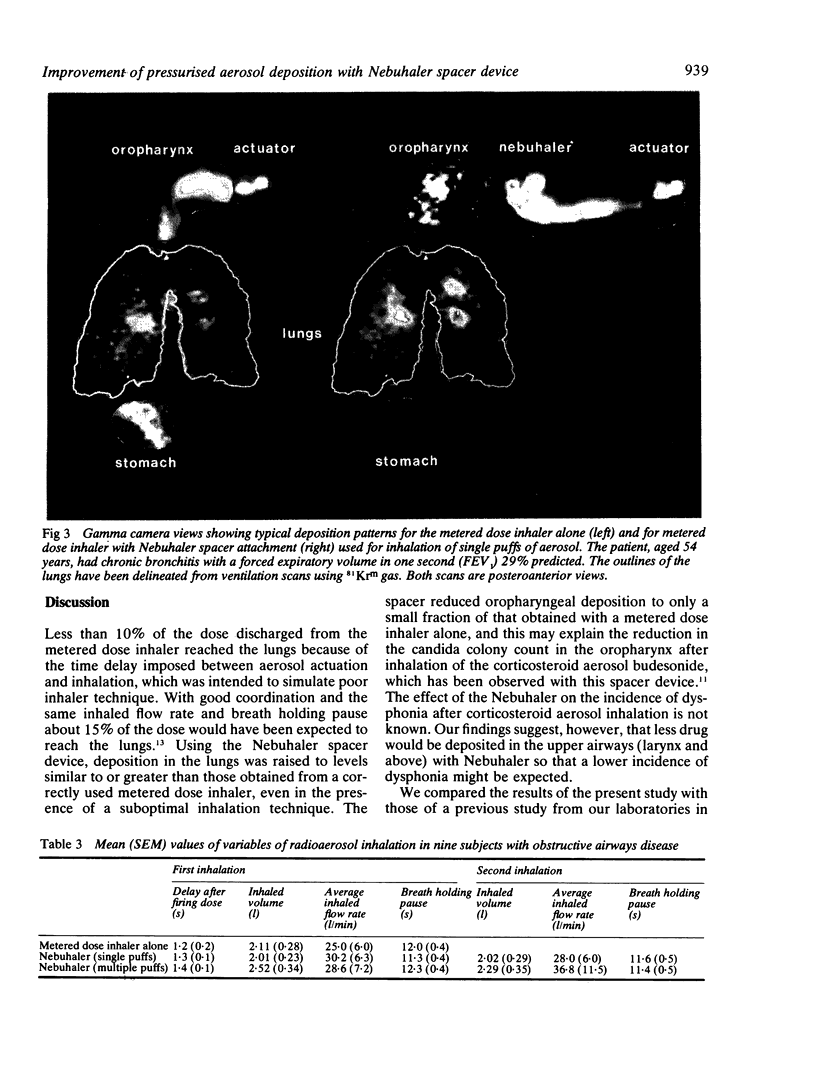


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloomfield P., Crompton G. K., Winsey N. J. A tube spacer to improve inhalation of drugs from pressurised aerosols. Br Med J. 1979 Dec 8;2(6203):1479–1479. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6203.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camner P., Philipson K. Human alveolar deposition of 4 micron teflon particles. Arch Environ Health. 1978 Jul-Aug;33(4):181–185. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1978.10667331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coady T. J., Stewart C. J., Davies H. J. Synchronization of bronchodilator release. Practitioner. 1976 Aug;217(1298):273–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton G. K. Problems patients have using pressurized aerosol inhalers. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1982;119:101–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushley M. J., Lewis R. A., Tattersfield A. E. Comparison of three techniques of inhalation on the airway response to terbutaline. Thorax. 1983 Dec;38(12):908–913. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.12.908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. S. Pharmacokinetics of inhaled substances. Postgrad Med J. 1975;51(7 Suppl):69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolovich M., Ruffin R., Corr D., Newhouse M. T. Clinical evaluation of a simple demand inhalation MDI aerosol delivery device. Chest. 1983 Jul;84(1):36–41. doi: 10.1378/chest.84.1.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellul-Micallef R., Morén F., Wetterlin K., Hidinger K. C. Use of a special inhaler attachment in asthmatic children. Thorax. 1980 Aug;35(8):620–623. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.8.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein S. W., Manning C. P., Ashley M. J., Corey P. N. Survey of the clinical use of pressurized aerosol inhalers. Can Med Assoc J. 1979 Apr 7;120(7):813–816. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller C., Mazumder M., Wilson D., Bone R. Aerodynamic size distribution of metered-dose bronchodilator aerosols. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Aug;118(2):311–317. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.2.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. D., Singh B. V., Frame M. H., Williams S. J. Terbutaline aerosol given through pear spacer in acute severe asthma. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Sep 25;285(6345):849–850. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6345.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. P., Morén F., Pavia D., Little F., Clarke S. W. Deposition of pressurized suspension aerosols inhaled through extension devices. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Sep;124(3):317–320. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.3.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. P., Pavia D., Garland N., Clarke S. W. Effects of various inhalation modes on the deposition of radioactive pressurized aerosols. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1982;119:57–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. P., Pavia D., Morén F., Sheahan N. F., Clarke S. W. Deposition of pressurised aerosols in the human respiratory tract. Thorax. 1981 Jan;36(1):52–55. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly J. F., Buchanan D. R., Sudlow M. F. Pressurised aerosol with conical spacer is an effective alternative to nebuliser in chronic stable asthma. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 May 14;286(6377):1548–1548. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6377.1548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin M. J., Jenouri G., Danta I., Kim C., Watson H., Sackner M. A. Response to bronchodilator drug administration by a new reservoir aerosol delivery system and a review of other auxiliary delivery systems. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Oct;126(4):670–675. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.4.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toogood J. H., Jennings B., Baskerville J., Johansson S. A. Clinical use of spacer systems for corticosteroid inhalation therapy: a preliminary analysis. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1982;122:100–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tothill P., Galt J. M. Quantitative profile scanning for the measurement of organ radioactivity. Phys Med Biol. 1971 Oct;16(4):625–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]