Abstract
RNase P is a ribozyme originally identified for its role in maturation of tRNAs by cleavage of precursor tRNAs (pre-tRNAs) at the 5′-end termini. RNase P is a ribonucleoprotein consisting of a catalytic RNA molecule and, depending on the organism, one or more cofactor proteins. The site of cleavage of a pre-tRNA is identified by its tertiary structure; and any RNA molecule can be cleaved by RNase P as long as the RNA forms a duplex that resembles the regional structure in the pre-tRNA. When the antisense sequence that forms the duplex with the strand that is subsequently cleaved by RNase P is in a separate molecule, it is called an external guide sequence (EGS). These fundamental observations are the basis for EGS technology, which consists of inhibiting gene expression by utilizing an EGS that elicits RNase P-mediated cleavage of a target mRNA molecule. EGS technology has been used to inhibit expression of a wide variety of genes, and may help development of novel treatments of diseases, including multidrug resistant bacterial and viral infections.
Background
RNase P, a ubiquitous ribozyme present in all living organisms, was originally identified for its role in the maturation of the 5′-end termini of tRNAs by a single endonucleolytic cleavage of the precursor tRNA (pre-tRNA) (Fig. 1A).1-5 Further functional studies found that RNase P of different organisms are required for synthesis of other natural RNA molecules, such as the precursors to 4.5S RNA, transfer messenger RNA, some multicistronic mRNAs, phage-related RNAs, small non-coding RNA genes, and others.4, 6-17
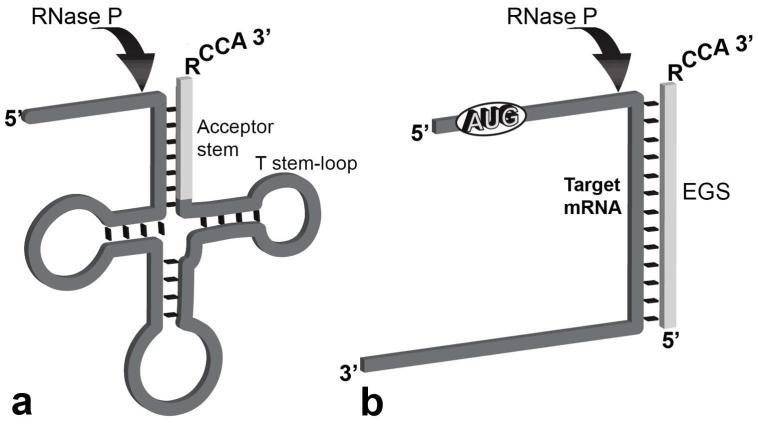
Fig. 1.
Cleavage of a pre-tRNA and an mRNA. (A) The arrow shows the site of action of RNase P on a pre-tRNA. The clear segment is the acceptor stem. (B) Complex between a target mRNA and an EGS that can be recognized as substrate by bacterial RNase P. In this example, the ATG sequence has been added to represent the possibility of using an mRNA as target. The RCCA sequence mimics the 3′-end of the pre-tRNA and facilitates interaction with RNase P. Redrawn from Ref. 4.
The RNase P holoenzyme is a ribonucleoprotein composed of the RNA molecule responsible for its catalytic activity 3 and one or more proteins as cofactors with different functions, which, in some cases, remain unknown.8, 18 Bacterial RNase P usually contains one protein, while archaeal and human counterparts include between 5 and 10 proteins.19 Although structural studies on RNase P holoenzymes are still at an early stage, the structure of a bacterial RNase P in complex to mature tRNA has been resolved at high resolution.20
Early applications of external guide sequence technology
The Escherichia coli RNase P consists of the 377-nucleotide catalytic RNA subunit M1 and the 119 amino acids cofactor protein C5.21-23 The holoenzyme recognizes the acceptor stem (Fig. 1A) and, possibly, the T stem-loop regions in pre-tRNAs, which form a particular structure recognized by RNase P.4, 22, 24-26 Experiments designed to determine domains in a pre-tRNA molecule without abolishing E. coli RNase P activity demonstrated that most of the pre-tRNA molecule could be removed; these experiments also showed that any bimolecular complex with the appropriate structure could also be a substrate for RNase P (Fig. 1B).24, 27-29 Importantly, the (antisense) complementary oligoribonucleotide was the only requirement to guide bacterial RNase P to cleave the target RNA molecule; when the antisense sequence that forms the duplex with the RNA is in a separate molecule, it is called an external guide sequence (EGS) (Fig. 1B).26-28 This fundamental finding led to the development of EGS technology, which consists of inhibiting gene expression by utilizing an EGS that elicits RNase P-mediated cleavage of a target RNA molecule.25, 26, 30-32
The general path to selection of EGSs consists of first identifying the regions in the target RNA molecule that are accessible for interaction with an antisense oligonucleotide (or oligonucleotide analog). This can be achieved by different methods, such as RNase H mapping,33, 34 cleavage assay by random EGSs,35 dimethyl sulfate in vivo mapping, 36-38 or digestion with specific enzymes.39-41 The results obtained can be further refined using computer prediction of the secondary structure of the RNA molecule using software such as mfold.42 EGSs are designed to target regions that are identified by one or more methods and then evaluated for their ability to elicit RNase P-mediated cleavage of the target RNA in vitro or in vivo (whole cells or animal models). EGS technology has been used to inhibit the expression of a wide range of genes.43-46 Early applications of the technology were in animal cell gene expression,47-51 plant cells,52, 53 parasites,54 as well as Saccharomyces cerevisiae.55
In this review, we briefly summarize illustrative examples of the utilization of EGS technology in development of antibacterial and antiviral compounds. A summary of applications of EGS technology to infectious agents is shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
EGS technology applied to infectious diseases
| Organism | Diseasea | Target | Chemical nature of EGS |
Proof-of-concept system |
Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV-1 | AIDS | tat and LTR | RNAb | COS cells (mouse) | 62 |
|
| |||||
| Hepatitis B virus | Hepatitis | pgRNA, S mRNA, pre-S/L mRNA | RNAb,c | HepG2 and HepG2.2.15 cells (human)b |
66, 67 |
| Micec | |||||
|
| |||||
| Murine cytomegalovirus | Cytomegalovirus infection |
mPR | RNAc | J774c, human U373MGb cells (human) | 36, 72, 74 |
| Micec | |||||
|
| |||||
| Herpes simplex virus 1 |
Herpes | thymidine kinase | RNAb | 143 tk- cells (human)b |
37, 76 |
|
| |||||
| Influenza virus | Flu | polymerase subunit 2 (PB2), nucleoprotein (NP) |
RNAb | C127 cells (mouse)b |
77 |
|
| |||||
| E. coli | NA | phoA, lacZ, | RNAb |
E. coli cells in culture |
56 |
|
| |||||
| E. coli | NA | bla, cat | RNAb |
E. coli cells in culture |
58 |
|
| |||||
| E. coli | NA | gyrA, rnpA | RNAb |
E. coli cells in culture |
79 |
|
| |||||
| E. coli | NA | aac(6′)-Ib | RNAb, LNA/DNAd |
E. coli cells in culture |
85, 97 |
|
| |||||
| E. coli | NA | ftsZ | RNAb |
E. coli cells in culture |
91 |
|
| |||||
| S. aureus | Wound infection | gyrA | PPMOe |
S. aureus cells in culture |
104 |
| Murine cutaneous wound model |
|||||
|
| |||||
| E. coli | NA (tularemia) | F. tularensis mlgB | RNAf |
E. coli
cells harboring heterologous gene in culture |
95 |
|
| |||||
| S. enterica | Salmonella infection | invB, invC | RNAb |
S. enterica invasion of Henle- 407 cells (human) |
39 |
|
| |||||
| E. coli | NA (plague) | Y. pestis yscN and yscS | RNAf |
E. coli
cells harboring heterologous gene in culture |
41 |
|
| |||||
| E. coli | NA (brucellosis) | B. melitensis vjbB | RNAf | In vitro cleavage of mRNA |
35 |
|
| |||||
|
E. coli
B. subtilis E. faecalis |
NA | gyrA | PPMOe | Bacterial cells in culture |
100 |
|
| |||||
|
P. aeruginosa
S. aureus |
NA | gyrA | PPMOe | In vitro cleavage of mRNA |
100 |
|
| |||||
|
E. coli
B. subtilis E. faecalis |
NA | rnpA | PPMOe | In vitro cleavage of mRNA |
100 |
|
| |||||
| E. coli | NA | cat | PPMOe | Bacterial cells in culture |
100 |
|
| |||||
|
Plasmodium
falciparum |
Malaria | gyrA | PPMOe |
P. falciparum cells in culture |
54 |
In those cases where the inhibition of expression of the gene(s) in question was done in E. coli harboring the gene(s), the disease caused by the bacterium providing the gene(s) is indicated in parenthesis. NA, not applicable.
Recombinant clones coding for EGSs were introduced in cells (prokaryotic or eukaryotic) as described in the text.
The EGS was in a recombinant clone harbored by a Salmonella strain constructed for delivery.
LNA/DNA, oligomer composed of LNA and deoxynucleotide residues.
PPMO, phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligonucleotide EGS conjugated to permeabilizer peptide.
A recombinant plasmid expressing both the EGS and the target gene was introduced in E. coli to test the EGS activity on gene expression.
First EGS application in E. coli
The first example of EGS-mediated gene-regulation was published by Guerrier-Takada et al.56 EGSs were utilized to reduce expression of β-galactosidase and alkaline phosphatase in E. coli. The EGSs used in E. coli and other bacterial systems usually include a 13–16 nucleotide antisense molecule complementary to the target region that also has the addition of an RCCA sequence at the 3′ end, which facilitates interaction with RNase P (Fig. 1B). 7, 57 Because RNA molecules are extremely unstable and do not penetrate E. coli cells readily, an appropriate recombinant plasmid that expresses the EGS was used. The release of the EGS sequence was achieved by designing a DNA insert consisting of a T7 promoter, the EGS sequence, a core hammerhead sequence, and a T7 terminator (T7p–EGS–HH–T7t). After induction and expression of the RNA, the core hammerhead ribozyme promotes self-cleavage and releases the EGS into the cytosol.58 An RNase P temperature-sensitive E. coli mutant was transformed with recombinant plasmids that expressed either specific EGSs antisense to regions in target mRNAs or non-complementary sequences as negative controls. Inhibition of gene expression was elicited by the specific EGSs, which did not occur when the cells were cultured at the restrictive temperature, indicating that RNase P mediated the cleavage of the mRNA. Similar experiments were then carried out in which the same strategy was applied except that the EGSs were complementary to blaTEM (the gene that encodes β-lactamase) and cat (the gene that encodes chloramphenicol acetyl transferase). In these cases, there was significant inhibition of expression of the respective gene products and thus resistance to ampicillin (in the case of blaTEM-directed EGS) and chloramphenicol (in the case of cat-directed EGS).58
EGS technology applied to human viruses
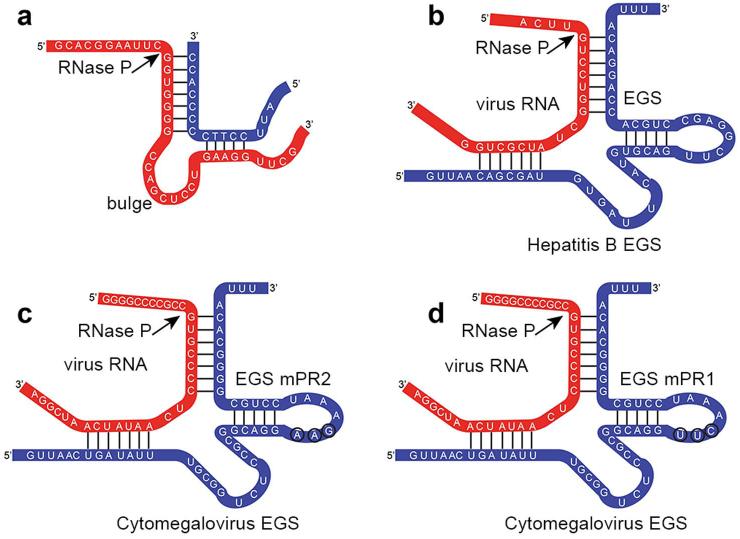
Yuan et al. 59 first showed that human RNase P can cleave an RNA substrate in the presence of an appropriate EGS that forms a bimolecular complex. However, the characteristics of the human EGSs were different from those designed for use with E. coli RNase P.32, 59 These studies showed that an EGS consisting of the sequence adjacent to a 5-or 6-base pair helix, connected through a bulge with a second 7–8 base pair helix, efficiently elicits cleavage of the target RNA by human RNase P (Fig. 2A).60, 61 It was later shown that exogenous administration of a 2′-O-methyl modified oligonucleotide analog EGS in complex with the transfecting reagent Lipofectin also induced cleavage of a target mRNA by RNase P in cells in culture.43
Fig. 2.
Schematic representation of complexes target RNA:EGS. (A) Bimolecular substrate of human RNase P. (B–D) Complexes between the hepatitis B pgRNA sequence (red),B, the mPR mRNA (red), C and D, and the respective EGSs (blue). The nucleotides substituted between EGSmPR1 and EGSmPR2 are circled. The arrow indicates the point of action of human RNase P. Redrawn from Refs. 36, 60, 66.
Anti-HIV EGS
Replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) was suppressed by designing EGSs targeting tat mRNA and the U5 region of the long terminal repeat (LTR).62 The Tat protein is a positive regulator of expression of HIV-1 genes at the level of transcriptional elongation.63 The LTR contains the viral promoter, which is responsible for viral gene expression in eukaryotic cells, and, is present in both early and late viral gene products.64, 65 Expression of EGSs in tissue culture cells (COS cells, a fibroblast-like cell line from monkey kidney tissue) was carried out by transfecting the cells with plasmids in which the EGS sequences were cloned into the mammalian expression vector pSV2neo, along with either the human tRNAmet or human U6 snRNA promoter upstream and the pol III termination downstream of the EGS sequences. Although EGSs specific for several HIV-1 genes efficiently inhibited replication of the virus, the highest inhibitory effect was observed with the EGS that targeted the HIV-1 tat gene. 62 Furthermore, no significant differences were found when the EGSs were expressed using either of the two promoters.
Anti-HBV EGS
Another study focused on inhibition of the hepatitis B virus (HBV). 66, 67 The HBV pre-genomic RNA (pgRNA), which is the template for DNA genome synthesis, and the mRNAs for the viral polymerase and core protein were mapped using the dimethyl sulphate method37 to identify regions accessible for interaction with EGSs. A region that when digested by RNase P would affect expression of essential viral proteins, as well as the level of viral genomic DNA, was chosen as the target. The bimolecular complex of EGS and target mRNA is shown in Fig. 2B. In vitro assays showed that the pgRNA substrate was efficiently cleaved when incubated in the presence of human RNase P and the EGS. The EGS sequence was then cloned into an expression vector under the control of the U6 promoter, along with the gene for green fluorescence protein (GFP). The recombinant plasmid was introduced into the attenuated Salmonella strain SL301, developed specifically for gene delivery.68 The transfected strain was then used to infect human hepatoma HepG2 cells; 24 hours after infection >70% of cells expressed GFP and the EGS at high levels.66 Experiments to determine inhibition of replication of HBV in infected cells in culture were performed by infecting hepatoma cells with HBV followed by delivery of the EGS using the Salmonella delivery strain. After treatment, the hepatoma cells were sorted based on expression of the green fluorescent protein (i.e., the cells that acquired and expressed the EGS-containing plasmid); these cells showed 92% and 93% reduction of the HBV 3.5 kb and 2.4/2.1 kb transcripts, respectively. Further experiments were carried out using an animal model consisting of mice injected with an HBV genomic DNA plasmid that reaches liver tissue and is expressed, leading to secretion of hepatitis B-related antigens.69 When the transfected mice were treated by oral inoculation of Salmonella expressing the EGS, a reduction of ~200,000-fold in viral DNA in the liver and serum was observed.66 This work was followed by an analysis of different EGS variants to maximize their ability to elicit RNase P-mediated cleavage of the HBV target.67
Anti-CMV EGS
Human cytomegalovirus, CMV, is a cause of serious disease for immunocompromised patients. Compounding this problem, numerous strains are becoming resistant to available treatments. CMV was the target for the first antisense therapeutic agent, fomivirsen, which was approved by the FDA in 1998 for intravitreal injectable treatment of CMV retinitis.70 Fomivirsen is a 21-base phosphorothioate oligonucleotide analog that functions by blocking translation of the viral immediate-early gene mRNA.71
The application of EGS technology may provide new therapeutic alternatives to prevent replication of CMV. For example, Jiang et al. mapped the mRNA encoding the protease (mPR) of murine CMV, whose infection of mice is similar to that of human CMV infection in humans, and selected a location 160 nucleotides downstream from the mPR translational initiation codon to design the EGS.36 Two identical EGSs were designed, with the exception of three highly conserved nucleotides within the T-loop that are important for interaction with RNase P (Fig. 2C and D). In vitro assays of RNase P cleavage showed that in spite of both EGSs having the same binding activity with the target mRNA, only the EGS with nucleotides corresponding to the tRNASer in the T loop was active. Thus, substitution of the three nucleotides rendered the mutated EGS inactive, proving the crucial role of these nucleotides in the action of RNase P.36
The active EGS was cloned into an expression vector that was introduced into a Salmonella strain for gene delivery in vivo; murine CMV–infected mice were treated orally with Salmonella carrying recombinant plasmids expressing either the EGS to be tested or EGSs controls. The infected mice treated with the active, but not control, EGS showed reduced levels of mPR and viral titers, and increased survival.36
In other experiments, the mRNA necessary for CMV capsid scaffolding protein expression and assembly, both essential for capsid formation, was targeted.72 An EGS lacking the anticodon loop was more effective in reducing expression of the proteins and viral growth in human CMV–infected cells in culture compared to an EGS that formed a tRNA-like structure when in complex with the target mRNA. The levels of reduction of protein expression and viral growth by the former EGS were 98% and 7000-fold, respectively, in contrast to 75% and 250-fold, respectively, by EGS that formed a tRNA-like structure.72
Both human and murine CMVs were also used to assess the efficiency of M1 guide sequence (M1GS) molecules (RNA molecules consisting of the EGS sequence linked to the 3′ end of the M1 RNA).73, 74 The overlapping region of the murine CMV mRNA that codes for the M80.5 protein and the viral protease, both essential for viral replication, was used as the target for an M1GS that mediated mRNA cleavage. The DNA sequences of M1GSs were cloned in a plasmid under the control of the U6 promoter and introduced in a Salmonella strain for gene delivery in vivo.73 CMV-infected macrophages and murine CMV–infected mice were treated with the Salmonella transformants. Macrophages treated with one of the M1GSs showed a reduction in the synthesis of both M80.5 and protease of about 80–85%, and a 2,500-fold reduction in viral growth, compared to the controls. Oral treatment of infected mice resulted in improved survival, as well as reduced viral titers.73
In yet another experiment, a M1GS that targeted the human CMV immediate-early protein 2 mRNA, using the wild-type sequence of the ribozyme, resulted in a 75% reduction in the expression of the protein and a100-fold reduction in viral production in infected human cells in culture. However, when a variant that included two point mutations in the ribozyme component of the M1GS (A94G and G194C), known to confer higher catalytic activity to the ribozyme in vitro,75 was used, significantly more activity was observed, with reductions of protein expression by 98% and virus production by 3500-fold.74
Anti-HSV-1 EGS
The thymidine kinase mRNA from the herpex simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) has been targeted by EGS for inhibition of HSV-1 viral gene expression.37, 76 The fragment around the translation initiation site of the mRNA was mapped in vivo using the dimethyl sulfate technique. The mRNA region selected to target with an EGS would result in cleavage at nucleotide 29 downstream of the translation initiation codon. The EGS designed was 71-nucleotides and formed a tRNA-like structure in complex with the target HSV-1 mRNA. Two additional EGSs were designed and tested, one with a C->G substitution at the highly conserved T-loop sequence and the other with a deletion of a portion equivalent to the anticodon domain of the EGS. The three EGSs were assayed to determine their ability to elicit cleavage of the thymidine kinase mRNA by RNase P. The EGS lacking the anticodon domain cleaved most efficiently, while the EGS with the C->G substitution showed very low activity. However, the binding affinity to the thymidine kinase mRNA substrate was similar for both EGSs, indicating that the nucleotide change interfered with formation of the adequate structure for the EGS–mRNA complex to be recognized by RNase P.32 In additional experiments, the DNAs coding for the EGSs were cloned under the control of the U6 promoter and the recombinant plasmids were transfected into human cells in culture that were then infected with HSV-1. A significant inhibition of expression of viral thymidine kinase was observed with the EGS that were shown to be active in the earlier assays.32 Following these results, a pool of EGSs generated with random mutations was put through an in vitro selection procedure to identify a highly active EGS that reduced expression of thymidine kinase in HSV-1-infected cells by 95%.37
Anti-Influenza virus EGSs
Production of influenza virus from infected cells in tissue culture has been inhibited by addition of two EGSs that target two flu virus mRNA molecules coding for the polymerase subunit 2 (PB2) and the nucleoprotein NP.77 Both proteins are essential for replication and production of viral particles.78 Target regions were selected by mapping RNase T1 digestion sites within mRNAs. EGSs were designed and cloned into the LSXN cloning vector under the control of the U6 promoter. The recombinant clones were introduced into mouse cells in culture, which were then infected with flu virus at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) high enough to ensure infection of all the cells. Inhibition of protein expression and production of viral particles was observed in those cases where the cells expressed the EGSs from recombinant clones. However, as anticipated, not all EGSs showed the same level of inhibition. The strongest inhibitions, ~90% (MOI = 3) and 50% (MOI = 10), were achieved with an EGS targeting the PB2 mRNA. Introduction of another recombinant clone consisting of the vector RVY with an EGS that targets the NP mRNA resulted in cells from which particle production was inhibited 90–100% at a MOI = 10.77 To demonstrate that RNase P mediated cleavage, an EGS was designed with a defective T-loop that prevented RNase P activity;77 all experiments using this control EGS showed no inhibition of virus replication.
EGS technology applied to bacterial pathogens
Following the pioneering work by Guerrier-Takada et al. 56, 58 described above, several groups attempted to overcome antibiotic resistance or target essential genes in a variety of bacterial pathogens (Table 1).
E. coli: GyrA and the C5 subunit of RNase P
McKinney et al. successfully designed EGSs that targeted mRNAs coding for GyrA and the C protein (C5) component of RNase P.79 Two EGSs targeting different regions of either the gyrA or the C5 mRNA were cloned in a single DNA sequence with the orientation T7p–EGS1–HH1–HH2–EGS2–HH3–T7t. E. coli cells were transformed with the recombinant clones and upon induction a decrease in viability of about 10-fold was observed targeting either the gyrA or the C5 mRNA.79 A recombinant clone that included all four EGSs, i.e., two specific for gyrA mRNA and two specific for C5 mRNA, was also tested. The results showed additive, but not synergistic, effects. An analysis of the efficiency of the EGSs targeting gyrA demonstrated that up to three mismatches did not impair the inhibitory effect of the EGS.79
E. coli: aac(6′)-Ib and ftsZ
The aminoglycoside 6′-N-acetyltransferase type Ib (AAC(6′)-Ib) is a clinically relevant enzyme that confers resistance to several aminoglycosides, including amikacin.80-82 The gene aac(6′)-Ib has been found in numerous plasmids, transposons, and integrons in Gram-negative bacteria.83, 84
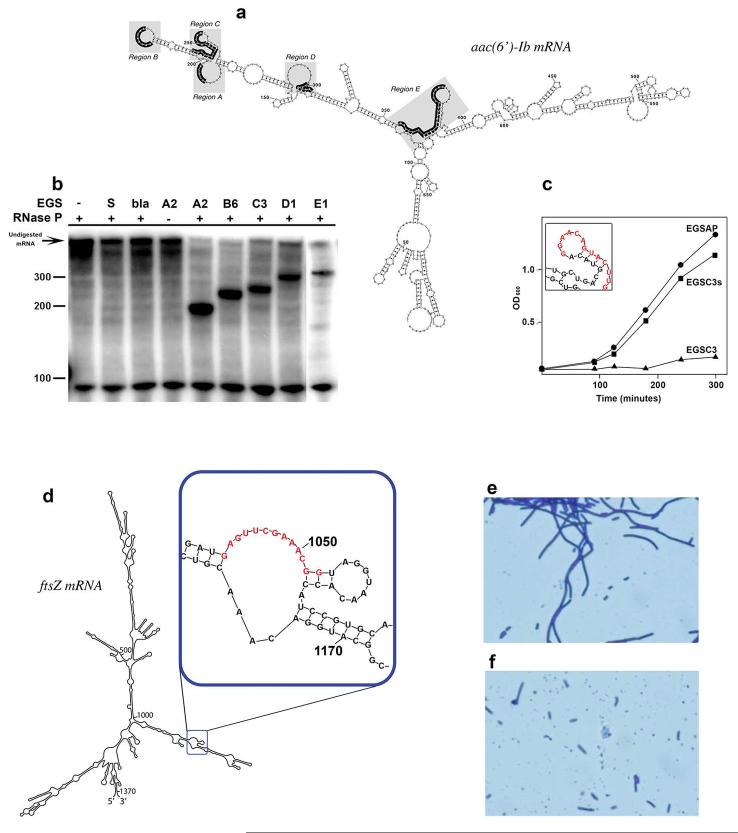
Available regions for interaction with EGSs were determined by a combination of a computer generated secondary structure and RNase H mapping (Fig. 3A).33, 34 A battery of EGSs targeting the selected regions was then tested in vitro to assess efficiency in eliciting RNase P-mediated cleavage (Fig. 3B).85 Those with the higher efficiency were cloned into a vector similar to that used by Guerrier-Takada et al. 58 (i.e., T7p–EGS–HH–T7t) and transferred to E. coli carrying aac(6′)-Ib. Cells with one of the EGSs, EGSC3, showed growth inhibition upon addition of amikacin (Fig. 3C).85 It is noteworthy that the target region (region C, Fig. 3B and C) is not entirely single-stranded in its predicted structure: four nucleotides are predicted to be in double-stranded form. Nevertheless, it was identified as region accessible for interaction with an antisense sequence by RNase H mapping (Fig. 3B and C). Possible explanations are that either the predicted structure may not reflect the precise structure of the mRNA or the structural complexity of the region permits breathing at the short double-stranded stems, allowing interaction with the EGS.34, 86
Fig. 3.
RNase P-mediated inhibition of amikacin resistance and cell division by endogeneously produced EGSs. (A) Secondary structure of the aac(6′)-Ib mRNA as determined by utilizing a combination of mfold software42 and RNase H mapping.33 Reproduced from Ref. 34. (B) Cleavage reactions carried out in vitro in the presence of several EGSs targeting different regions in the mRNA (A2, B6, C3, D1, and E1). Controls lacked EGS or RNase P, or included EGSs targeting a different gene (bla) or carrying the sense nucleotide sequence. The RNase P components, M1 RNA and C5 protein, were incubated with end-labeled aac(6′)-Ib mRNA and the EGSs. The products were analyzed on 6% denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Reproduced from Ref. 85. (C) E. coli BL21(DE3) harboring the aac(6′)-Ib gene and recombinant plasmids coding for the EGSs indicated in the figure were cultured in the presence of 15 μg of amikacin/ml. Growth was monitored by measuring the OD600. The EGSs were: EGSC3, targets the sequence shown in red in the inset, EGSAP, targets the alkaline phosphatase gene, and EGSC3s has the sense sequence. The inset shows the region targeted by EGSC3 (nucleotides in red). Reproduced from Ref. 34. (D) Secondary structure of the ftsZ mRNA as determined by mfold software. The boxed region is shown in detail and the sequence in red is the target of the most efficient EGS tested. Redrawn from Ref. 91. (E and F) E. coli BL21(DE3)(pLysS) harboring recombinant plasmids coding for the EGS that targets ftsZ, E, or the complementary sequence, F, under the control of the T7 promoter were induced by addition of isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside, incubated for 60 minutes at 37 °C and examined by microscopy.
A strategy similar was used to interfere with normal expression of the ftsZ gene. FtsZ is essential for cell division and together with FtsA and ZipA participate in the first event of construction of the divisome, the formation of the proto-ring, which continues with the assembly of other proteins and protein complexes. FtsZ functions as a scaffold for the divisome and generates the constrictive force to initiate cell division.87-90
The ftsZ mRNA was mapped and EGS targeting regions accessible for interaction with antisense sequences were tested in vitro to determine the best candidates to elicit cleavage by RNase P (Fig. 3D).91 These assays led to selection of a few EGSs that were promising with respect to interfering with expression of ftsZ and disrupting cell division. The selected EGSs were cloned as part of a DNA fragment with the structure T7p–EGS–HH–T7t, and the recombinant clones were introduced in E. coli. Upon induction of the T7 promoter, cells expressing specific EGSs showed filamentation, indicating that cell division had been disrupted (see Fig. 3E and F).91
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
McKinney et al. designed EGSs that target the invC and invB genes found in the Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.39 The invC and invB genes code for an ATPase required for host cell invasion and a type III secretion chaperone, respectively.92, 93 Mapping of mRNA was carried out by RNase T1 digestion and four EGSs, three of them targeting invC, were designed on the basis of the mapping results. The EGSs were capable of inducing digestion of the target mRNAs in vitro and were cloned into high and low copy number vectors to be expressed within a Salmonella strain. Expression of all four EGSs resulted in a decrease in invC mRNA, consistent with the existence of a dicistronic mRNA. Assays to determine the effect on InvC-dependent type III secretion expressing two EGSs, both targeting invB or invC or one targeting invB and the other targeting invC, showed a reduction in secretion of the protein SipB and the levels of reduction were dependent on the copy number of the recombinant plasmids used. Expression of two EGSs, one targeting invC and the other invB, also resulted in inhibition of expression of InvC.
Finally, in cell invasion assays, Salmonella expressing EGSs targeting invB or invC from a high copy number plasmid exhibit about 90% reduction in invasion with respect to the controls.39 The authors proposed that both invC and invB are encoded in the same mRNA and the 3′ nucleotide of the final codon of invB is the 5′ nucleotide of the initial codon of invC. Then, since all four EGSs resulted in inhibition of expression of invC, it is possible that the mRNA is destabilized or functionally disrupted after cleavage at the invB location. This result suggests the non-surprising possibility that EGS targeting one region of an mRNA may have deleterious effects on the rest of the molecule.39
Yersinia pestis, Francisella tularensis, and Brucella melitensis
Ko et al. 41 applied EGS technology to inactivate the Yersinia pestis virulence genes yscN and yscS, which are part of a group of more than 20 genes that form a Type III secretion system, which is induced upon entry of Y. pestis into the mammalian host and when the bacterium makes contact with the mammalian cell it mediates injection of the effectors, known as Yop proteins, through the cell membrane. Once inside the eukaryotic cell, the effectors inhibit bacterial phagocytosis and suppress the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.94
Messenger RNAs for both yscN and yscS were mapped and EGSs were designed that proved active in in vitro assays. To test their ability to elicit RNase P-mediated cleavage of the mRNAs in vivo using E. coli as host, the EGSs and the target mRNA were cloned into expression vectors.41 The results showed that the most effective EGSs reduced the target mRNAs to 37–40% compared to the control condition of expressing the mRNA in the absence of an EGS.
A similar strategy was used to design EGSs that inhibit expression of the global virulence regulator MglB from Francisella tularensis,95 an intracellular pathogen that causes tularemia.96 The mglB mRNA was mapped and EGSs were designed and tested in vitro and then recombinant plasmids equivalent to those described for the Y. pestis system were constructed and assayed. Two EGSs alone or expressed tethered to M1 RNA reduced mRNA levels significantly.
Likewise, EGSs that reduce levels of the Brucella melitensis vjbB gene, which codes for the virulence regulator VjbB, have been identified following the same methodologies.35, 95
Modifications of EGSs to aid stability
While the recombinant plasmid based expression of EGSs from within the cells cytosol is appropriate as a general strategy to demonstrate proof of concept, it is not viable for therapeutic purposes because the EGSs added exogenously must penetrate the cells to exert their action. Furthermore, because oligoribonucleotides are rapidly degraded by nucleases, successful development of EGS technology depends on finding nuclease-resistant analogs that induce RNase P-mediated degradation of the target mRNA.
In the case of aac(6′)-Ib, locked nucleic acid (LNA)/DNA co-oligomers in the appropriate configuration efficiently elicited RNase P-mediated cleavage of the mRNA in vitro.97 Interestingly, unlike most oligonucleotides and oligonucleotide analogs that are not internalized, LNA/DNA co-oligomers were able to penetrate E. coli cells, but with very low efficiency.98 Therefore, their ability to interfere with amikacin resistance was assessed using the hyperpermeable E. coli AS19 strain.99 Administration of an LNA/DNA co-oligomer at 50 nM to E. coli AS19 cells harboring the aac(6′)-Ib gene significantly reduced the levels of resistance to amikacin.97
In a different study, phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligonucleotide EGSs conjugated to permeabilizer peptide (PPMO) efficiently inhibited expression of Gram-negative and Gram-positive genes.100, 101 Interestingly, these experiments showed that a mix of the PPMO that specifically targets an mRNA and permeabilizer peptide that remained in the mix as unreacted substrate during the conjugation reaction act as a powerful antibiotic.102, 103 The permeabilizer peptide possessed an unspecific antibacterial activity, while the PPMO functioned as a specific agent targeting a unique mRNA.102
PPMOs were also successfully used in experimental treatment of Staphylococcus aureus wound infection.104 A PPMO EGS was designed to target the gyrA mRNA and it proved effective in interfering with growth of S. aureus in liquid cultures.103 Furthermore, the PPMO was combined with a gel to assess its activity as a topical treatment in a mouse model of S. aureus infected skin wounds.105 Mice that were treated with the PPMO-containing gel showed faster re-epithelization and healing when compared to the controls.104
Concluding remarks
Infectious diseases are one of the leading causes of loss of human life. The continuous emergence of new threats and development of resistance to available treatments requires novel approaches to find means to extend the useful life of existing therapies and design new ones. EGS technology is a relatively new strategy that shows promise in the struggle to design novel therapeutic agents. Future research could focus on targeting conserved genes present in viruses or multidrug resistant bacterial pathogens such as efflux pumps, the replication machinery or selected virulence factors genes. Heretofore, success has been demonstrated in a variety of cell processes. Although this bodes well for the future of EGS technology, many challenges still lie ahead before EGS-based therapeutics can be introduced in the clinics. Successful delivery of the drugs to the appropriate targets, achieving high levels of inhibition of gene expression, and low toxicity to the host are just some them. The various strategies and approaches to design efficient EGSs and delivery vehicles described in this review attempt to overcome them.
Acknowledgments
Authors’ work cited in this review article was funded by Public Health Service grant 2R15AI047115 (to M.E.T.) from the National Institutes of Health and X-240 Universidad de Buenos Aires (to A.Z.). A.Z. is a career member of Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET). C.D.S. was supported by a fellowship from CONICET. For RAB, the writing of this manuscript was supported in part by funds and/or facilities provided by the Cleveland Department of Veterans Affairs, the Veterans Affairs Merit Review Program Award 1I01BX001974 and the Geriatric Research Education and Clinical Center VISN 10.
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest
REFERENCES
- 1.Schedl P, Primakoff P, Roberts J. Processing of E. coli tRNA precursors. Brookhaven Symp. Biol. 1975:53–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Altman S. A view of RNase P. Mol Biosyst. 2007;3:604–607. doi: 10.1039/b707850c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Guerrier-Takada C, et al. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell. 1983;35:849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Altman S. Ribonuclease P. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2011;366:2936–2941. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kazantsev AV, Pace NR. Bacterial RNase P: a new view of an ancient enzyme. Nature reviews. Microbiology. 2006;4:729–740. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bothwell AL, Garber RL, Altman S. Nucleotide sequence and in vitro processing of a precursor molecule to Escherichia coli 4.5 S RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1976;251:7709–7716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lundblad EW, Altman S. Inhibition of gene expression by RNase P. N Biotechnol. 2010;27:212–221. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2010.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jarrous N, Gopalan V. Archaeal/eukaryal RNase P: subunits, functions and RNA diversification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:7885–7894. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jarrous N, Reiner R. Human RNase P: a tRNA-processing enzyme and transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:3519–3524. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Komine Y, et al. A tRNA-like structure is present in 10Sa RNA, a small stable RNA from Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1994;91:9223–9227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Reiner R, et al. A role for the catalytic ribonucleoprotein RNase P in RNA polymerase III transcription. Genes Dev. 2006;20:1621–1635. doi: 10.1101/gad.386706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Reiner R, et al. Function and assembly of a chromatin-associated RNase P that is required for efficient transcription by RNA polymerase I. PLoS One. 2008;3:e4072. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hartmann RK, et al. Precursor of C4 antisense RNA of bacteriophages P1 and P7 is a substrate for RNase P of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1995;92:5822–5826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.13.5822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Forti F, et al. Immunity determinant of phage-plasmid P4 is a short processed RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 1995;249:869–878. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Alifano P, et al. Ribonuclease E provides substrates for ribonuclease P-dependent processing of a polycistronic mRNA. Genes Dev. 1994;8:3021–3031. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.3021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ko JH, Altman S. OLE RNA, an RNA motif that is highly conserved in several extremophilic bacteria, is a substrate for and can be regulated by RNase P RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007;104:7815–7820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701715104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yang L, Altman S. A noncoding RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is an RNase P substrate. RNA. 2007;13:682–690. doi: 10.1261/rna.460607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Marvin MC, Engelke DR. RNase P: increased versatility through protein complexity? RNA Biol. 2009;6:40–42. doi: 10.4161/rna.6.1.7566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mondragon A. Structural studies of RNase P. Annu Rev Biophys. 2013;42:537–557. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-083012-130406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Reiter NJ, et al. Structure of a bacterial ribonuclease P holoenzyme in complex with tRNA. Nature. 2010;468:784–789. doi: 10.1038/nature09516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Evans D, Marquez SM, Pace NR. RNase P: interface of the RNA and protein worlds. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006;31:333–341. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Torres-Larios A, et al. Crystal structure of the RNA component of bacterial ribonuclease P. Nature. 2005;437:584–587. doi: 10.1038/nature04074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sun L, et al. Evidence that substrate-specific effects of C5 protein lead to uniformity in binding and catalysis by RNase P. EMBO J. 2006;25:3998–4007. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kirsebom LA, Svard SG. The kinetics and specificity of cleavage by RNase P is mainly dependent on the structure of the amino acid acceptor stem. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992;20:425–432. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kirsebom LA. RNase P RNA mediated cleavage: substrate recognition and catalysis. Biochimie. 2007;89:1183–1194. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2007.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gopalan V, Vioque A, Altman S. RNase P: variations and uses. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:6759–6762. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R100067200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Forster AC, Altman S. External guide sequences for an RNA enzyme. Science. 1990;249:783–786. doi: 10.1126/science.1697102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.McClain WH, Guerrier-Takada C, Altman S. Model substrates for an RNA enzyme. Science. 1987;238:527–530. doi: 10.1126/science.2443980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Svard SG, Kirsebom LA. Determinants of Escherichia coli RNase P cleavage site selection: a detailed in vitro and in vivo analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993;21:427–434. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kole R, Krainer AR, Altman S. RNA therapeutics: beyond RNA interference and antisense oligonucleotides. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012;11:125–140. doi: 10.1038/nrd3625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Li Y, Guerrier-Takada C, Altman S. Targeted cleavage of mRNA in vitro by RNase P from Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1992;89:3185–3189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yuan Y, Altman S. Selection of guide sequences that direct efficient cleavage of mRNA by human ribonuclease P. Science. 1994;263:1269–1273. doi: 10.1126/science.8122108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ho SP, et al. Potent antisense oligonucleotides to the human multidrug resistance-1 mRNA are rationally selected by mapping RNA-accessible sites with oligonucleotide libraries. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996;24:1901–1907. doi: 10.1093/nar/24.10.1901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sarno R, et al. Inhibition of aminoglycoside 6′-N-acetyltransferase type Ib-mediated amikacin resistance by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003;47:3296–3304. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.10.3296-3304.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lundblad EW, et al. Rapid selection of accessible and cleavable sites in RNA by Escherichia coli RNase P and random external guide sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2008;105:2354–2357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0711977105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jiang X, et al. Effective inhibition of cytomegalovirus infection by external guide sequences in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2012;109:13070–13075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201620109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhou T, et al. In vitro selection of external guide sequences for directing RNase P-mediated inhibition of viral gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:30112–30120. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200183200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Climie SC, Friesen JD. In vivo and in vitro structural analysis of the rplJ mRNA leader of Escherichia coli. Protection by bound L10-L7/L12. J. Biol. Chem. 1988;263:15166–15175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.McKinney JS, et al. Disruption of type III secretion in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium by external guide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:848–854. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Guerrier-Takada C, Altman S. Inactivation of gene expression using ribonuclease P and external guide sequences. Methods Enzymol. 2000;313:442–456. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(00)13028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ko JH, Izadjoo M, Altman S. Inhibition of expression of virulence genes of Yersinia pestis in Escherichia coli by external guide sequences and RNase P. RNA. 2008;14:1656–1662. doi: 10.1261/rna.1120508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zuker M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3406–3415. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ma M, et al. Intracellular mRNA cleavage induced through activation of RNase P by nuclease-resistant external guide sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000;18:58–61. doi: 10.1038/71924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bassett T, et al. Effective stimulation of growth in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by inhibition of syntaxin18 by external guide sequence and ribonuclease P. Cancer Lett. 2008;272:167–175. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zhu J, et al. Effective inhibition of Rta expression and lytic replication of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus by human RNase P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2004;101:9073–9078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403164101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Dreyfus DH, Ghoda L. A review of recent patents concerning therapy of respiratory diseases using gene silencing by RNAi (RISC) and EGS (RNAse P) Recent patents on inflammation & allergy drug discovery. 2007;1:49–55. doi: 10.2174/187221307779815147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Dreyfus DH, Matczuk A, Fuleihan R. An RNA external guide sequence ribozyme targeting human interleukin-4 receptor alpha mRNA. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2004;4:1015–1027. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2004.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Pei DS, et al. Inhibition of no tail (ntl) gene expression in zebrafish by external guide sequence (EGS) technique. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2008;35:139–143. doi: 10.1007/s11033-007-9063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yen L, et al. Reduction of functional N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in neurons by RNase P-mediated cleavage of the NR1 mRNA. J. Neurochem. 2001;76:1386–1394. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00153.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kovrigina E, Wesolowski D, Altman S. Coordinate inhibition of expression of several genes for protein subunits of human nuclear RNase P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003;100:1598–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0337661100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Zhang H, Altman S. Inhibition of the expression of the human RNase P protein subunits Rpp21, Rpp25, Rpp29 by external guide sequences (EGSs) and siRNA. J. Mol. Biol. 2004;342:1077–1083. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Raj ML, et al. Cleavage of bipartite substrates by rice and maize ribonuclease P. Application to degradation of target mRNAs in plants. Plant Physiol. 2001;125:1187–1190. doi: 10.1104/pp.125.3.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Rangarajan S, et al. RNase P as a tool for disruption of gene expression in maize cells. Biochem. J. 2004;380:611–616. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Augagneur Y, et al. Gene selective mRNA cleavage inhibits the development of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2012;109:6235–6240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203516109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Cheng X, Ko JH, Altman S. Inactivation of expression of two genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae with the external guide sequence methodology. RNA. 2011;17:544–549. doi: 10.1261/rna.2538711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Guerrier-Takada C, Li Y, Altman S. Artificial regulation of gene expression in Escherichia coli by RNase P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1995;92:11115–11119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.24.11115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wegscheid B, Hartmann RK. The precursor tRNA 3′-CCA interaction with Escherichia coli RNase P RNA is essential for catalysis by RNase P in vivo. RNA. 2006;12:2135–2148. doi: 10.1261/rna.188306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Guerrier-Takada C, Salavati R, Altman S. Phenotypic conversion of drug-resistant bacteria to drug sensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1997;94:8468–8472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.16.8468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Yuan Y, Hwang ES, Altman S. Targeted cleavage of mRNA by human RNase P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1992;89:8006, 8010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Werner M, et al. Short oligonucleotides as external guide sequences for site-specific cleavage of RNA molecules with human RNase P. RNA. 1998;4:847–855. doi: 10.1017/s1355838298980323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Werner M, et al. Targeted cleavage of RNA molecules by human RNase P using minimized external guide sequences. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1999;9:81–88. doi: 10.1089/oli.1.1999.9.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Barnor JS, et al. Effective inhibition of HIV-1 replication in cultured cells by external guide sequences and ribonuclease P. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004;14:4941–4944. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.07.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Laspia MF, Rice AP, Mathews MB. HIV-1 Tat protein increases transcriptional initiation and stabilizes elongation. Cell. 1989;59:283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90290-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Kashanchi F, Wood C. Human immunodeficiency viral long terminal repeat is functional and can be trans-activated in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1989;86:2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Turner BG, Summers MF. Structural biology of HIV. J. Mol. Biol. 1999;285:1–32. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Xia C, et al. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus gene expression and replication by ribonuclease P. Mol. Ther. 2013;21:995–1003. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Zhang Z, et al. Engineered external guide sequences are highly effective in inhibiting gene expression and replication of hepatitis B virus in cultured cells. PLoS One. 2013;8:e65268. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Bijlsma JJ, Groisman EA. The PhoP/PhoQ system controls the intramacrophage type three secretion system of Salmonella enterica. Mol. Microbiol. 2005;57:85–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Yang PL, et al. Hydrodynamic injection of viral DNA: a mouse model of acute hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2002;99:13825–13830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.202398599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Roehr B. Fomivirsen approved for CMV retinitis. Journal of the International Association of Physicians in AIDS Care. 1998;4:14–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Azad RF, et al. Antiviral activity of a phosphorothioate oligonucleotide complementary to human cytomegalovirus RNA when used in combination with antiviral nucleoside analogs. Antiviral Res. 1995;28:101–111. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(95)00035-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Jiang X, et al. Ribonuclease P-mediated inhibition of human cytomegalovirus gene expression and replication induced by engineered external guide sequences. RNA Biol. 2012;9:1186–1195. doi: 10.4161/rna.21724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Bai Y, et al. Oral delivery of RNase P ribozymes by Salmonella inhibits viral infection in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2011;108:3222–3227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014975108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Yang Z, et al. Engineered RNase P ribozymes effectively inhibit human cytomegalovirus gene expression and replication. Viruses. 2014;6:2376–2391. doi: 10.3390/v6062376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kilani AF, et al. RNase P ribozymes selected in vitro to cleave a viral mRNA effectively inhibit its expression in cell culture. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:10611–10622. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.14.10611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kawa D, et al. Inhibition of viral gene expression by human ribonuclease P. RNA. 1998;4:1397–1406. doi: 10.1017/s1355838298980918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Plehn-Dujowich D, Altman S. Effective inhibition of influenza virus production in cultured cells by external guide sequences and ribonuclease P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1998;95:7327–7332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.13.7327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Manz B, Schwemmle M, Brunotte L. Adaptation of avian influenza A virus polymerase in mammals to overcome the host species barrier. J. Virol. 2013;87:7200–7209. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00980-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.McKinney J, et al. Inhibition of Escherichia coli viability by external guide sequences complementary to two essential genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2001;98:6605–6610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.121180398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Ramirez MS, Nikolaidis N, Tolmasky ME. Rise and dissemination of aminoglycoside resistance: the aac(6′)-Ib paradigm. Front Microbiol. 2013;4:121. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Ramirez MS, Tolmasky ME. Aminoglycoside modifying enzymes. Drug Resist Updat. 2010;13:151–171. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2010.08.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Shaw KJ, et al. Molecular genetics of aminoglycoside resistance genes and familial relationships of the aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Microbiol. Rev. 1993;57:138–163. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.138-163.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Ramirez MS, et al. Plasmid-mediated antibiotic resistance and virulence in Gram-negatives: the Klebsiella pneumoniae paradigm. Microbiology Spectrum. 2014;2 doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.PLAS-0016-2013. PLAS-0016-2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Tolmasky ME. Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes: characteristics, localization, and dissemination. In: Bonomo R, Tolmasky ME, editors. Enzyme-Mediated Resistance to Antibiotics: Mechanisms, Dissemination, and Prospects for Inhibition. ASM Press; Washington, DC: 2007. pp. 35–52. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Soler Bistue AJ, et al. External guide sequences targeting the aac(6′)-Ib mRNA induce inhibition of amikacin resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007;51:1918–1925. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01500-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Kuwabara T, Warashina M, Taira K. Cleavage of an inaccessible site by the maxizyme with two independent binding arms: an alternative approach to the recruitment of RNA helicases. J. Biochem. 2002;132:149–155. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a003193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.de Boer PA. Advances in understanding E. coli cell fission. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010;13:730–737. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2010.09.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Erickson HP, Anderson DE, Osawa M. FtsZ in bacterial cytokinesis: cytoskeleton and force generator all in one. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010;74:504–528. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00021-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Mingorance J, et al. Strong FtsZ is with the force: mechanisms to constrict bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2010;18:348–356. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2010.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Vivancos AP, et al. Strand-specific deep sequencing of the transcriptome. Genome Res. 2010;20:989–999. doi: 10.1101/gr.094318.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Davies Sala C, et al. Inhibition of cell division induced by external guide sequences (EGS Technology) targeting ftsZ. PLoS One. 2012;7:e47690. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Bronstein PA, Miao EA, Miller SI. InvB is a type III secretion chaperone specific for SspA. J. Bacteriol. 2000;182:6638–6644. doi: 10.1128/jb.182.23.6638-6644.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Eichelberg K, Ginocchio CC, Galan JE. Molecular and functional characterization of the Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes invB and invC: homology of InvC to the F0F1 ATPase family of proteins. J. Bacteriol. 1994;176:4501–4510. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.15.4501-4510.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Plano GV, Schesser K. The Yersinia pestis type III secretion system: expression, assembly and role in the evasion of host defenses. Immunol. Res. 2013;57:237–245. doi: 10.1007/s12026-013-8454-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Xiao G, et al. Inhibition of expression in Escherichia coli of a virulence regulator MglB of Francisella tularensis using external guide sequence technology. PLoS One. 2008;3:e3719. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Steiner DJ, Furuya Y, Metzger DW. Host-pathogen interactions and immune evasion strategies in Francisella tularensis pathogenicity. Infection and drug resistance. 2014;7:239–251. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S53700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Soler Bistue AJ, et al. Inhibition of aac(6′)-Ib-mediated amikacin resistance by nuclease-resistant external guide sequences in bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009;106:13230–13235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906529106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Traglia GM, et al. Internalization of Locked Nucleic Acids/DNA Hybrid Oligomers into Escherichia coli. BioResearch open access. 2012;1:260–263. doi: 10.1089/biores.2012.0257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Sekiguchi M, Iida S. Mutants of Escherichia coli permeable to actinomycin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1967;58:2315–2320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Shen N, et al. Inactivation of expression of several genes in a variety of bacterial species by EGS technology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009;106:8163–8168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903491106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Altman S. Antibiotics present and future. FEBS Lett. 2014;588:1–2. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.10.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Wesolowski D, Alonso D, Altman S. Combined effect of a peptide-morpholino oligonucleotide conjugate and a cell-penetrating peptide as an antibiotic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2013;110:8686–8689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1306911110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Wesolowski D, et al. Basic peptide-morpholino oligomer conjugate that is very effective in killing bacteria by gene-specific and nonspecific modes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2011;108:16582–16587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112561108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Sawyer AJ, et al. A peptide-morpholino oligomer conjugate targeting Staphylococcus aureus gyrA mRNA improves healing in an infected mouse cutaneous wound model. Int. J. Pharm. 2013;453:651–655. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.05.041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Kyriakides TR, et al. Mice that lack matrix metalloproteinase-9 display delayed wound healing associated with delayed reepithelization and disordered collagen fibrillogenesis. Matrix Biol. 2009;28:65–73. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2009.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]