Abstract
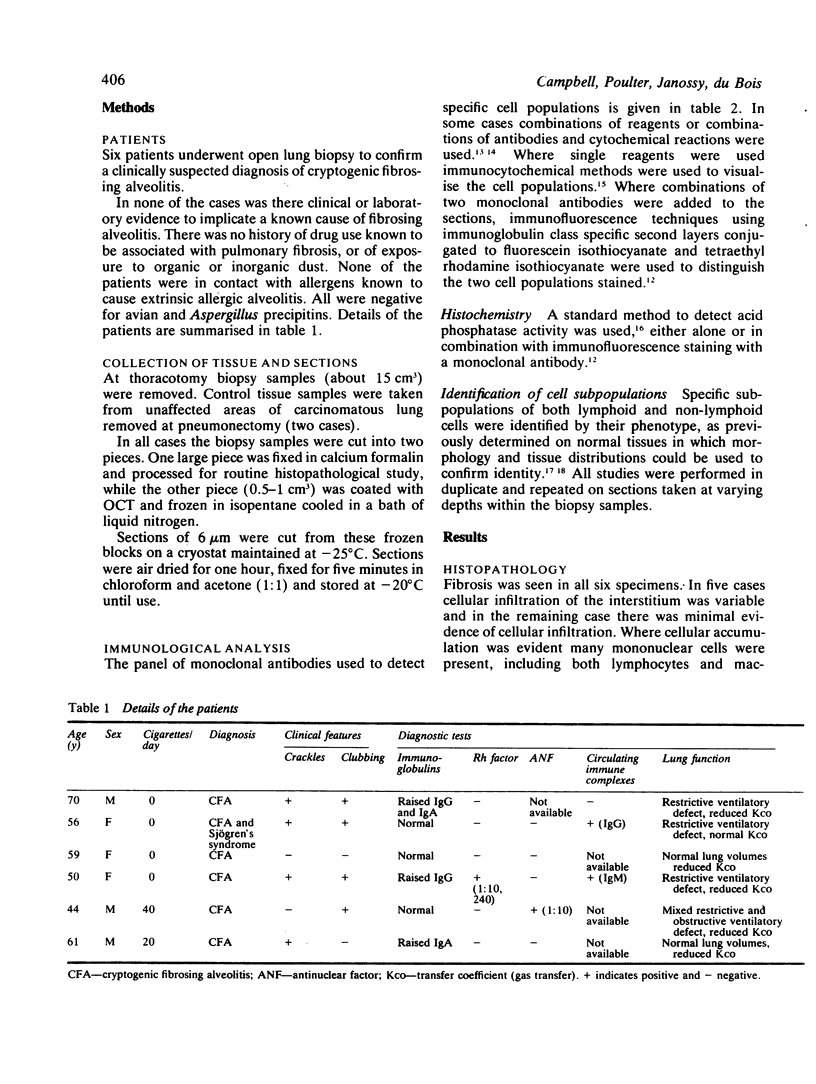
Immunohistological analysis using monoclonal antibodies in conjunction with histochemical techniques has been applied to lung biopsy material from patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Subsets of lymphoid and non-lymphoid cells have been identified in situ. This analysis showed that the inflammatory cells present were predominantly mononuclear. Most of the lymphoid cells were B lymphocytes, organised into follicles with occasional germinal centre formation. IgM was the major class of immunoglobulin expressed. Both T4+ and T8+ lymphocytes were seen diffusely distributed in the interstitium. The T4+ positive cells were also seen within the B lymphoid follicles. Almost all non-lymphoid cells expressed the phenotype of inflammatory macrophages, but a few also expressed a phenotype characteristic of interdigitating cells. These results suggest that a local B lymphoid immune response is occurring in cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. The possibility that a cell mediated immune response is also emerging is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benacerraf B. Role of MHC gene products in immune regulation. Science. 1981 Jun 12;212(4500):1229–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.6165083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Hance A. J., Keogh B. A. Interstitial lung diseases of unknown cause. Disorders characterized by chronic inflammation of the lower respiratory tract (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):154–166. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Gadek J. E., Ferrans V. J., Fulmer J. D., Line B. R., Hunninghake G. W. Interstitial lung disease: current concepts of pathogenesis, staging and therapy. Am J Med. 1981 Mar;70(3):542–568. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90577-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreisin R. B., Schwarz M. I., Theofilopoulos A. N., Stanford R. E. Circulating immune complexes in the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. N Engl J Med. 1978 Feb 16;298(7):353–357. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197802162980701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke O., Panayi G. S., Janossy G., Poulter L. W. An immunohistological analysis of lymphocyte subpopulations and their microenvironment in the synovial membranes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis using monoclonal antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jul;49(1):22–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee J. B., Fick R. B., Jr Bronchoalveolar lavage. Thorax. 1980 Jan;35(1):1–8. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Lawley T. J., Crystal R. G. Mechanisms of neutrophil accumulation in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):259–269. doi: 10.1172/JCI110242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G., Humphrey J. H., Kunkl A., Dongworth D. W. The follicular dendritic cell: its role in antigen presentation in the generation of immunological memory. Immunol Rev. 1980;53:3–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb01038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kravis T. C., Ahmed A., Brown T. E., Fulmer J. D., Crystal R. G. Pathogenic mechanisms in pulmonary fibrosis: collagen-induced migration inhibition factor production and cytotoxicity mediated by lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1223–1232. doi: 10.1172/JCI108576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert I. A. Expression of HLA-DR (Ia like) antigen on epidermal keratinocytes in human dermatoses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):93–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence E. C., Martin R. R., Blaese R. M., Teague R. B., Awe R. J., Wilson R. K., Deaton W. J., Bloom K., Greenberg S. D., Stevens P. M. Increased bronchoalveolar IgG-secreting cells in interstitial lung diseases. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 22;302(21):1186–1188. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005223022106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishra B. B., Poulter L. W., Janossy G., James D. G. The distribution of lymphoid and macrophage like cell subsets of sarcoid and Kveim granulomata: possible mechanism of negative PPD reaction in sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Dec;54(3):705–715. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Hofman F. M., Meyer P. R., Sharma O. P., Taylor C. R., Rea T. H. In situ demonstration of T lymphocyte subsets in granulomatous inflammation: leprosy, rhinoscleroma and sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Mar;51(3):430–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W. Antigen presenting cells in situ: their identification and involvement in immunopathology. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Sep;53(3):513–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W., Collings L. A., Tung K. S., Waters M. F. Parasitism of antigen presenting cells in hyperbacillary leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Mar;55(3):611–617. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W., Duke O., Hobbs S., Janossy G., Panayi G., Seymour G. The involvement of interdigitating (antigen-presenting) cells in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Feb;51(2):247–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W., Seymour G. J., Duke O., Janossy G., Panayi G. Immunohistological analysis of delayed-type hypersensitivity in man. Cell Immunol. 1982 Dec;74(2):358–369. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razma A. G., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Wilson B. S., Ward P. A., Kunkel S. L. Expression of Ia-like (DR) antigen on human alveolar macrophages isolated by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Mar;129(3):419–424. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.3.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y. Immunologic lung disease (part 2). Chest. 1982 Jun;81(6):745–751. doi: 10.1016/s0012-3692(16)57764-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd R. M., Haslam P. L., Turner-Warwick M. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Relationships of pulmonary physiology and bronchoalveolar lavage to response to treatment and prognosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jul;124(1):1–8. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier D. J., Phan S. H., Ward P. A. Cellular sensitivity to collagen in bleomycin-treated rats. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2156–2159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider G. L. Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis--which cell is the culprit? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5):535–539. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Gerdes J., Mason D. Y. The normal and malignant germinal centre. Clin Haematol. 1982 Oct;11(3):531–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrall R. S., Barton R. W. A comparison of lymphocyte populations in lung tissue and in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of rats at various times during the development of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Feb;129(2):279–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Warwick M., Burrows B., Johnson A. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis: clinical features and their influence on survival. Thorax. 1980 Mar;35(3):171–180. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.3.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Beller D. I., Lu C. Y., Allen P. M. Antigen presentation: comments on its regulation and mechanism. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- du Bois R. M., Townsend P. J., Cole P. J. Alveolar macrophage lysosomal enzyme and C3b receptors in cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Apr;40(1):60–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]