Abstract
Human leukotriene C4 (LTC4) synthase was purified > 25,000-fold to homogeneity from the monocytic leukemia cell line THP-1. Beginning with taurocholate-solubilized microsomal membranes, LTC4 synthase was chromatographically resolved by (i) anion exchange, (ii) affinity chromatography (through a resin of biotinylated LTC2 immobilized on streptavidin-agarose), and then (iii) gel filtration. The final preparation contained only an 18-kDa polypeptide. The molecular mass of the pure polypeptide was consistent with an 18-kDa polypeptide from THP-1 cell membranes that was specifically photolabeled by an LTC4 photoaffinity probe, 125I-labeled azido-LTC4. On calibrated gel-filtration columns, purified LTC4 synthase activity eluted at a volume corresponding to 39.2 +/- 3.3 kDa (n = 12). The sequence of the N-terminal 35 amino acids was determined and found to be a unique sequence composed predominantly of hydrophobic amino acids and containing a consensus sequence for protein kinase C phosphorylation. We therefore conclude that human LTC4 synthase is a glutathione S-transferase composed of an 18-kDa polypeptide that is enzymatically active as a homodimer and may be phosphoregulated in vivo.
Full text
PDF

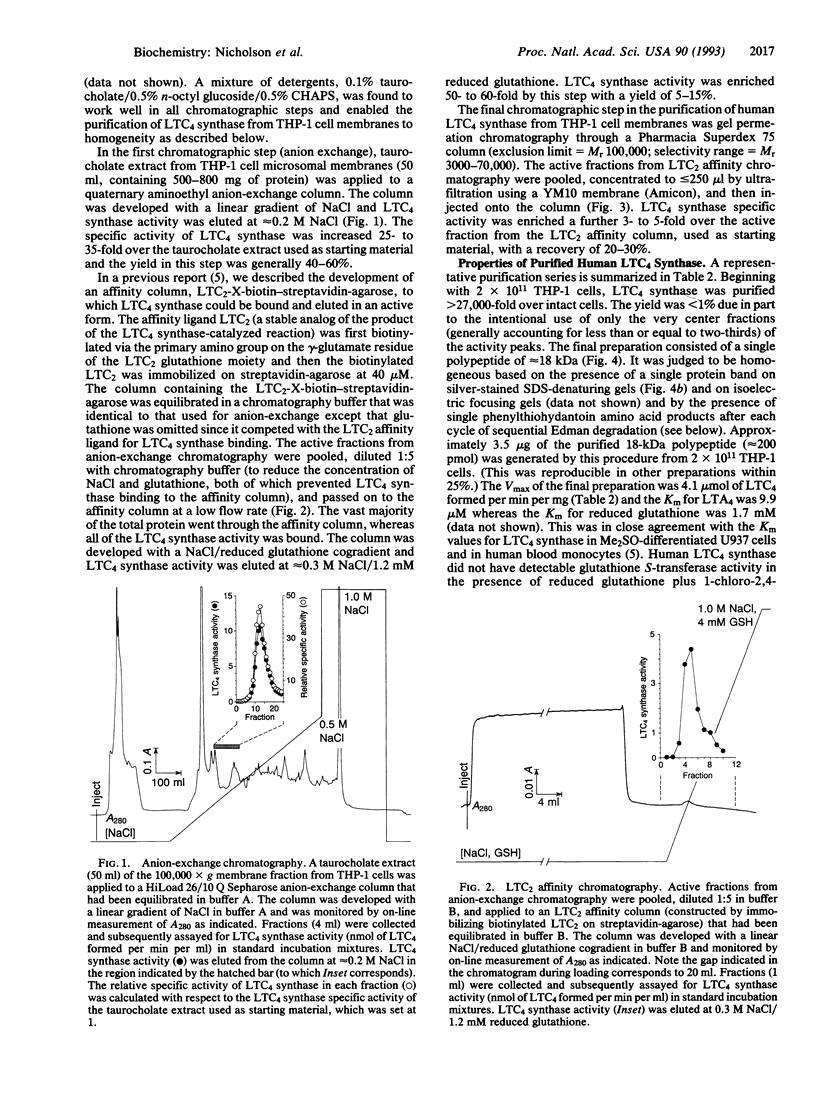
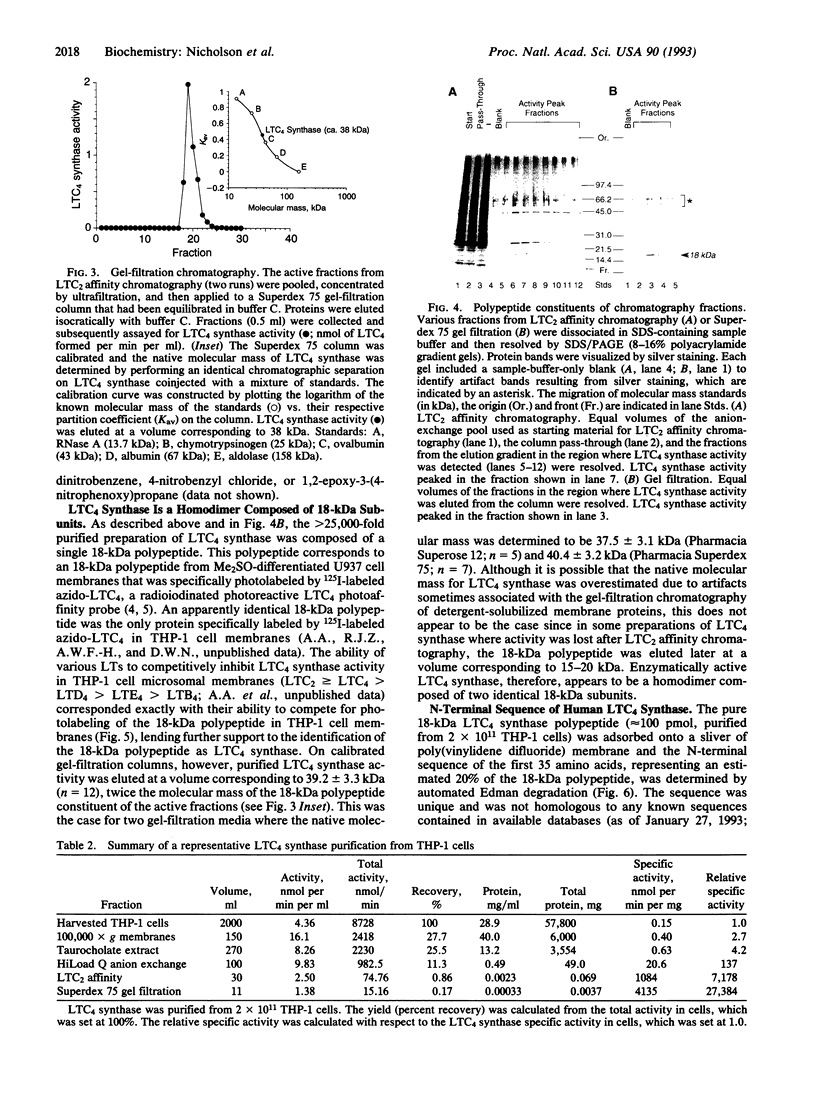

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford-Hutchinson A. W. Leukotriene B4 in inflammation. Crit Rev Immunol. 1990;10(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habig W. H., Pabst M. J., Jakoby W. B. Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7130–7139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolskee D. J. Clinical experience with MK-571. A potent and specific LTD4 receptor antagonist. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;629:148–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb37972.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLellan L. I., Wolf C. R., Hayes J. D. Human microsomal glutathione S-transferase. Its involvement in the conjugation of hexachlorobuta-1,3-diene with glutathione. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 15;258(1):87–93. doi: 10.1042/bj2580087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosialou E., Morgenstern R. Inhibition studies on rat liver microsomal glutathione transferase. Chem Biol Interact. 1990;74(3):275–280. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(90)90044-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson D. W., Ali A., Klemba M. W., Munday N. A., Zamboni R. J., Ford-Hutchinson A. W. Human leukotriene C4 synthase expression in dimethyl sulfoxide-differentiated U937 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17849–17857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson D. W., Klemba M. W., Rasper D. M., Metters K. M., Zamboni R. J., Ford-Hutchinson A. W. Purification of human leukotriene C4 synthase from dimethylsulfoxide-differentiated U937 cells. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Oct 15;209(2):725–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs D. Protein contaminants of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Dec;135(2):470–474. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90714-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett C. B., Lu A. Y. Glutathione S-transferases: gene structure, regulation, and biological function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:743–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B. Leukotrienes: mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions and inflammation. Science. 1983 May 6;220(4597):568–575. doi: 10.1126/science.6301011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. E., Miller P., Ronk M. Microsequence analysis of peptides and proteins. VI. A continuous flow reactor for sample concentration and sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jun;163(2):517–529. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90257-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida S., Sato K. Glutathione transferases and cancer. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;27(4-5):337–384. doi: 10.3109/10409239209082566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya S., Yamabe M., Yamaguchi Y., Kobayashi Y., Konno T., Tada K. Establishment and characterization of a human acute monocytic leukemia cell line (THP-1). Int J Cancer. 1980 Aug;26(2):171–176. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910260208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R., Gould K. L., Hunter T. Substrate specificity of protein kinase C. Use of synthetic peptides corresponding to physiological sites as probes for substrate recognition requirements. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]