Abstract
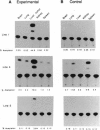
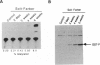
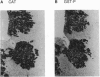
Glutathione transferase P (GST-P; glutathione transferase, EC 2.5.1.18) is known to be specifically expressed at high levels in precancerous lesions and in hepatocellular carcinomas from a very early phase of chemically induced hepatocarcinogenesis in the rat. The almost invariable occurrence of this phenotype in these lesions strongly suggests a mechanism by which GST-P gene is activated together with a crucial transforming gene of liver cells. To distinguish the two alternative possibilities--either the GST-P gene is coactivated with a closely located transforming gene by a cis mechanism or it is activated in trans by a common trans-acting factor--we carried out carcinogenesis experiments using transgenic rats harboring the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter gene ligated to the upstream regulatory sequence of the GST-P gene. In each of three independent lines tested, liver foci and nodules produced by chemical carcinogens (Solt-Farber procedure) were found to express high levels of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activity, indicating clearly that the GST-P gene is activated by a trans mechanism during hepatocarcinogenesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blom van Assendelft G., Hanscombe O., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. The beta-globin dominant control region activates homologous and heterologous promoters in a tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):969–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90630-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis P., Antoniou M., Grosveld F. Definition of the minimal requirements within the human beta-globin gene and the dominant control region for high level expression. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):233–240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews S., Barth R., Hood L., Prehn J., Calame K. Mouse c-myc oncogene is located on chromosome 15 and translocated to chromosome 12 in plasmacytomas. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1319–1321. doi: 10.1126/science.7146913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Takegawa S., Papayannopoulou T., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Groudine M. Evidence for a locus activation region: the formation of developmentally stable hypersensitive sites in globin-expressing hybrids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10159–10177. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatayama I., Satoh K., Sato K. Developmental and hormonal regulation of the major form of hepatic glutathione S-transferase in male mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 30;140(2):581–588. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90771-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisterkamp N., Stam K., Groffen J., de Klein A., Grosveld G. Structural organization of the bcr gene and its role in the Ph' translocation. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):758–761. doi: 10.1038/315758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Osada S., Koyama Y., Suzuki T., Hirom P. C., Diccianni M. B., Morimura S., Muramatsu M. SF-B that binds to a negative element in glutathione transferase P gene is similar or identical to trans-activator LAP/IL6-DBP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91368-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Osada S., Okuda A., Muramatsu M. Silencer binding proteins function on multiple cis-elements in the glutathione transferase P gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):5–10. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda A., Imagawa M., Maeda Y., Sakai M., Muramatsu M. Structural and functional analysis of an enhancer GPEI having a phorbol 12-O-tetradecanoate 13-acetate responsive element-like sequence found in the rat glutathione transferase P gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16919–16926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda A., Imagawa M., Sakai M., Muramatsu M. Functional cooperativity between two TPA responsive elements in undifferentiated F9 embryonic stem cells. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1131–1135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08219.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda A., Sakai M., Muramatsu M. The structure of the rat glutathione S-transferase P gene and related pseudogenes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3858–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. M., Behringer R. R., Martin N. C., Townes T. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. A single erythroid-specific DNase I super-hypersensitive site activates high levels of human beta-globin gene expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):314–323. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai M., Okuda A., Muramatsu M. Multiple regulatory elements and phorbol 12-O-tetradecanoate 13-acetate responsiveness of the rat placental glutathione transferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9456–9460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K. Glutathione S-transferases and hepatocarcinogenesis. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1988 May;79(5):556–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1988.tb00022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh K., Kitahara A., Soma Y., Inaba Y., Hatayama I., Sato K. Purification, induction, and distribution of placental glutathione transferase: a new marker enzyme for preneoplastic cells in the rat chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3964–3968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Keath E. J., Piccoli S. P., Cole M. D. Novel myc oncogene RNA from abortive immunoglobulin-gene recombination in mouse plasmacytomas. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugioka Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Kitagawa T., Muramatsu M. Changes in polypeptide pattern of rat liver cells during chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1985 Jan;45(1):365–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suguoka Y., Kano T., Okuda A., Sakai M., Kitagawa T., Muramatsu M. Cloning and the nucleotide sequence of rat glutathione S-transferase P cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6049–6057. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Collis P., Antoniou M., Vidal M., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. A dominant control region from the human beta-globin locus conferring integration site-independent gene expression. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):352–355. doi: 10.1038/338352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall L., deBoer E., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin gene 3' enhancer contains multiple binding sites for an erythroid-specific protein. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1089–1100. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]