Abstract
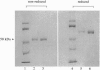
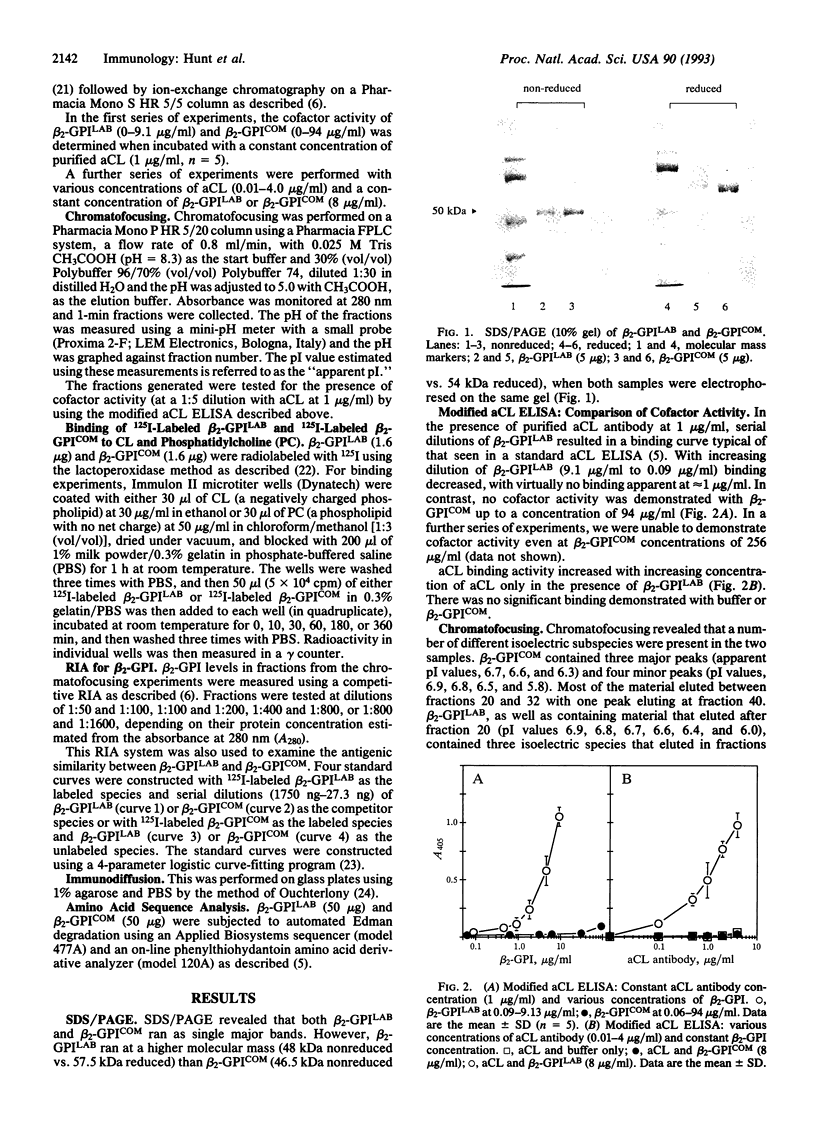
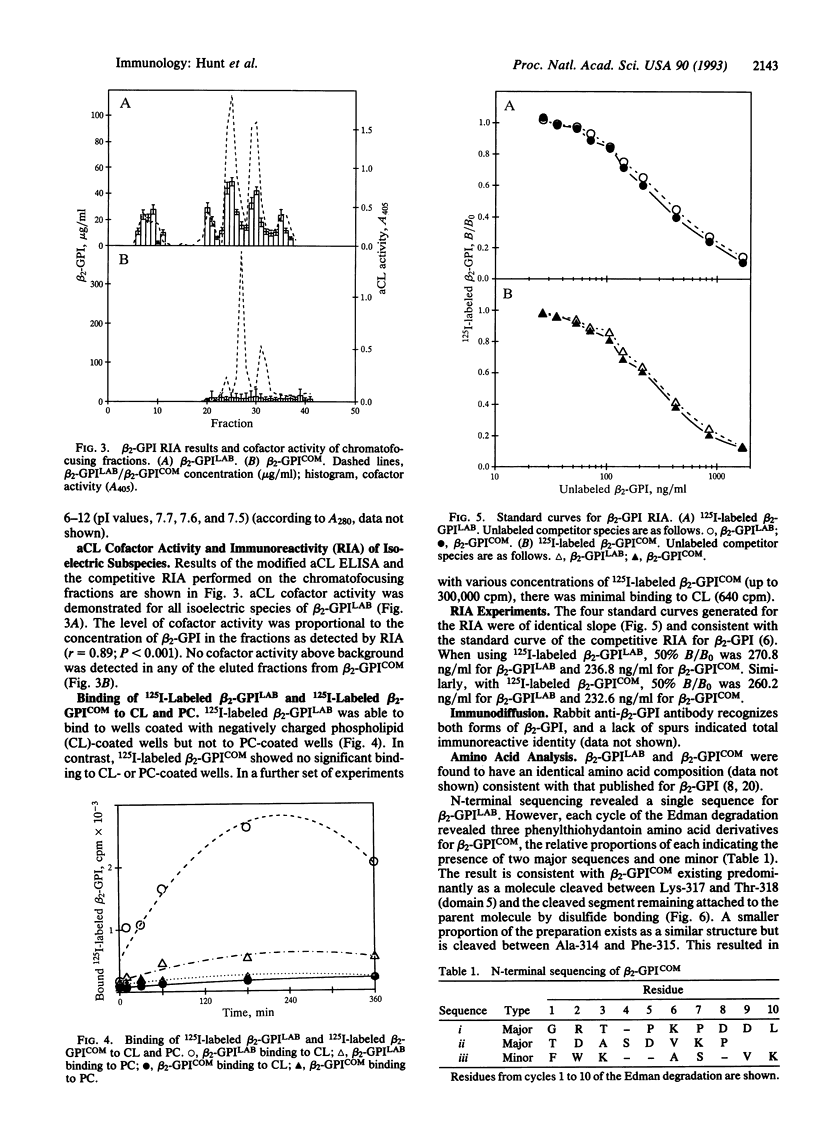
beta 2-Glycoprotein I (beta 2-GPI), a phospholipid-binding plasma protein, is an absolute requirement (cofactor) for the binding of autoimmune-type anti-cardiolipin (aCL) antibodies to cardiolipin (CL). The nature of this cofactor activity and the specific regions of the molecule involved have not yet been determined. We have identified a preparation of beta 2-GPI that lacks aCL antibody cofactor activity. Analysis of the structural differences between the active and inactive forms enabled identification of the region of beta 2-GPI critically important for aCL cofactor activity. The active form of beta 2-GPI bound CL and displayed cofactor activity down to 1 microgram/ml. The inactive form failed to bind CL and possessed no cofactor activity even at concentrations up to 94 micrograms/ml, indicating that the ability of beta 2-GPI to bind lipids is an absolute requirement for aCL cofactor activity. Both forms possessed identical N-terminal sequences and were recognized as essentially immunoreactively identical by polyclonal antisera to beta 2-GPI. However, the inactive form has undergone proteolytic cleavage and exists primarily as a "clipped" molecule, the polypeptide chain being cleaved between Lys-317 and Thr-318 (a potential thrombin cleavage site), with the two cleaved segments linked as a disulfide-bonded complex. This indicates that the C-terminal region is critically important for beta 2-GPI to bind lipid and for aCL cofactor activity. The clipped form of beta 2-GPI would not be suitable for use as aCL cofactor and its use may have led some investigators to conclude incorrectly that beta 2-GPI does not interact with aCL antibodies.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blewett E. L., Misra V. Cleavage of the bovine herpesvirus glycoprotein B is not essential for its function. J Gen Virol. 1991 Sep;72(Pt 9):2083–2090. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-9-2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. Y. Thrombin specificity. Requirement for apolar amino acids adjacent to the thrombin cleavage site of polypeptide substrate. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):217–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gries A., Nimpf J., Wurm H., Kostner G. M., Kenner T. Characterization of isoelectric subspecies of asialo-beta 2-glycoprotein I. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 1;260(2):531–534. doi: 10.1042/bj2600531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Boey M. L., Patel B. M., Mackworth-Young C. G., Loizou S., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: detection by radioimmunoassay and association with thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1983 Nov 26;2(8361):1211–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Pierangeli S., Barquinero J., Ordi-Ros J. Anticardiolipin antibodies and binding of anionic phospholipids and serum protein. Lancet. 1990 Aug 25;336(8713):505–506. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92053-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. E., McNeil H. P., Morgan G. J., Crameri R. M., Krilis S. A. A phospholipid-beta 2-glycoprotein I complex is an antigen for anticardiolipin antibodies occurring in autoimmune disease but not with infection. Lupus. 1992 Feb;1(2):75–81. doi: 10.1177/096120339200100204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Enjyoji K. Amino acid sequence and location of the disulfide bonds in bovine beta 2 glycoprotein I: the presence of five Sushi domains. Biochemistry. 1991 Dec 17;30(50):11687–11694. doi: 10.1021/bi00114a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshin M. D., Druzin M. L., Goei S., Qamar T., Magid M. S., Jovanovic L., Ferenc M. Antibody to cardiolipin as a predictor of fetal distress or death in pregnant patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 18;313(3):152–156. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198507183130304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love P. E., Santoro S. A. Antiphospholipid antibodies: anticardiolipin and the lupus anticoagulant in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and in non-SLE disorders. Prevalence and clinical significance. Ann Intern Med. 1990 May 1;112(9):682–698. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-9-682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier J., Takahashi N., Putnam F. W. Complete amino acid sequence of human plasma beta 2-glycoprotein I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3640–3644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Krilis S. A., Chesterman C. N. Purification of antiphospholipid antibodies using a new affinity method. Thromb Res. 1988 Dec 15;52(6):641–648. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Simpson R. J., Chesterman C. N., Krilis S. A. Anti-phospholipid antibodies are directed against a complex antigen that includes a lipid-binding inhibitor of coagulation: beta 2-glycoprotein I (apolipoprotein H). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimpf J., Bevers E. M., Bomans P. H., Till U., Wurm H., Kostner G. M., Zwaal R. F. Prothrombinase activity of human platelets is inhibited by beta 2-glycoprotein-I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 29;884(1):142–149. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polz E., Kostner G. M. The binding of beta 2-glycoprotein-I to human serum lipoproteins: distribution among density fractions. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80955-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polz E., Wurm H., Kostner G. M. Investigations on beta 2-glycoprotein-I in the rat: isolation from serum and demonstration in lipoprotein density fractions. Int J Biochem. 1980;11(3-4):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90229-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Day A. J. Structure-function relationships of the complement components. Immunol Today. 1989 Jun;10(6):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90317-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schousboe I. Binding of beta 2-glycoprotein I to platelets: effect of adenylate cyclase activity. Thromb Res. 1980 Jul 1;19(1-2):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90421-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schousboe I. Characterization of the interaction between beta 2-glycoprotein I and mitochondria, platelets, liposomes and bile acids. Int J Biochem. 1983;15(12):1393–1401. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(83)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schousboe I. In vitro activation of the contact activation system (Hageman factor system) in plasma by acidic phospholipids and the inhibitory effect of beta 2-glycoprotein I on this activation. Int J Biochem. 1988;20(3):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(88)90356-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schousboe I. Inositolphospholipid-accelerated activation of prekallikrein by activated factor XII and its inhibition by beta 2-glycoprotein I. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 1;176(3):629–636. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schousboe I. Purification, characterization and identification of an agglutinin in human serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 28;579(2):396–408. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinkasserer A., Estaller C., Weiss E. H., Sim R. B., Day A. J. Complete nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of human beta 2-glycoprotein I. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 15;277(Pt 2):387–391. doi: 10.1042/bj2770387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorell J. I., Johansson B. G. Enzymatic iodination of polypeptides with 125I to high specific activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):363–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaarala O., Palosuo T., Kleemola M., Aho K. Anticardiolipin response in acute infections. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Oct;41(1):8–15. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurm H., Beubler E., Polz E., Holasek A., Kostner G. Studies on the possible function of beta 2-glycoprotein-I: influence in the triglyceride metabolism in the rat. Metabolism. 1982 May;31(5):484–486. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90238-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurm H. beta 2-Glycoprotein-I (apolipoprotein H) interactions with phospholipid vesicles. Int J Biochem. 1984;16(5):511–515. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(84)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]