Abstract
B lymphocytes from patients with X chromosome-linked immunoglobulin deficiency with normal or elevated serum IgM are unable to switch from the synthesis of IgM/IgD to that of other immunoglobulin isotypes. Isotype switch recombination was evaluated in three affected males by examining interleukin 4-driven IgE synthesis. T-cell-dependent IgE synthesis was completely absent in the B lymphocytes of the patients. In contrast, CD40 mAb plus interleukin 4 induced the patients' B cells to synthesize IgE and to undergo deletional switch recombination. Because interaction between CD40 and its ligand on activated T cells is critical for T-cell-driven isotype switching, we examined CD40 ligand expression. In contrast to normal T cells, lymphocytes from the patients expressed no detectable CD40 ligand on their surface after stimulation with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and ionomycin, although the mRNA of the ligand was expressed normally. These results suggest that defective expression of the CD40 ligand underlies the failure of isotype switching in this disease.
Full text
PDF
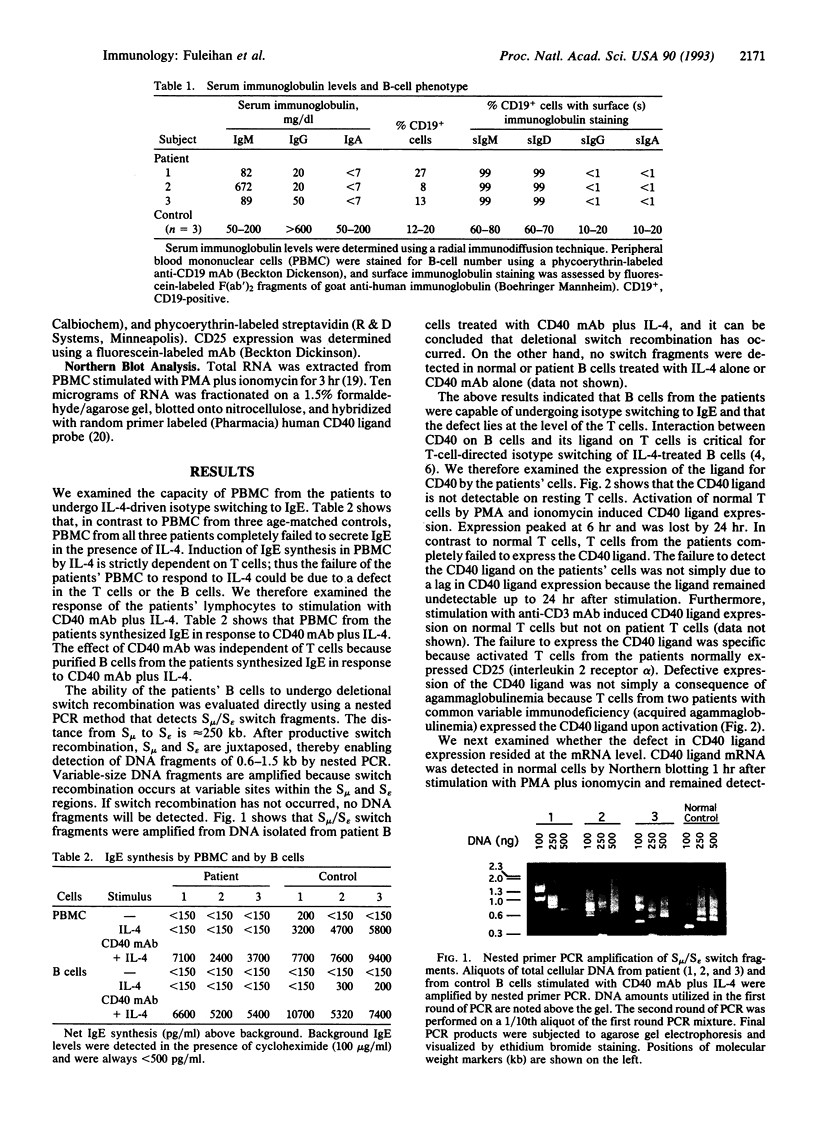
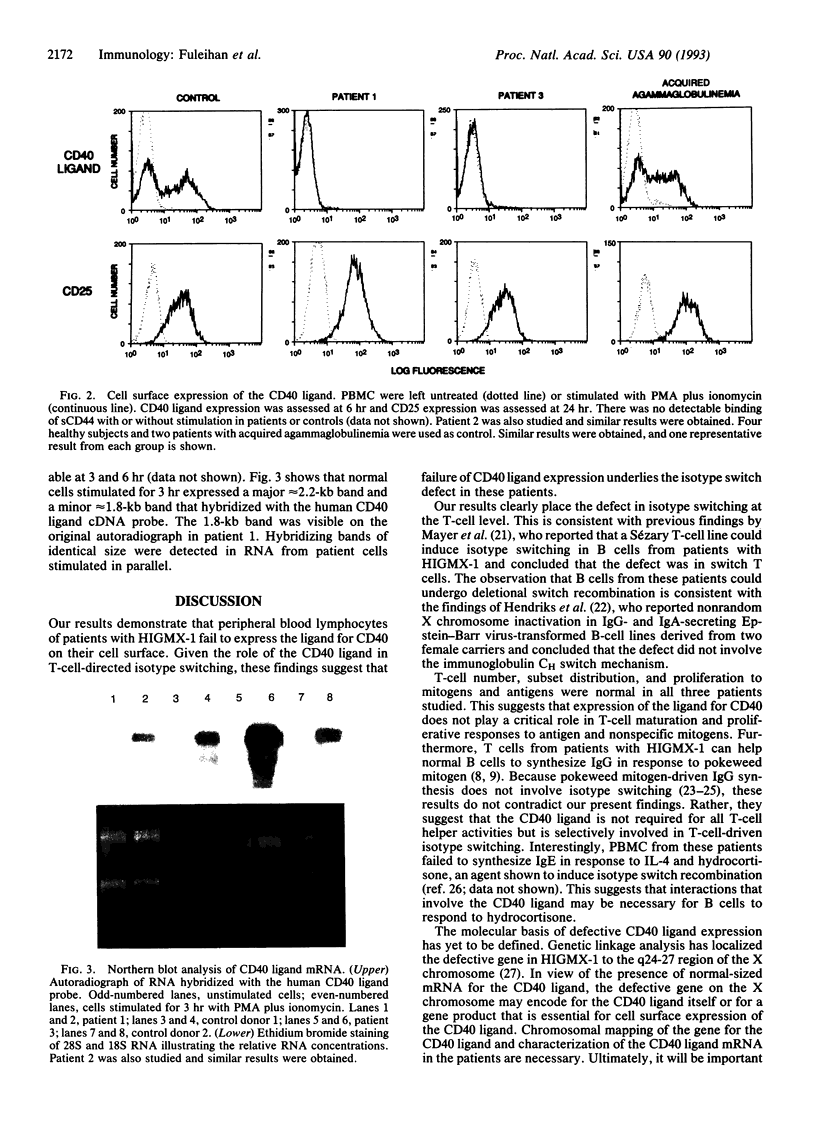

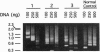
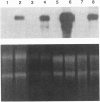
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage R. J., Fanslow W. C., Strockbine L., Sato T. A., Clifford K. N., Macduff B. M., Anderson D. M., Gimpel S. D., Davis-Smith T., Maliszewski C. R. Molecular and biological characterization of a murine ligand for CD40. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):80–82. doi: 10.1038/357080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aruffo A., Stamenkovic I., Melnick M., Underhill C. B., Seed B. CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1303–1313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90694-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser C., Radbruch A. Immunoglobulin class switching: molecular and cellular analysis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:717–735. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanslow W. C., Anderson D. M., Grabstein K. H., Clark E. A., Cosman D., Armitage R. J. Soluble forms of CD40 inhibit biologic responses of human B cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 15;149(2):655–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Hyslop N., Alami S., Farah F., Schneeberger E. E., Rosen F. S. Hyper immunoglobulin M immunodeficiency. (Dysgammaglobulinemia). Presence of immunoglobulin M-secreting plasmacytoid cells in peripheral blood and failure of immunoglobulin M-immunoglobulin G switch in B-cell differentiation. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):385–391. doi: 10.1172/JCI109473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber M. F., Bjorndahl J. M., Nakamura S., Fu S. M. Anti-CD45 inhibition of human B cell proliferation depends on the nature of activation signals and the state of B cell activation. A study with anti-IgM and anti-CDw40 antibodies. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4144–4152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks R. W., Kraakman M. E., Craig I. W., Espanol T., Schuurman R. K. Evidence that in X-linked immunodeficiency with hyperimmunoglobulinemia M the intrinsic immunoglobulin heavy chain class switch mechanism is intact. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Dec;20(12):2603–2608. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenbaugh D., Grosmaire L. S., Kullas C. D., Chalupny N. J., Braesch-Andersen S., Noelle R. J., Stamenkovic I., Ledbetter J. A., Aruffo A. The human T cell antigen gp39, a member of the TNF gene family, is a ligand for the CD40 receptor: expression of a soluble form of gp39 with B cell co-stimulatory activity. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4313–4321. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05530.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabara H. H., Ahern D. J., Vercelli D., Geha R. S. Hydrocortisone and IL-4 induce IgE isotype switching in human B cells. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1557–1560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabara H. H., Schneider L. C., Shapira S. K., Alfieri C., Moody C. T., Kieff E., Geha R. S., Vercelli D. Induction of germ-line and mature C epsilon transcripts in human B cells stimulated with rIL-4 and EBV. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3468–3473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuritani T., Cooper M. D. Human b-cell differentiation. I. Analysis of immunoglobulin heavy chain switching using monoclonal anti-immunoglobulin M, G, and A antibodies and pokeweed mitogen-induced plasma cell differentiation. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):839–851. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D., Dagg M. K. Human B-lymphocyte subpopulations. II. Plasma cell differentiation of isotype-specific B lymphocytes from peripheral blood. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Oct;21(1):50–61. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90194-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D., Haber P., Rich K., Cooper M. D. Hyper IgM immunodeficiency. A primary dysfunction of B lymphocyte isotype switching. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1650–1657. doi: 10.1172/JCI111124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L., Kwan S. P., Thompson C., Ko H. S., Chiorazzi N., Waldmann T., Rosen F. Evidence for a defect in "switch" T cells in patients with immunodeficiency and hyperimmunoglobulinemia M. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 13;314(7):409–413. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602133140703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noelle R. J., Roy M., Shepherd D. M., Stamenkovic I., Ledbetter J. A., Aruffo A. A 39-kDa protein on activated helper T cells binds CD40 and transduces the signal for cognate activation of B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6550–6554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancho J., Silverman L. B., Castigli E., Ahern D., Laudano A. P., Terhorst C., Geha R. S., Chatila T. A. Developmental regulation of transmembrane signaling via the T cell antigen receptor/CD3 complex in human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 1;148(5):1315–1321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Vercelli D., Jabara H. H., Fu S. M., Geha R. S. Molecular analysis of the induction of immunoglobulin E synthesis in human B cells by interleukin 4 and engagement of CD40 antigen. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):289–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamenkovic I., Amiot M., Pesando J. M., Seed B. A lymphocyte molecule implicated in lymph node homing is a member of the cartilage link protein family. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1057–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90638-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamenkovic I., Clark E. A., Seed B. A B-lymphocyte activation molecule related to the nerve growth factor receptor and induced by cytokines in carcinomas. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1403–1410. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03521.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. H., Macy E., Thiele C. J. Evidence that pokeweed-mitogen-reactive B cells are pre-committed in vivo to the high-rate secretion of a single immunoglobulin isotype in vitro. Scand J Immunol. 1981 Nov;14(5):449–457. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Geha R. S. Regulation of IgE synthesis in humans: a tale of two signals. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Sep;88(3 Pt 1):285–295. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Jabara H. H., Arai K., Geha R. S. Induction of human IgE synthesis requires interleukin 4 and T/B cell interactions involving the T cell receptor/CD3 complex and MHC class II antigens. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1295–1307. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Jabara H. H., Lauener R. P., Geha R. S. IL-4 inhibits the synthesis of IFN-gamma and induces the synthesis of IgE in human mixed lymphocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):570–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]