Abstract
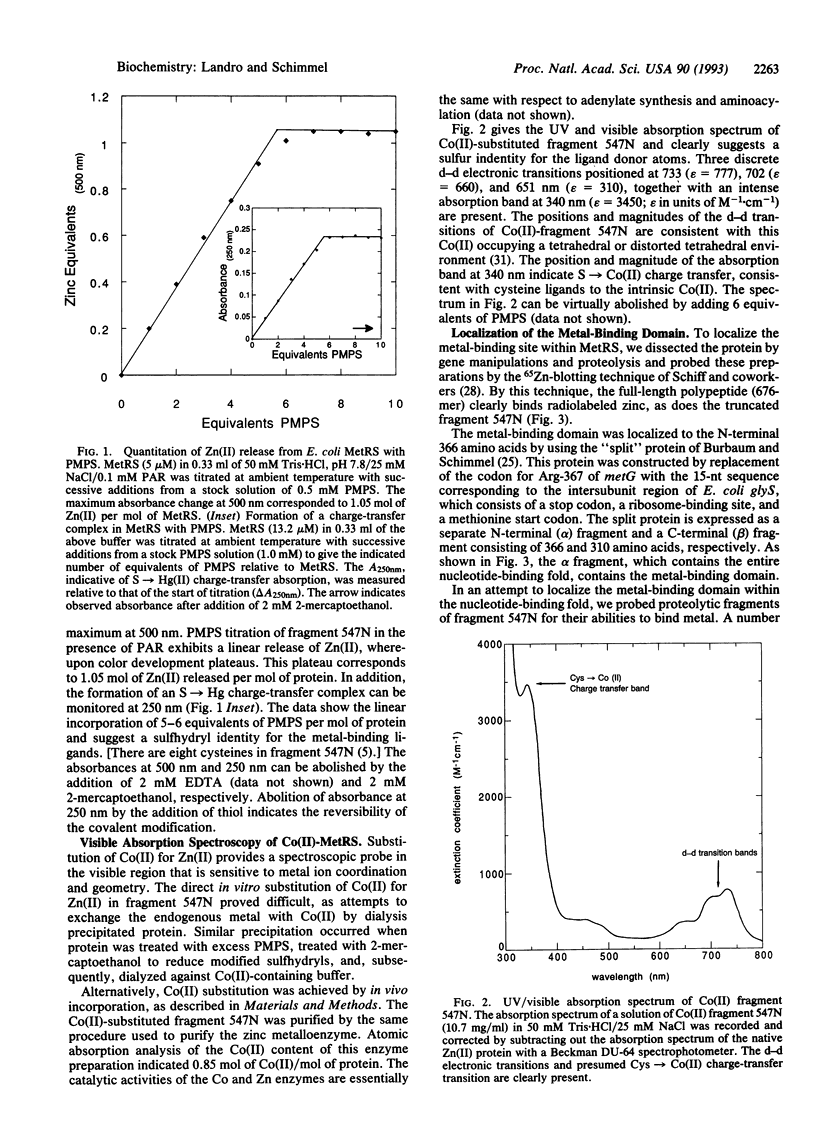
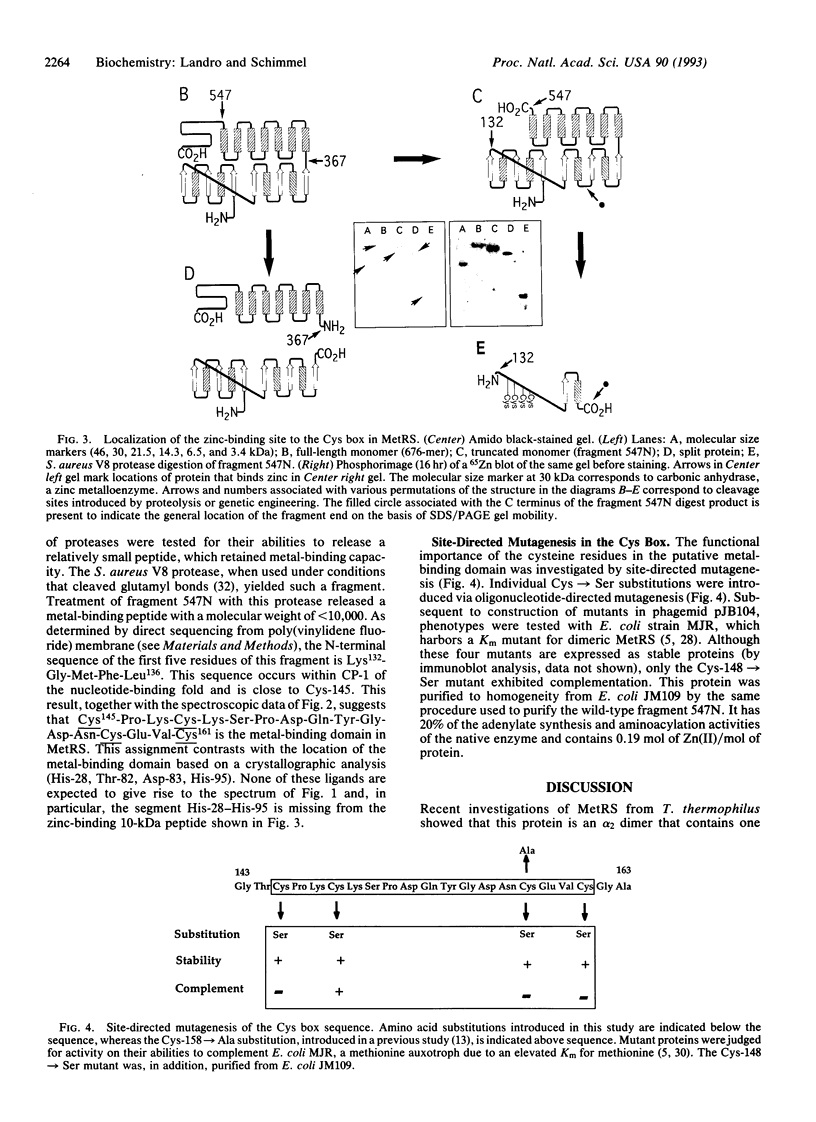
The 10 class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases share a common N-terminal nucleotide-binding fold. Idiosyncratic polypeptide insertions into this fold introduce residues important for activity, including those that interact with the tRNA acceptor helix. The class I Escherichia coli methionyl-tRNA synthetase (L-methionine:tRNA(Met) ligase, EC 6.1.1.10), a 676-amino acid homodimer, was shown previously by others to contain zinc and to have an activity dependent on its presence. We show here by atomic absorption spectroscopy and zinc titrations the presence of 1 mol of zinc per polypeptide. Replacement of zinc with cobalt yields an active enzyme with a visible absorption spectrum characteristic of tetrahedral coordination to sulfur ligands and an intense metal-to-sulfur charge-transfer band at 340 nm. Mapping of the metal-binding site by zinc blotting of recombinant and proteolytic fragments localized the site to a polypeptide insertion between two strands and a beta-sheet in the N-terminal nucleotide-binding fold that contains the catalytic site. Beginning at Cys-145, this insertion contains a Cys-Xaa2-Cys-Xaa9-Cys-Xaa2-Cys motif. Site-directed substitution of these cysteines with serines yielded proteins that were stable but generally devoid of activity. With this result there is now at least one example of a class I and of a class II E. coli tRNA synthetase with a metal-binding domain important for activity inserted into the catalytic domain.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auld D. S. Metal-free dialysis tubing. Methods Enzymol. 1988;158:13–14. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)58043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. G., Ebel J. P., Jakes R., Bruton C. J. Methionyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli. Primary structure of the active crystallised tryptic fragment. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(3):449–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. R., Park J. B., Bryant F. O., Aono S., Magnuson J. K., Eccleston E., Howard J. B., Summers M. F., Adams M. W. Determinants of protein hyperthermostability: purification and amino acid sequence of rubredoxin from the hyperthermophilic archaebacterium Pyrococcus furiosus and secondary structure of the zinc adduct by NMR. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 12;30(45):10885–10895. doi: 10.1021/bi00109a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunie S., Zelwer C., Risler J. L. Crystallographic study at 2.5 A resolution of the interaction of methionyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli with ATP. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 20;216(2):411–424. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80331-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbaum J. J., Schimmel P. Amino acid binding by the class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases: role for a conserved proline in the signature sequence. Protein Sci. 1992 May;1(5):575–581. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbaum J. J., Schimmel P. Assembly of a class I tRNA synthetase from products of an artificially split gene. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 15;30(2):319–324. doi: 10.1021/bi00216a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassio D., Waller J. P. Modification of methionyl-tRNA synthetase by proteolytic cleavage and properties of the trypsin-modified enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1971 May 28;20(2):283–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusack S., Berthet-Colominas C., Härtlein M., Nassar N., Leberman R. A second class of synthetase structure revealed by X-ray analysis of Escherichia coli seryl-tRNA synthetase at 2.5 A. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):249–255. doi: 10.1038/347249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G. R. Cleavage at glutamic acid with staphylococcal protease. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:189–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriani G., Delarue M., Poch O., Gangloff J., Moras D. Partition of tRNA synthetases into two classes based on mutually exclusive sets of sequence motifs. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):203–206. doi: 10.1038/347203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayat G., Waller J. P. The mechanism of action of methionyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli. Equilibrium-dialysis studies on the binding of methionine, ATP and ATP-Mg2+ by the native and trypsin-modified enzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 15;44(2):335–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. B., Neece S. H., Schachman H. K., Ginsburg A. Mercurial-promoted Zn2+ release from Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14793–14803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Schimmel P. Function independence of microhelix aminoacylation from anticodon binding in a class I tRNA synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15563–15567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohda D., Yokoyama S., Miyazawa T. Functions of isolated domains of methionyl-tRNA synthetase from an extreme thermophile, Thermus thermophilus HB8. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):558–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohda D., Yokoyama S., Miyazawa T. Thermostable valyl-tRNA, isoleucyl-tRNA and methionyl-tRNA synthetases from an extreme thermophile Thermus thermophilus HB8: protein structure and Zn2+ binding. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 20;174(1):20–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludmerer S. W., Schimmel P. Gene for yeast glutamine tRNA synthetase encodes a large amino-terminal extension and provides a strong confirmation of the signature sequence for a group of the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10801–10806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayaux J. F., Kalogerakos T., Brito K. K., Blanquet S. Removal of the tightly bound zinc from Escherichia coli trypsin-modified methionyl-tRNA synthetase. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov;128(1):41–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. T., Hill K. A., Schimmel P. Evidence for a "cysteine-histidine box" metal-binding site in an Escherichia coli aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 16;30(28):6970–6976. doi: 10.1021/bi00242a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. T., Schimmel P. A retroviral-like metal binding motif in an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase is important for tRNA recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2032–2035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nureki O., Muramatsu T., Suzuki K., Kohda D., Matsuzawa H., Ohta T., Miyazawa T., Yokoyama S. Methionyl-tRNA synthetase gene from an extreme thermophile, Thermus thermophilus HB8. Molecular cloning, primary-structure analysis, expression in Escherichia coli, and site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3268–3277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perona J. J., Rould M. A., Steitz T. A., Risler J. L., Zelwer C., Brunie S. Structural similarities in glutaminyl- and methionyl-tRNA synthetases suggest a common overall orientation of tRNA binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2903–2907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posorske L. H., Cohn M., Yanagisawa N., Auld D. S. Methionyl-tRNA synthetase of Escherichia coli. A zinc metalloprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 25;576(1):128–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90491-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff M., Krishnaswamy S., Boeglin M., Poterszman A., Mitschler A., Podjarny A., Rees B., Thierry J. C., Moras D. Class II aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetases: crystal structure of yeast aspartyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Asp). Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1682–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.2047877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff L. A., Nibert M. L., Fields B. N. Characterization of a zinc blotting technique: evidence that a retroviral gag protein binds zinc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4195–4199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel P. R., Söll D. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases: general features and recognition of transfer RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:601–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel P. Alanine transfer RNA synthetase: structure-function relationships and molecular recognition of transfer RNA. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1990;63:233–270. doi: 10.1002/9780470123096.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzyk R. M., Burbaum J. J., Schimmel P. Insertion of new sequences into the catalytic domain of an enzyme. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8479–8484. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzyk R. M., Webster T. A., Schimmel P. Evidence for dispensable sequences inserted into a nucleotide fold. Science. 1987 Sep 25;237(4822):1614–1618. doi: 10.1126/science.3306924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers M. F., South T. L., Kim B., Hare D. R. High-resolution structure of an HIV zinc fingerlike domain via a new NMR-based distance geometry approach. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):329–340. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L., Galdes A. The metallobiochemistry of zinc enzymes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1984;56:283–430. doi: 10.1002/9780470123027.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster T., Tsai H., Kula M., Mackie G. A., Schimmel P. Specific sequence homology and three-dimensional structure of an aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetase. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1315–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.6390679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




