Abstract
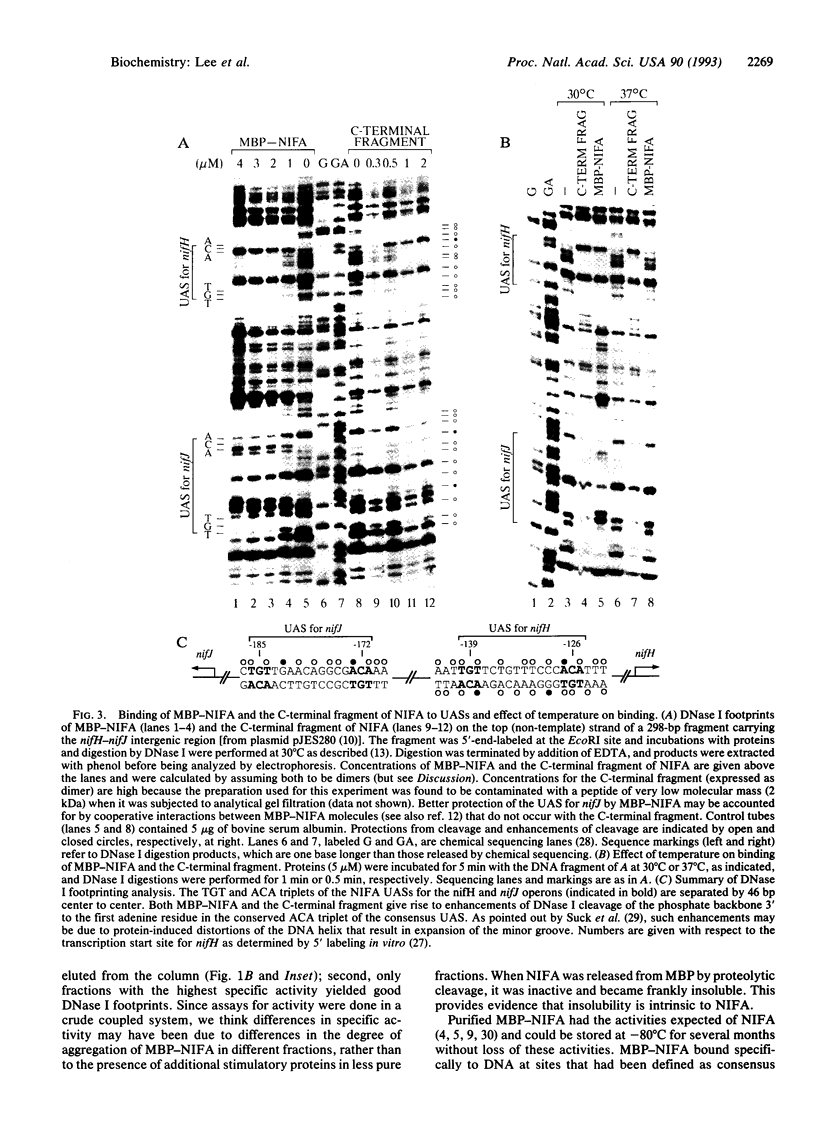
The NIFA protein activates transcription of nitrogen fixation (nif) operons by the sigma 54-holoenzyme form of RNA polymerase. We purified active NIFA from Klebsiella pneumoniae in the form of a maltose-binding protein (MBP)-NIFA fusion; proteolytic release of MBP yielded inactive and insoluble NIFA. MBP-NIFA activated transcription from the nifHDK promoter in a purified transcription system. Like the related transcriptional activator NTRC, MBP-NIFA catalyzed the ATP-dependent isomerization of closed complexes between sigma 54-holoenzyme and a promoter to open complexes. MBP-NIFA had a broader nucleotide specificity than NTRC, being able to utilize pyrimidine in addition to purine nucleoside triphosphates. Both MBP-NIFA and a purified C-terminal fragment of NIFA bound to the upstream activation sequence for the nifHDK promoter, as assessed by DNAse I footprinting. When assays were performed at 37 degrees C instead of the usual 30 degrees C, transcriptional activation, open complex formation, and DNA binding by MBP-NIFA were all abolished, consistent with the known heat lability of NIFA. However, the purified C-terminal fragment of NIFA still bound the upstream activation sequence at 37 degrees C, indicating that the function of the helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motif is not inherently heat-labile.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin S., Henderson N., Dixon R. Characterisation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogen-fixation regulatory proteins NIFA and NIFL in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 26;187(2):353–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks S. J., Collins J. J., Brill W. J. Repression of nitrogen fixation in Klebsiella pneumoniae at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):460–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.460-464.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon W. V., Kreutzer R., Kent H. M., Morett E., Buck M. Activation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifU promoter: identification of multiple and overlapping upstream NifA binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1693–1701. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon W., Charlton W., Buck M. Organization and function of binding sites for the transcriptional activator NifA in the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifE and nifU promoters. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 20;220(4):915–931. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90363-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M., Whitty P., Wootton J. Sequence and domain relationships of ntrC and nifA from Klebsiella pneumoniae: homologies to other regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):441–447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng J., Atkinson M. R., McCleary W., Stock J. B., Wanner B. L., Ninfa A. J. Role of phosphorylated metabolic intermediates in the regulation of glutamine synthetase synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(19):6061–6070. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.19.6061-6070.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin G. N., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Regulation of nitrogen fixation genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:567–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennecke H., Shanmugam K. T. Temperature control of nitrogen fixation in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Arch Microbiol. 1979;123(3):259–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00406659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover T. R., Santero E., Porter S., Kustu S. The integration host factor stimulates interaction of RNA polymerase with NIFA, the transcriptional activator for nitrogen fixation operons. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90284-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Santero E., Keener J., Popham D., Weiss D. Expression of sigma 54 (ntrA)-dependent genes is probably united by a common mechanism. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):367–376. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.367-376.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Buck M. In vivo studies on the interaction of RNA polymerase-sigma 54 with the Klebsiella pneumoniae and Rhizobium meliloti nifH promoters. The role of NifA in the formation of an open promoter complex. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 5;210(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Buck M. NifA-dependent in vivo protection demonstrates that the upstream activator sequence of nif promoters is a protein binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9401–9405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Cannon W., Buck M. The DNA-binding domain of the transcriptional activator protein NifA resides in its carboxy terminus, recognises the upstream activator sequences of nif promoters and can be separated from the positive control function of NifA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11469–11488. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D. L., Szeto D., Keener J., Kustu S. Function of a bacterial activator protein that binds to transcriptional enhancers. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):629–635. doi: 10.1126/science.2563595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D., Keener J., Kustu S. Purification of the alternative sigma factor, sigma 54, from Salmonella typhimurium and characterization of sigma 54-holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19510–19518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santero E., Hoover T. R., North A. K., Berger D. K., Porter S. C., Kustu S. Role of integration host factor in stimulating transcription from the sigma 54-dependent nifH promoter. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 5;227(3):602–620. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santero E., Hoover T., Keener J., Kustu S. In vitro activity of the nitrogen fixation regulatory protein NIFA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7346–7350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasse-Dwight S., Gralla J. D. Footprinting protein-DNA complexes in vivo. Methods Enzymol. 1991;208:146–168. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)08012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Use of bacteriophage T7 lysozyme to improve an inducible T7 expression system. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 5;219(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90855-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Lahm A., Oefner C. Structure refined to 2A of a nicked DNA octanucleotide complex with DNase I. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):464–468. doi: 10.1038/332464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny B., Hennecke H. The -24/-12 promoter comes of age. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;5(4):341–357. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuli R., Merrick M. J. Over-production and characterization of the nifA gene product of Klebsiella pneumoniae--the transcriptional activator of nif gene expression. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Feb;134(2):425–432. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-2-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss D. S., Batut J., Klose K. E., Keener J., Kustu S. The phosphorylated form of the enhancer-binding protein NTRC has an ATPase activity that is essential for activation of transcription. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):155–167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90579-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Popham D., Keener J., Kustu S. In vitro transcription of the nitrogen fixation regulatory operon nifLA of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2876–2880. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2876-2880.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J., Brill W. J. Temperature sensitivity of the regulation of nitrogenase synthesis by Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1116–1118. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1116-1118.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]