Abstract
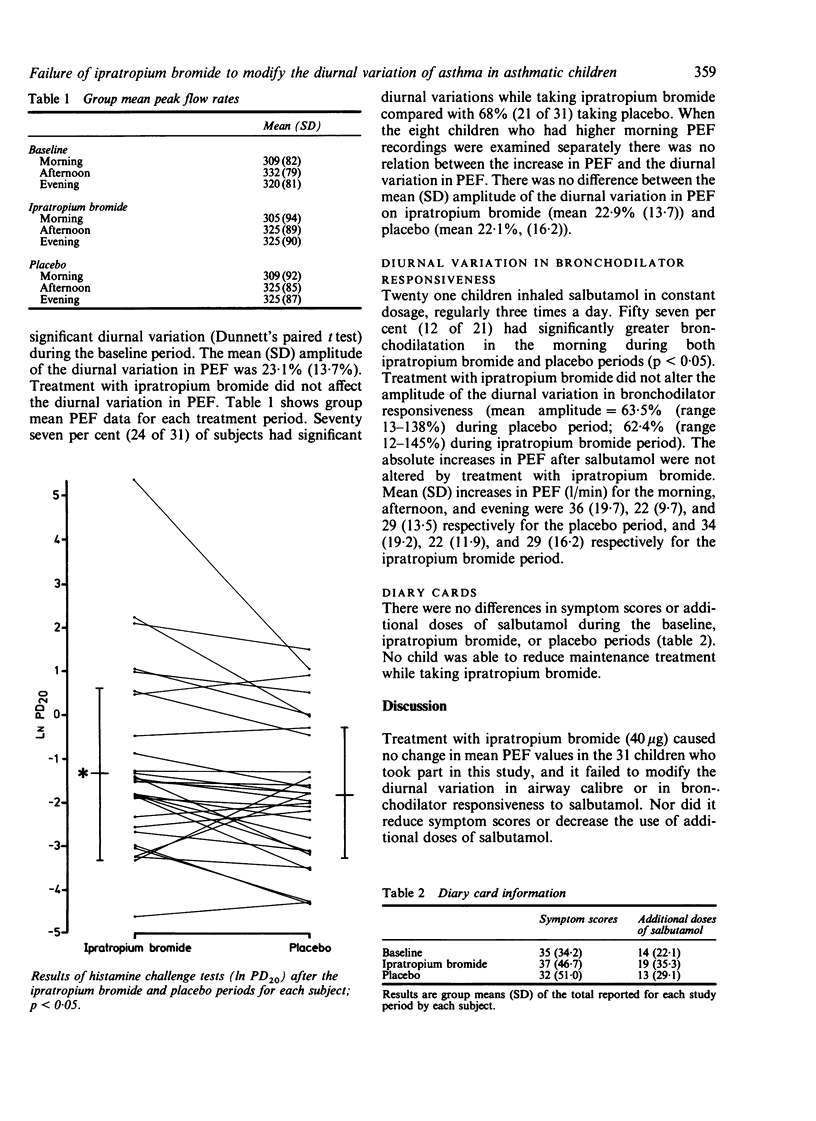
Thirty one children with asthma were given 40 micrograms of ipratropium bromide and identical placebo by inhalation three times a day in a double blind, randomised crossover study to test the ability of an anticholinergic drug to modify the diurnal variation in airway calibre and bronchial reactivity. Subjects measured peak expiratory flow rate approximately eight hourly, before and after inhaled salbutamol, for four week periods. Paired t tests and cosinor analysis were used to assess the diurnal variation in airway calibre from the peak expiratory flow rate recorded before salbutamol and to assess the diurnal variation in bronchodilator responsiveness from the increase in peak expiratory flow rate after salbutamol. Maintenance treatment with ipratropium bromide 40 micrograms three times daily reduced the provocative dose of histamine which caused a 20% fall in FEV1 (geometric mean PD20 = 0.78 v 0.49 mg/ml, p less than 0.05), despite an eight to 12 hour gap between the last dose of ipratropium and histamine challenge. It did not, however, diminish the diurnal variation in airway calibre (mean amplitude = 12.7 v 10.1) or in bronchodilator responsiveness (mean amplitude = 62.4 v 63.5). There was no improvement in the clinical state of subjects while they were taking ipratropium bromide.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boushey H. A., Holtzman M. J., Sheller J. R., Nadel J. A. Bronchial hyperreactivity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Feb;121(2):389–413. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.2.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell F. Thirty deaths from asthma. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Jan;60(1):25–28. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox I. D., Hughes D. T., McDonnell K. A. Ipratropium bromide in patients with nocturnal asthma. Postgrad Med J. 1984 Aug;60(706):526–528. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.60.706.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross N. J., Skorodin M. S. Anticholinergic, antimuscarinic bronchodilators. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 May;129(5):856–870. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.5.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetzel M. R., Clark T. J. Comparison of normal and asthmatic circadian rhythms in peak expiratory flow rate. Thorax. 1980 Oct;35(10):732–738. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.10.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann N. P., Hiller E. J. Ipratropium bromide in children with asthma. Thorax. 1982 Jan;37(1):72–74. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakes G. E., Brogden R. N., Heel R. C., Speight T. M., Avery G. S. Ipratropium bromide: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in asthma and chronic bronchitis. Drugs. 1980 Oct;20(4):237–266. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198020040-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sly P. D., Hibbert M. E., Landau L. I. Diurnal variation of peak expiratory flow rate in asthmatic children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1986 May-Jun;2(3):141–146. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950020305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de VRIES, GOEI J. T., BOOY-NOORD H., ORIE N. G. Changes during 24 hours in the lung function and histamine hyperreactivity of the bronchial tree in asthmatic and bronchitic patients. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1962;20:93–101. doi: 10.1159/000229248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


