Abstract
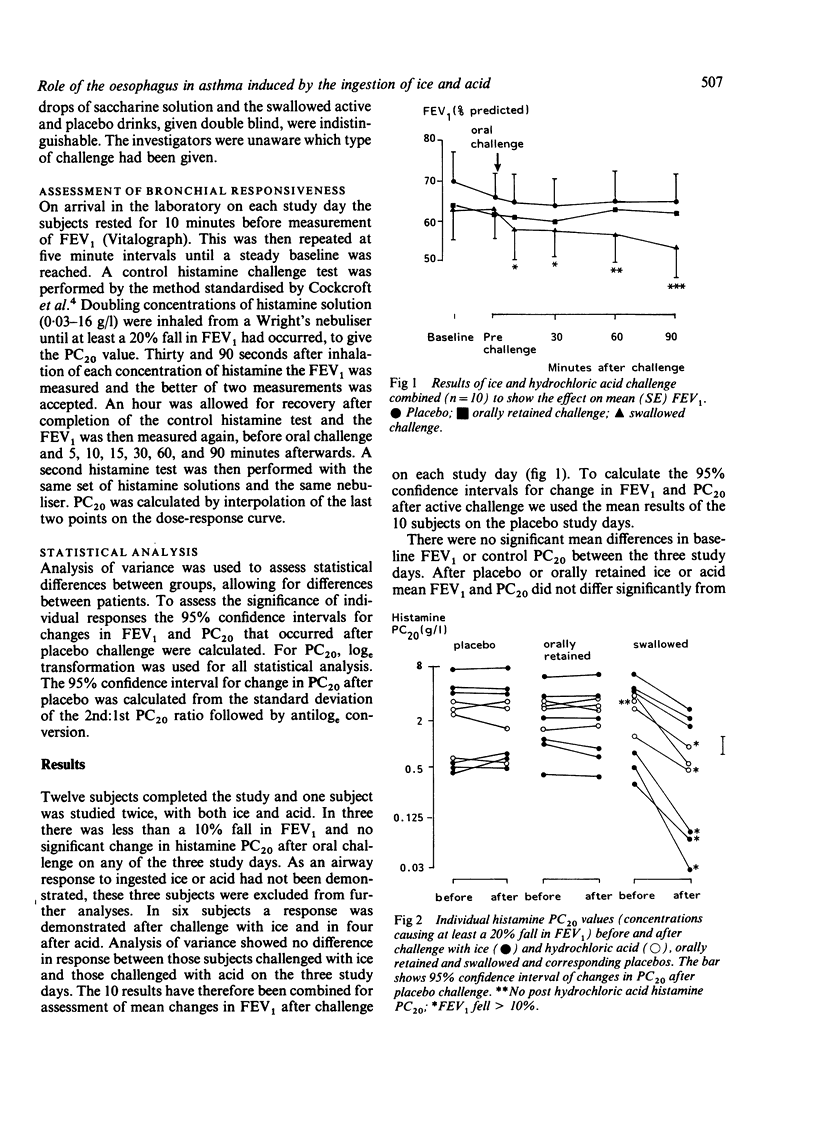
Twelve Asian patients with a history of asthma exacerbated by ingestion of ice and acidic drinks were selected for study. To determine the site of response to ingested ice and acid they were challenged with ice or dilute hydrochloric acid, which was orally retained on one day and swallowed on another. On a third day a placebo was given. The airway response was assessed by measuring FEV1 and the provocative concentration of histamine that reduced the FEV1 by at least 20% (PC20). There was no significant change in FEV1 or histamine PC20 after placebo or the orally retained challenges for the group as a whole or for any individual. After the ice and hydrochloric acid had been swallowed there was a small but statistically significant mean fall in FEV1, increasing to a maximum 90 minutes after ingestion, together with a significant increase in bronchial responsiveness. As conditioning of the inspired air would have been similar after orally retained and after swallowed ice or acid, the response is likely to be due to oesophageal stimulation. The mechanism of the response to oesophageal stimulation is unclear, but the slow time course seems to preclude a simple neural reflex.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson M. K. Bronchial hyperreactivity. Br J Dis Chest. 1975 Oct;69(0):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(75)90090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. Y., Horton D. J. Airways obstruction in asthmatics induced by body cooling. Scand J Respir Dis. 1978 Feb;59(1):13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Killian D. N., Mellon J. J., Hargreave F. E. Bronchial reactivity to inhaled histamine: a method and clinical survey. Clin Allergy. 1977 May;7(3):235–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1977.tb01448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. S., Larsen G. L., Grunstein M. M. Respiratory response to intraesophageal acid infusion in asthmatic children during sleep. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Oct;72(4):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90505-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deal E. C., Jr, McFadden E. R., Jr, Ingram R. H., Jr, Jaeger J. J. Esophageal temperature during exercise in asthmatic and nonasthmatic subjects. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Mar;46(3):484–490. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.46.3.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolovich M. B., Sanchis J., Rossman C., Newhouse M. T. Aerosol penetrance: a sensitive index of peripheral airways obstruction. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Mar;40(3):468–471. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.40.3.468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Ouazzani T., Mei N. Electrophysiologic properties and role of the vagal thermoreceptors of lower esophagus and stomach of cat. Gastroenterology. 1982 Nov;83(5):995–1001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorevic P. D., Kaplan A. P. The physical urticarias. Int J Dermatol. 1980 Oct;19(8):417–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1980.tb05893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. Near fatal asthma after eating deeply frozen ice cream. J R Army Med Corps. 1983 Feb;129(1):52–53. doi: 10.1136/jramc-129-01-16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellén G., Tibbling L., Wranne B. Bronchial obstruction after oesophageal acid perfusion in asthmatics. Clin Physiol. 1981 Jun;1(3):285–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-097x.1981.tb00897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau L. I., Mellis C. M., Phelan P. D., Bristowe B., McLennan L. "Small airways disease" in children: no test is best. Thorax. 1979 Apr;34(2):217–223. doi: 10.1136/thx.34.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laube B. L., Swift D. L., Wagner H. N., Jr, Norman P. S., Adams G. K., 3rd The effect of bronchial obstruction on central airway deposition of a saline aerosol in patients with asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 May;133(5):740–743. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.5.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLAR J. S., NAIR N., Jr, UNKLES R. D., MCNEILL R. S. COLD AIR AND VENTILATORY FUNCTION. Br J Dis Chest. 1965 Jan;59:23–27. doi: 10.1016/s0007-0971(65)80032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield L. E., Hameister H. H., Spaulding H. S., Smith N. J., Glab N. The role of the vague nerve in airway narrowing caused by intraesophageal hydrochloric acid provocation and esophageal distention. Ann Allergy. 1981 Dec;47(6):431–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mays E. E. Intrinsic asthma in adults. Association with gastroesophageal reflux. JAMA. 1976 Dec 6;236(23):2626–2628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Byrne P. M., Leikauf G. D., Aizawa H., Bethel R. A., Ueki I. F., Holtzman M. J., Nadel J. A. Leukotriene B4 induces airway hyperresponsiveness in dogs. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Dec;59(6):1941–1946. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.6.1941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey J. M. Time course of bronchoconstrictive response in asthmatic subjects to reduced temperature. Thorax. 1977 Feb;32(1):26–28. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaulding H. S., Jr, Mansfield L. E., Stein M. R., Sellner J. C., Gremillion D. E. Further investigation of the association between gastroesophageal reflux and bronchoconstriction. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Jun;69(6):516–521. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utell M. J., Morrow P. E., Speers D. M., Darling J., Hyde R. W. Airway responses to sulfate and sulfuric acid aerosols in asthmatics. An exposure-response relationship. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Sep;128(3):444–450. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.3.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson N. M., Charette L., Thomson A. H., Silverman M. Gastro-oesophageal reflux and childhood asthma: the acid test. Thorax. 1985 Aug;40(8):592–597. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.8.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson N. M., Dixon C., Silverman M. Increased bronchial responsiveness caused by ingestion of ice. Eur J Respir Dis. 1985 Jan;66(1):25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson N. M. Food related asthma: a difference between two ethnic groups. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Sep;60(9):861–865. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.9.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson N., Vickers H., Taylor G., silverman M. Objective test for food sensitivity in asthmatic children: increased bronchial reactivity after cola drinks. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Apr 24;284(6324):1226–1228. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6324.1226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


