Abstract
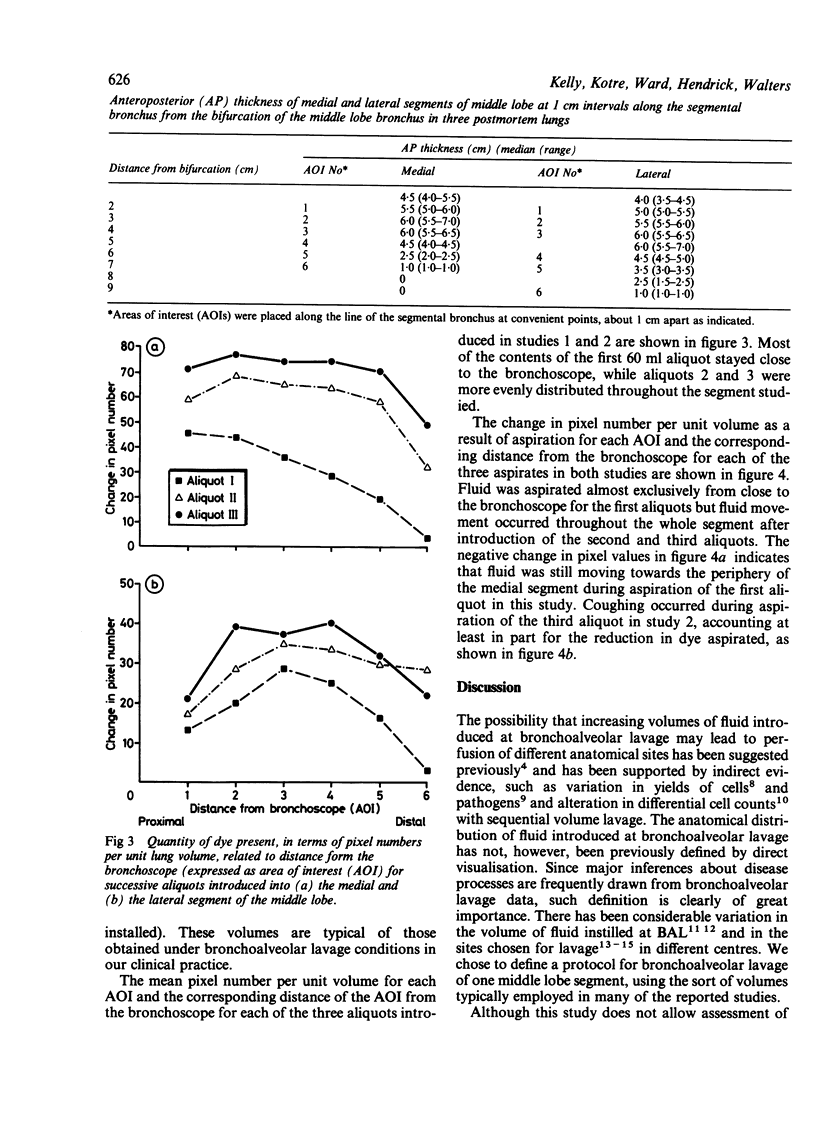
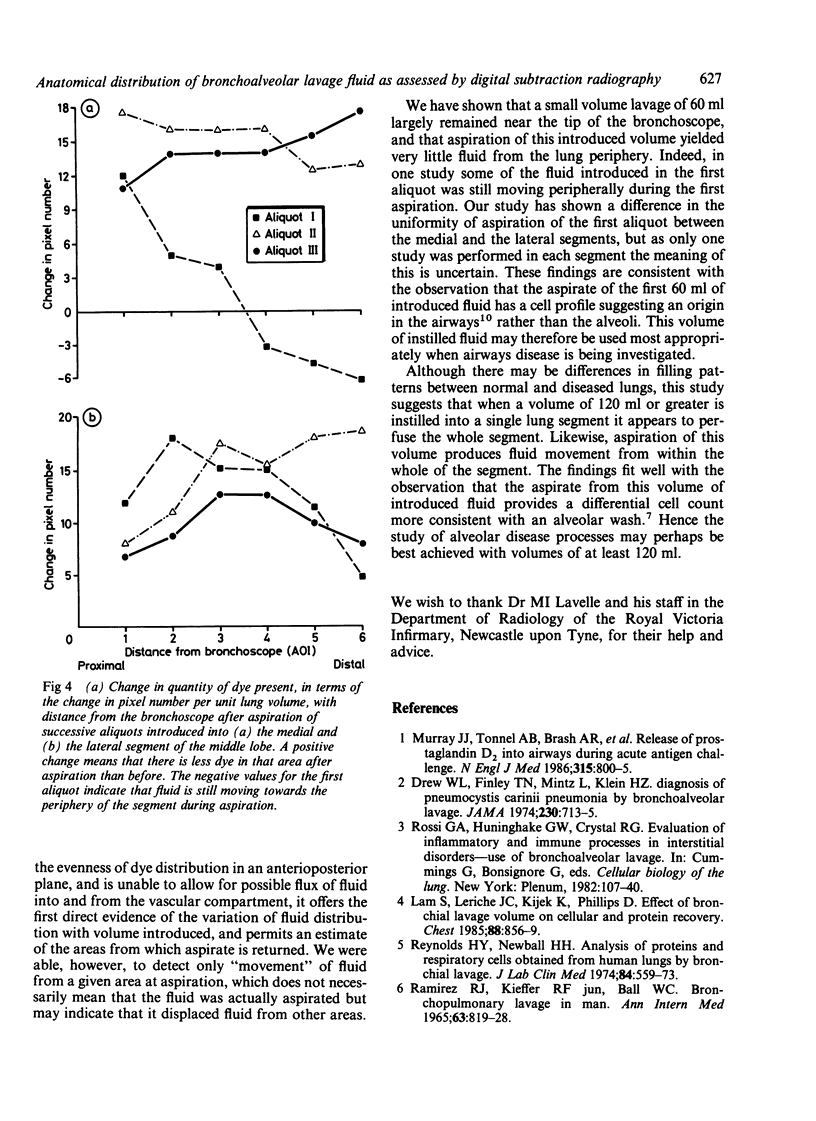
A digital subtraction imaging technique was used to visualise directly the anatomical distribution of 3 X 60 ml aliquots of saline containing a low concentration of radio-opaque dye, introduced sequentially into a segment of the middle lobe. It was possible to estimate the relative movement of fluid within the segment during the sequential aspiration of each of these aliquots. The first 60 ml aliquot introduced stayed close to the bronchoscope and probably sampled only the proximal airways. With the introduction of cumulative volumes of 120 ml or more, the fluid filled the segment more evenly. Aspiration then moved fluid back from the periphery, implying that the aspirate had also lavaged both distal airways and alveoli.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Drew W. L., Finley T. N., Mintz L., Klein H. Z. Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia by bronchopulmonary lavage. JAMA. 1974 Nov 4;230(5):713–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulmer J. D. Bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Dec;126(6):961–963. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.6.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. G., Wolven R. G., Garcia P. L., Keogh B. A. Assessment of interlobar variation of bronchoalveolar lavage cellular differentials in interstitial lung diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Mar;133(3):444–449. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.3.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam S., Leriche J. C., Kijek K., Phillips D. Effect of bronchial lavage volume on cellular and protein recovery. Chest. 1985 Dec;88(6):856–859. doi: 10.1378/chest.88.6.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill W., O'Hearn E., Rankin J., Naegel G., Matthay R. A., Reynolds H. Y. Kinetic analysis of respiratory tract proteins recovered during a sequential lavage protocol. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Oct;126(4):617–620. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.4.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. J., Tonnel A. B., Brash A. R., Roberts L. J., 2nd, Gosset P., Workman R., Capron A., Oates J. A. Release of prostaglandin D2 into human airways during acute antigen challenge. N Engl J Med. 1986 Sep 25;315(13):800–804. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198609253151304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pingleton S. K., Harrison G. F., Stechschulte D. J., Wesselius L. J., Kerby G. R., Ruth W. E. Effect of location, pH, and temperature of instillate in bronchoalveolar lavage in normal volunteers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Dec;128(6):1035–1037. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.6.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez J., Kieffer R. F., Jr, Ball W. C., Jr Bronchopulmonary lavage in man. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Nov;63(5):819–828. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-63-5-819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin J. A., Snyder P. E., Schachter E. N., Matthay R. A. Bronchoalveolar lavage. Its safety in subjects with mild asthma. Chest. 1984 Jun;85(6):723–728. doi: 10.1378/chest.85.6.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Newball H. H. Analysis of proteins and respiratory cells obtained from human lungs by bronchial lavage. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Oct;84(4):559–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]