Abstract
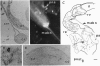
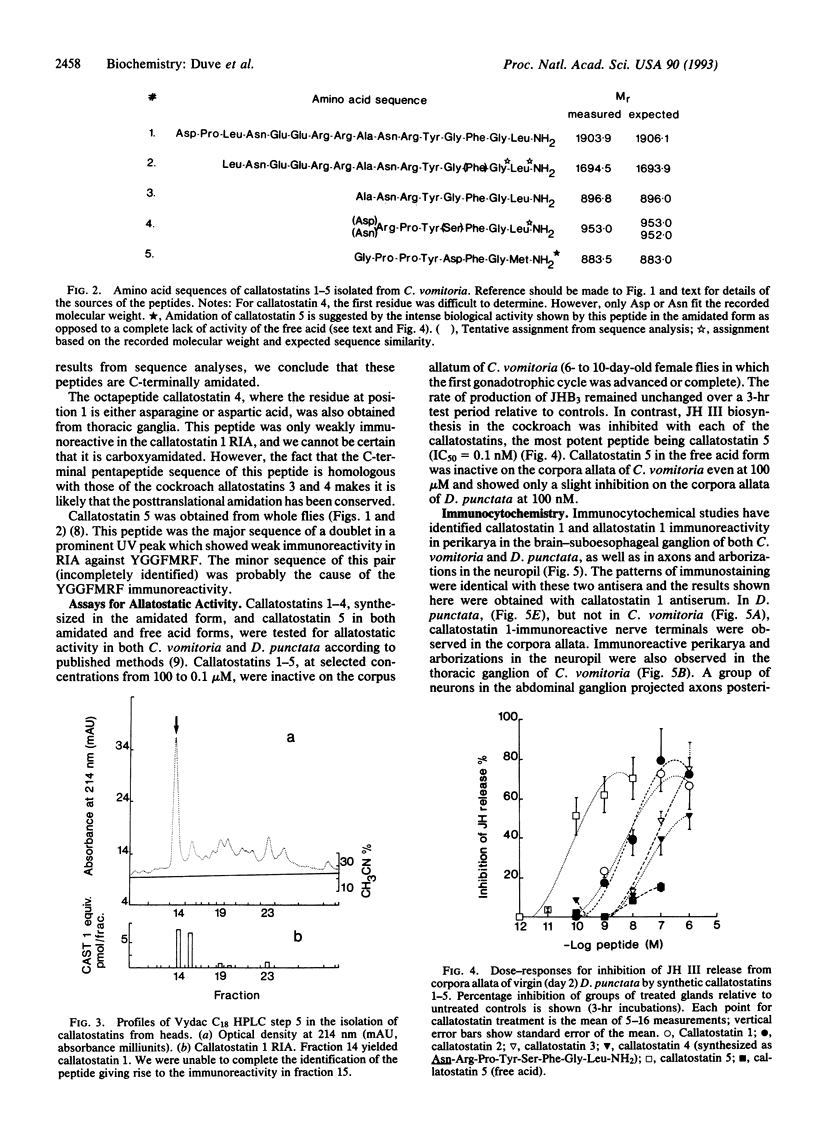
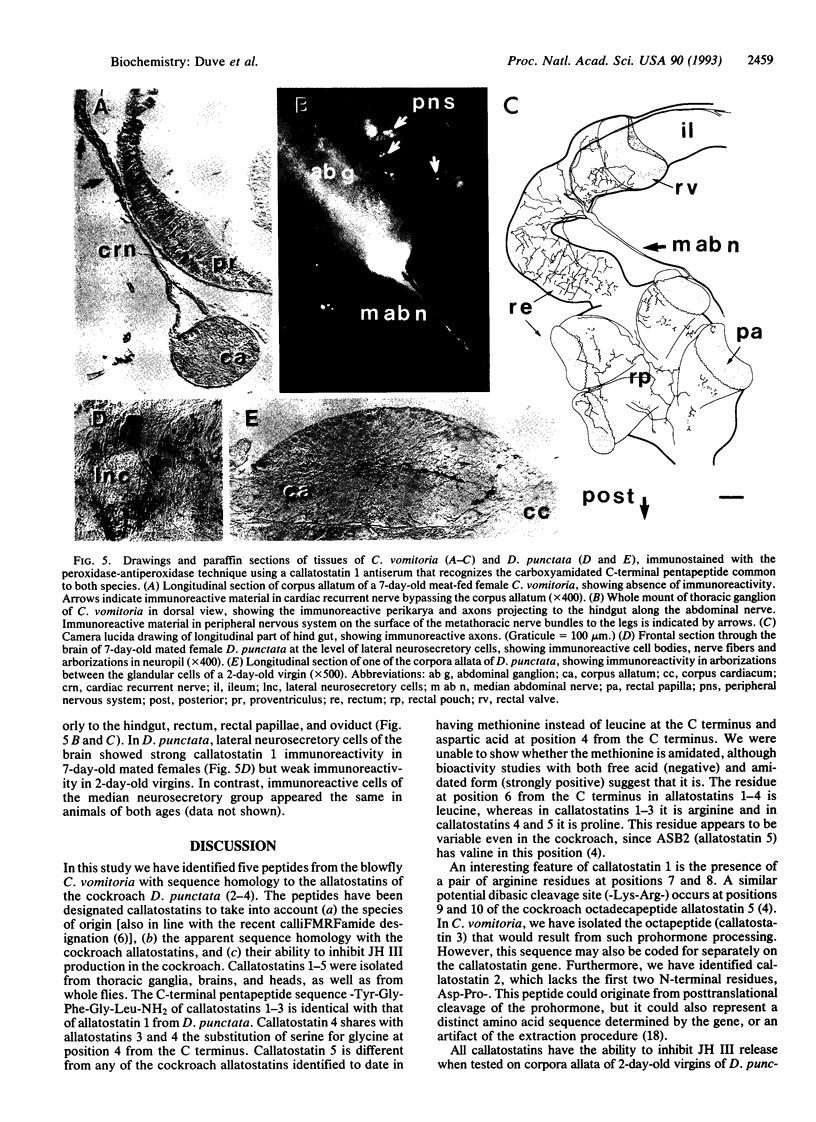
Five neuropeptides with C-terminal amino acid sequence homology to cockroach allatostatins have been identified in the blowfly Calliphora vomitoria. Three have the same pentapeptide C-terminal amino acid sequence as allatostatin 1 of the cockroach Diploptera punctata. A hexadecapeptide designated callatostatin 1, isolated from thoracic ganglia, brains, and heads, has the sequence Asp-Pro-Leu-Asn-Glu-Glu-Arg-Arg-Ala-Asn-Arg-Tyr-Gly-Phe-Gly-Leu-NH2. Callatostatins 2 and 3 have been isolated from heads and thoracic ganglia, respectively; they comprise the last 14 and 8 residues of callatostatin 1. Callatostatin 4, isolated from thoracic ganglia, has the sequence Xaa-Arg-Pro-Tyr-Ser-Phe-Gly-Leu-NH2, where Xaa is either Asp or Asn. This peptide, with a serine substitution for glycine at position 5, has a C-terminal pentapeptide sequence identical to that of allatostatins 3 and 4 of D. punctata. Callatostatin 5, with the sequence Gly-Pro-Pro-Tyr-Asp-Phe-Gly-Met-NH2, was identified from whole flies. All five peptides inhibit juvenile hormone production by the corpora allata of D. punctata in vitro. Callatostatin 5 was the most potent allatostatin so far tested in this species, with maximum inhibition occurring at 1 nM. In contrast, none of the callatostatins or the allatostatins showed allatostatic activity in mature female C. vomitoria when tested at concentrations of 100 to 0.1 microM. In accordance with these results, immunoreactivity to an antiserum directed against the common C terminus of callatostatin 1 and allatostatin 1 was observed in the corpora allata of D. punctata but not in the corpus allatum of C. vomitoria, despite its presence in neurons of the brain. Neurons in the thoracic ganglion of C. vomitoria that are immunoreactive against this antiserum project to the hindgut, rectum, rectal papillae, and oviduct, suggestive of a function different from that of a true allatostatin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conlon J. M., Arnold-Reed D. E., Balment R. J. Urotensin I and its N-terminal flanking peptide from the flounder, Platichthys flesus. Peptides. 1990 Sep-Oct;11(5):895–895. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(90)90004-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duve H., Johnsen A. H., Sewell J. C., Scott A. G., Orchard I., Rehfeld J. F., Thorpe A. Isolation, structure, and activity of -Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-NH2 neuropeptides (designated calliFMRFamides) from the blowfly Calliphora vomitoria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2326–2330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duve H., Sewell J. C., Scott A. G., Thorpe A. Chromatographic characterisation and biological activity of neuropeptides immunoreactive to antisera against Met5-enkephalin-Arg6-Phe7 (YGGFMRF) extracted from the blowfly Calliphora vomitoria (Diptera). Regul Pept. 1991 Aug 13;35(2):145–159. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(91)90477-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duve H., Thorpe A. Distribution of functional significance of Met-enkephalin-Arg6-Phe7- and Met-enkephalin-Arg6-Gly7-Leu8-like peptides in the blowfly Calliphora vomitoria. II. Immunocytochemical mapping of neuronal pathways in the retrocerebral complex and thoracic ganglion. Cell Tissue Res. 1990 Jan;259(1):147–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00571439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duve H., Thorpe A., Tobe S. S. Immunocytochemical mapping of neuronal pathways from brain to corpora cardiaca/corpora allata in the cockroach Diploptera punctata with antisera against Met-enkephalin-Arg6-Gly7-Leu8. Cell Tissue Res. 1991 Feb;263(2):285–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00318770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay I., Coast G. M., Cusinato O., Wheeler C. H., Totty N. F., Goldsworthy G. J. Isolation and characterization of a diuretic peptide from Acheta domesticus. Evidence for a family of insect diuretic peptides. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1991 Jul;372(7):505–512. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1991.372.2.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer S. J., Toschi A., Miller C. A., Kataoka H., Quistad G. B., Li J. P., Carney R. L., Schooley D. A. Identification of an allatostatin from the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9458–9462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt G. E., Farnsworth D. E., Fok K. F., Siegel N. R., McCormack A. L., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Feyereisen R. Identity of a second type of allatostatin from cockroach brains: an octadecapeptide amide with a tyrosine-rich address sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt G. E., Farnsworth D. E., Siegel N. R., Fok K. F., Feyereisen R. Identification of an allatostatin from adult Diploptera punctata. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 29;163(3):1243–1247. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt G. E., Tobe S. S. Juvenile hormones radiobiosynthesised by corpora allata of adult female locusts in vitro. Life Sci. 1974 Feb 1;14(3):575–586. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90372-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbo G., Højrup P., Rahbek-Nielsen H., Andersen S. O., Roepstorff P. Determination of the covalent structure of an N- and C-terminally blocked glycoprotein from endocuticle of Locusta migratoria. Combined use of plasma desorption mass spectrometry and Edman degradation to study post-translationally modified proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jan 30;195(2):495–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe S. S., Pratt G. E. The influence of substrate concentrations on the rate of insect juvenile hormone biosynthesis by corpora allata of the desert locust in vitro. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;144(1):107–113. doi: 10.1042/bj1440107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang P. W., Orchard I. Distribution of FMRFamide-related peptides in the blood-feeding bug, Rhodnius prolixus. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Sep 1;311(1):17–32. doi: 10.1002/cne.903110103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead A. P., Stay B., Seidel S. L., Khan M. A., Tobe S. S. Primary structure of four allatostatins: neuropeptide inhibitors of juvenile hormone synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5997–6001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]