Full text
PDF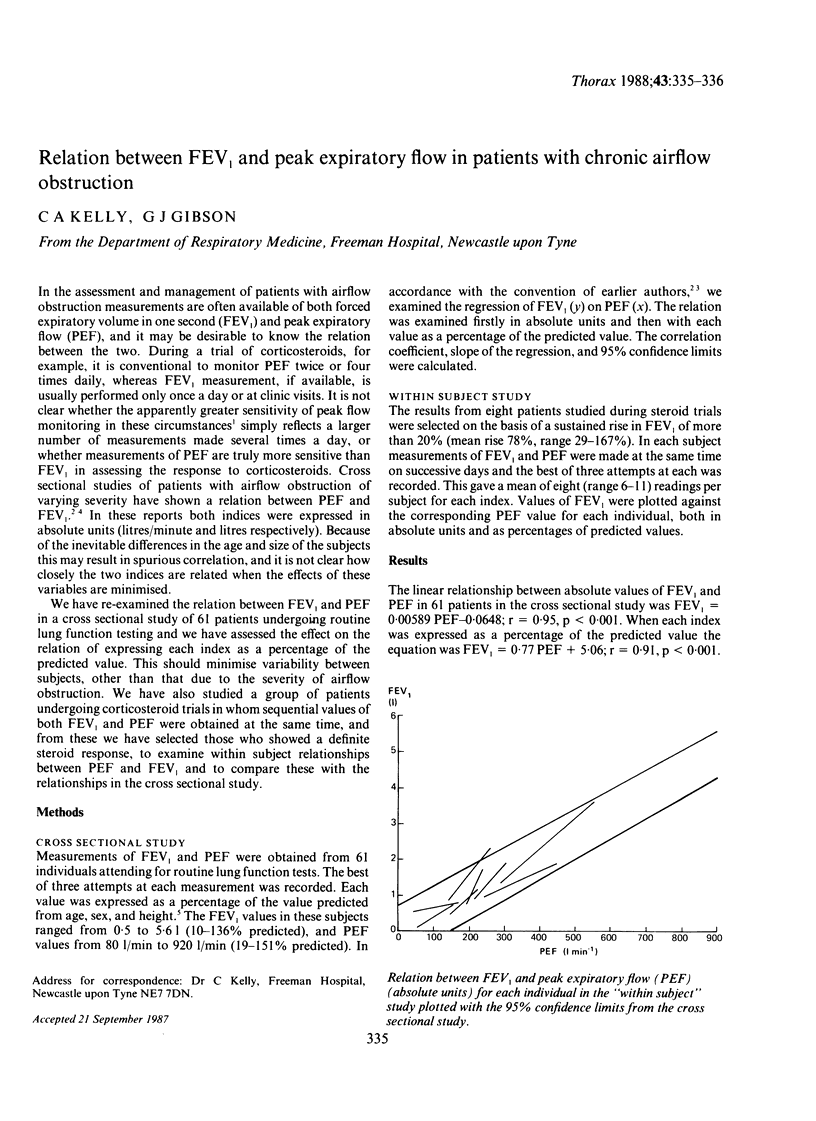

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FAIRBAIRN A. S., FLETCHER C. M., TINKER C. M., WOOD C. H. A comparison of spirometric and peak expiratory flow measurements in men with and without chronic bronchitis. Thorax. 1962 Jun;17:168–174. doi: 10.1136/thx.17.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. M., Gildeh P., Dimond A. H., Collins J. V. Value of serial peak expiratory flow measurements in assessing treatment response in chronic airflow limitation. Thorax. 1986 Aug;41(8):606–610. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.8.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITCHIE B. THE APPLICATION OF SIMPLE METHODS IN THE FUNCTIONAL ASSESSMENT OF OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE AND RESPIRATORY FAILURE. Med J Aust. 1963 Aug 17;2:259–262. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1963.tb24987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


