Abstract
A 65-kDa protein and a 10-kDa protein are two of the more strongly immunoreactive components of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the causative agent of tuberculosis. The 65-kDa antigen has homology with members of the GroEL or chaperonin-60 (Cpn60) family of heat shock proteins. The 10-kDa antigen has homology with the GroES or chaperonin-10 family of heat shock proteins. These two proteins are encoded by separate genes in M. tuberculosis. The studies reported here reveal that M. tuberculosis contains a second Cpn60 homolog located 98 bp downstream of the 10-kDa antigen gene. The second Cpn60 homolog (Cpn60-1) displays 61% amino acid sequence identity with the 65-kDa antigen (Cpn60-2) and 53% and 41% identity with the Escherichia coli GroEL protein and the human P60 protein, respectively. Primer-extension analysis revealed that transcription starts 29 bp upstream of the translation start of the Cpn60-1 homolog and protein purification studies indicate that the cpn60-1 gene is expressed as an approximately 60-kDa polypeptide.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. C., Barry M. E., Buchanan T. M. Exact definition of species-specific and cross-reactive epitopes of the 65-kilodalton protein of Mycobacterium leprae using synthetic peptides. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):607–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird P. N., Hall L. M., Coates A. R. A major antigen from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which is homologous to the heat shock proteins groES from E. coli and the htpA gene product of Coxiella burneti. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):9047–9047. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.9047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird P. N., Hall L. M., Coates A. R. Cloning and sequence analysis of the 10 kDa antigen gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Apr;135(4):931–939. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-4-931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. F., Mehra V., Rivoire B., Fong S. J., Brennan P. J., Voegtline M. S., Minden P., Houghten R. A., Bloom B. R., Modlin R. L. Immunoreactivity of a 10-kDa antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1835–1840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born W., Hall L., Dallas A., Boymel J., Shinnick T., Young D., Brennan P., O'Brien R. Recognition of a peptide antigen by heat shock--reactive gamma delta T lymphocytes. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.1695022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruyn J., Bosmans R., Turneer M., Weckx M., Nyabenda J., Van Vooren J. P., Falmagne P., Wiker H. G., Harboe M. Purification, partial characterization, and identification of a skin-reactive protein antigen of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):245–252. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.245-252.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J., van der Vies S. M. Molecular chaperones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:321–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulle H., Schoel B., Kaufmann S. H. Direct blotting with viable cells of protein mixtures separated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Oct 19;133(2):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90366-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen S. M., Woolford C., van der Vies S. M., Tilly K., Dennis D. T., Georgopoulos C. P., Hendrix R. W., Ellis R. J. Homologous plant and bacterial proteins chaperone oligomeric protein assembly. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):330–334. doi: 10.1038/333330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochuli E., Döbeli H., Schacher A. New metal chelate adsorbent selective for proteins and peptides containing neighbouring histidine residues. J Chromatogr. 1987 Dec 18;411:177–184. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93969-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jindal S., Dudani A. K., Singh B., Harley C. B., Gupta R. S. Primary structure of a human mitochondrial protein homologous to the bacterial and plant chaperonins and to the 65-kilodalton mycobacterial antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2279–2283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Kabelitz D. Gamma/delta T lymphocytes and heat shock proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;167:191–207. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75875-1_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungquist C., Breitholtz A., Brink-Nilsson H., Moks T., Uhlén M., Nilsson B. Immobilization and affinity purification of recombinant proteins using histidine peptide fusions. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 22;186(3):563–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazodier P., Guglielmi G., Davies J., Thompson C. J. Characterization of the groEL-like genes in Streptomyces albus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7382–7386. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7382-7386.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Sweetser D., Young R. A. Efficient mapping of protein antigenic determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7013–7017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munk M. E., Shinnick T. M., Kaufmann S. H. Epitopes of the mycobacterial heat shock protein 65 for human T cells comprise different structures. Immunobiology. 1990 Feb;180(2-3):272–277. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. J., Styblo K., Rouillon A. Tuberculosis in developing countries: burden, intervention and cost. Bull Int Union Tuberc Lung Dis. 1990 Mar;65(1):6–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinke de Wit T. F., Bekelie S., Osland A., Miko T. L., Hermans P. W., van Soolingen D., Drijfhout J. W., Schöningh R., Janson A. A., Thole J. E. Mycobacteria contain two groEL genes: the second Mycobacterium leprae groEL gene is arranged in an operon with groES. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jul;6(14):1995–2007. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M. Heat shock proteins as antigens of bacterial and parasitic pathogens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;167:145–160. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75875-1_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Krat C., Schadow S. Isolation and restriction site maps of the genes encoding five Mycobacterium tuberculosis proteins. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1718–1721. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1718-1721.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Plikaytis B. B., Hyche A. D., Van Landingham R. M., Walker L. L. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis BCG-a protein has homology with the Escherichia coli GroES protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1254–1254. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Sweetser D., Thole J., van Embden J., Young R. A. The etiologic agents of leprosy and tuberculosis share an immunoreactive protein antigen with the vaccine strain Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1932–1935. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1932-1935.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M. The 65-kilodalton antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1080–1088. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1080-1088.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Vodkin M. H., Williams J. C. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis 65-kilodalton antigen is a heat shock protein which corresponds to common antigen and to the Escherichia coli GroEL protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):446–451. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.446-451.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stover C. K., Marana D. P., Dasch G. A., Oaks E. V. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the Sta58 major antigen gene of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi: sequence homology and antigenic comparison of Sta58 to the 60-kilodalton family of stress proteins. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1360–1368. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1360-1368.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thole J. E., Keulen W. J., De Bruyn J., Kolk A. H., Groothuis D. G., Berwald L. G., Tiesjema R. H., van Embden J. D. Characterization, sequence determination, and immunogenicity of a 64-kilodalton protein of Mycobacterium bovis BCG expressed in escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1466–1475. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1466-1475.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schooten W. C., Elferink D. G., Van Embden J., Anderson D. C., De Vries R. R. DR3-restricted T cells from different HLA-DR3-positive individuals recognize the same peptide (amino acids 2-12) of the mycobacterial 65-kDa heat-shock protein. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Nov;19(11):2075–2079. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Jarjour W. N. Stress proteins, autoimmunity, and autoimmune disease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;167:161–189. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75875-1_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Mehlert A., Bal V., Mendez-Samperio P., Ivanyi J., Lamb J. R. Stress proteins and the immune response to mycobacteria--antigens as virulence factors? Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1988;54(5):431–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00461861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., Lathigra R., Hendrix R., Sweetser D., Young R. A. Stress proteins are immune targets in leprosy and tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4267–4270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Bloom B. R., Grosskinsky C. M., Ivanyi J., Thomas D., Davis R. W. Dissection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens using recombinant DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2583–2587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A. Stress proteins and immunology. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:401–420. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
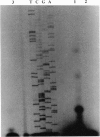
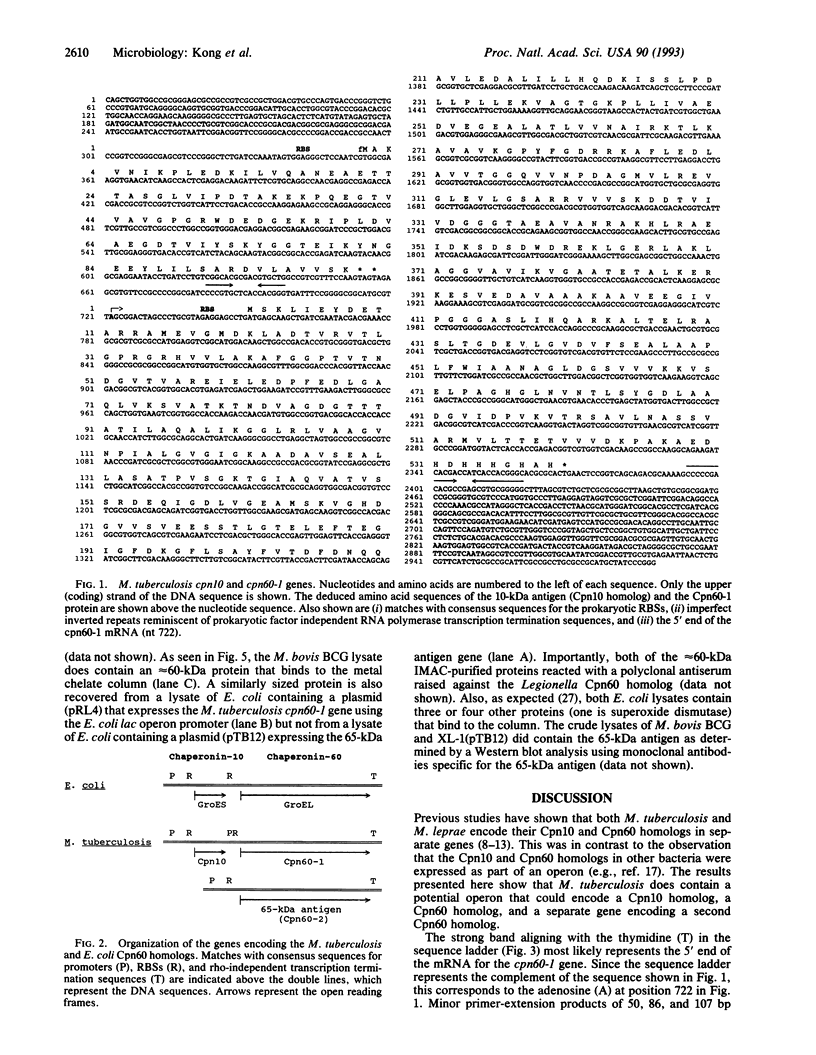
- van Eden W., Thole J. E., van der Zee R., Noordzij A., van Embden J. D., Hensen E. J., Cohen I. R. Cloning of the mycobacterial epitope recognized by T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):171–173. doi: 10.1038/331171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]