Abstract
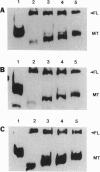
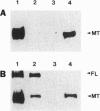
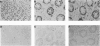
The APC gene has been found to be mutated during the development of sporadic colorectal tumors as well as in the germ line of familial adenomatous polyposis patients. To facilitate the characterization of both normal and mutant APC protein, a series of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies specific for the APC protein was produced. When lymphoblastoid cell lines derived from seven familial adenomatous polyposis patients with known mutations were analyzed by Western blot, an approximately 300-kDa protein corresponding to the predicted size of full-length APC was detected in all 7 cell lines. In addition, truncated APC proteins corresponding to the product of the known mutated alleles could be detected in 4 of the 7 lines. Similar analysis of 23 colon carcinoma and 9 adenoma cell lines revealed truncated proteins in 24 (75%) of the cell lines. Moreover, 26 (81%) of the colon tumor lines were totally devoid of the normal, full-length protein. In contrast, Western blot analysis of 40 cell lines derived from sporadic tumors of other organs detected only full-length APC. Immunohistochemical analysis of APC in normal colonic mucosa revealed cytoplasmic staining with more intense staining in the basolateral margins of the epithelial cell. This staining was markedly increased in the upper portions of the crypts, suggesting an increased level of expression with maturation. These studies provide some initial clues to the function of the cytoplasmic protein APC and demonstrate the feasibility of identifying APC mutations by direct analysis of the APC protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashton-Rickardt P. G., Wyllie A. H., Bird C. C., Dunlop M. G., Steel C. M., Morris R. G., Piris J., Romanowski P., Wood R., White R. MCC, a candidate familial polyposis gene in 5q.21, shows frequent allele loss in colorectal and lung cancer. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1881–1886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. A., Grossman A. D., Gross C. A. A gene regulating the heat shock response in Escherichia coli also affects proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6779–6783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boynton R. F., Blount P. L., Yin J., Brown V. L., Huang Y., Tong Y., McDaniel T., Newkirk C., Resau J. H., Raskind W. H. Loss of heterozygosity involving the APC and MCC genetic loci occurs in the majority of human esophageal cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3385–3388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amico D., Carbone D. P., Johnson B. E., Meltzer S. J., Minna J. D. Polymorphic sites within the MCC and APC loci reveal very frequent loss of heterozygosity in human small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 1;52(7):1996–1999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. M., Phillips R. A., Zhu X., Becker A., Gallie B. L. Mutations in the RB1 gene and their effects on transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4596–4604. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groden J., Thliveris A., Samowitz W., Carlson M., Gelbert L., Albertsen H., Joslyn G., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):589–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joslyn G., Carlson M., Thliveris A., Albertsen H., Gelbert L., Samowitz W., Groden J., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification of deletion mutations and three new genes at the familial polyposis locus. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):601–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Nilbert M. C., Su L. K., Vogelstein B., Bryan T. M., Levy D. B., Smith K. J., Preisinger A. C., Hedge P., McKechnie D. Identification of FAP locus genes from chromosome 5q21. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):661–665. doi: 10.1126/science.1651562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. High-expression vectors with multiple cloning sites for construction of trpE fusion genes: pATH vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:477–490. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94036-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovitz A., Stinson J. C., McCombs W. B., 3rd, McCoy C. E., Mazur K. C., Mabry N. D. Classification of human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1976 Dec;36(12):4562–4569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. K., Sigmund C. D., Gross K. W., Maquat L. E. Nonsense codons in human beta-globin mRNA result in the production of mRNA degradation products. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1149–1161. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBain J. A., Weese J. L., Meisner L. F., Wolberg W. H., Willson J. K. Establishment and characterization of human colorectal cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1984 Dec;44(12 Pt 1):5813–5821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. J., Marks P. J., Lam T., Morgan J., Panicali D. L., Trimpe K. L., Carney W. P. Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for the human neu oncogene product, p185. Oncogene. 1989 May;4(5):543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi Y., Ando H., Nagase H., Nishisho I., Horii A., Miki Y., Mori T., Utsunomiya J., Baba S., Petersen G. Germ-line mutations of the APC gene in 53 familial adenomatous polyposis patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4452–4456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi Y., Nagase H., Ando H., Horii A., Ichii S., Nakatsuru S., Aoki T., Miki Y., Mori T., Nakamura Y. Somatic mutations of the APC gene in colorectal tumors: mutation cluster region in the APC gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):229–233. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.4.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishisho I., Nakamura Y., Miyoshi Y., Miki Y., Ando H., Horii A., Koyama K., Utsunomiya J., Baba S., Hedge P. Mutations of chromosome 5q21 genes in FAP and colorectal cancer patients. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):665–669. doi: 10.1126/science.1651563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Kinzler K. W., Meltzer P. S., George D. L., Vogelstein B. Amplification of a gene encoding a p53-associated protein in human sarcomas. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):80–83. doi: 10.1038/358080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paraskeva C., Buckle B. G., Sheer D., Wigley C. B. The isolation and characterization of colorectal epithelial cell lines at different stages in malignant transformation from familial polyposis coli patients. Int J Cancer. 1984 Jul 15;34(1):49–56. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910340109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paraskeva C., Finerty S., Mountford R. A., Powell S. C. Specific cytogenetic abnormalities in two new human colorectal adenoma-derived epithelial cell lines. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 1;49(5):1282–1286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell S. M., Zilz N., Beazer-Barclay Y., Bryan T. M., Hamilton S. R., Thibodeau S. N., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. APC mutations occur early during colorectal tumorigenesis. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):235–237. doi: 10.1038/359235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield J. B., Graff D., Li H. P. A solid-phase method for the quantitation of protein in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate and other interfering substances. Anal Biochem. 1987 Oct;166(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90544-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprott S. C., Hammond K. D., Savage N. Subcellular fractionation of murine erythroleukemic cells: distribution of protein kinases. Anal Biochem. 1991 May 1;194(2):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90249-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. C., Harper S. J., Marshall C. J., Gill R. W., Mountford R. A., Paraskeva C. Specific cytogenetic abnormalities and k-ras mutation in two new human colorectal-adenoma-derived cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1992 Nov 11;52(5):785–790. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willson J. K., Bittner G. N., Oberley T. D., Meisner L. F., Weese J. L. Cell culture of human colon adenomas and carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1987 May 15;47(10):2704–2713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]