Abstract
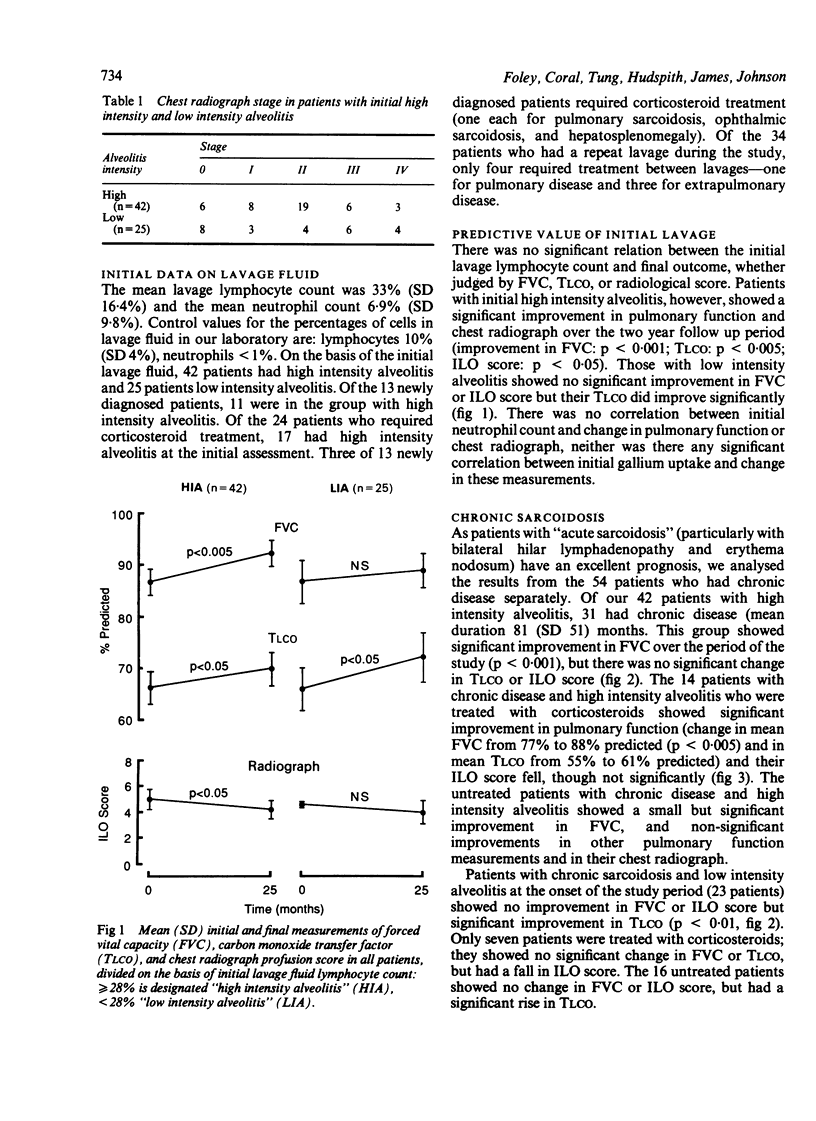
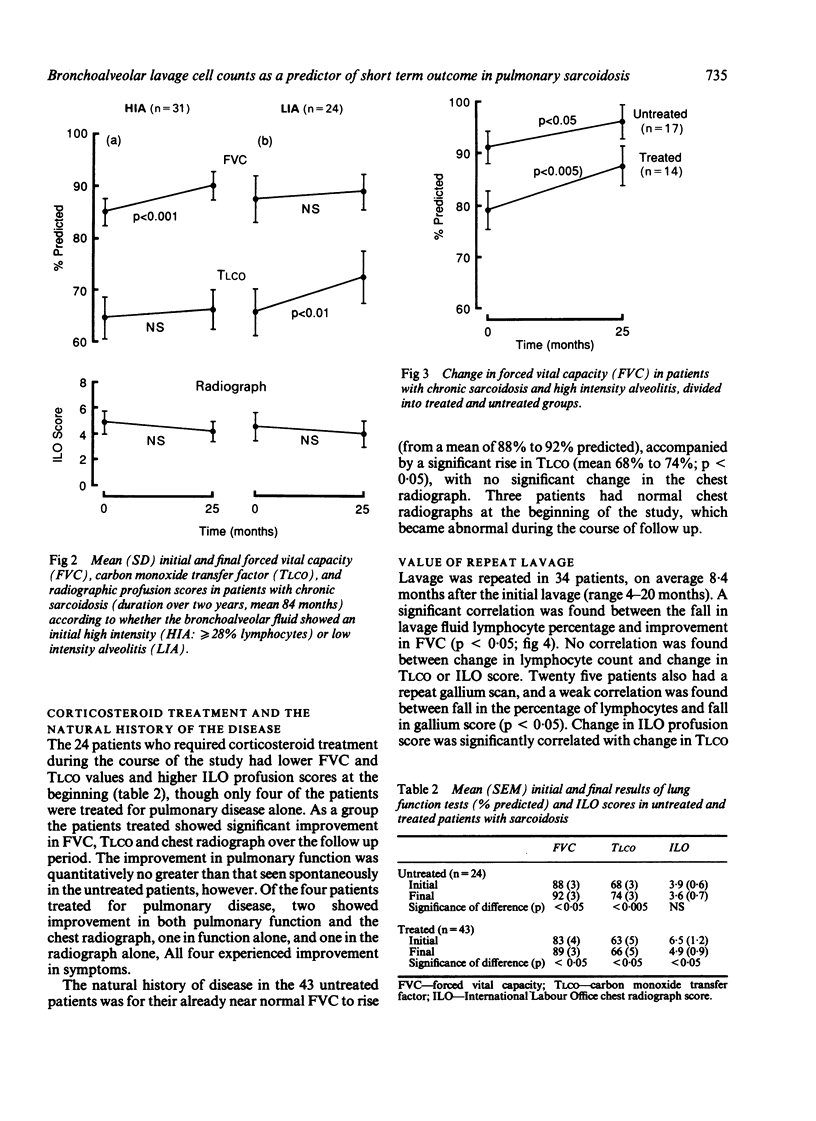
Sixty seven patients with biopsy proven pulmonary sarcoidosis were prospectively studied to determine whether single point bronchoalveolar lavage cell counts were a useful indicator of functional outcome and whether repeated lavage helped in management. The mean follow up period was 25 (range 13-37) months. No patient was having corticosteroid treatment at the time of initial bronchoalveolar lavage. "High intensity alveolitis" (lymphocyte count greater than or equal to 28%) was present at the initial lavage in 42 patients. These patients showed a significant improvement in their pulmonary function and chest radiographs over the follow up period whereas patients with "low intensity alveolitis" did not. Of the 42 patients with high intensity alveolitis, 31 had chronic sarcoidosis (duration over two years, mean 80 months). These patients showed a significant improvement in FVC but not in TLCO. Corticosteroids resulted in greater functional and radiological improvement in the patients with high intensity alveolitis than in those with low intensity alveolitis. Repeat bronchoalveolar lavage in 34 patients, mean 8.4 months after the original lavage, showed a weak inverse relation between a reduced lymphocyte count and change in forced vital capacity and isotope uptake on a gallium scan. These correlations were too weak to make repeated cell counts useful in management. Our results suggest that high intensity alveolitis may be a favourable prognostic factor for lung function in pulmonary sarcoidosis, even in patients with chronic disease, but that repeat lavage adds little to the management of the individual patient.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe S., Munakata M., Nishimura M., Tsuneta Y., Terai T., Nakano I., Ohsaki Y., Kawakami Y. Gallium-67 scintigraphy, bronchoalveolar lavage, and pathologic changes in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. Chest. 1984 May;85(5):650–655. doi: 10.1378/chest.85.5.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughman R. P., Fernandez M., Bosken C. H., Mantil J., Hurtubise P. Comparison of gallium-67 scanning, bronchoalveolar lavage, and serum angiotensin-converting enzyme levels in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Predicting response to therapy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 May;129(5):676–681. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.5.676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchalter S., App W., Jackson L., Chandler D., Jackson R., Fulmer J. Bronchoalveolar lavage cell analysis in sarcoidosis. A comparison of lymphocyte counts and clinical course. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;465:678–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb18545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. D., Bunting P. S., Meindok H. O., Chamberlain D. W., Rebuck A. S. Does serum angiotensin converting enzyme reflect intensity of alveolitis in sarcoidosis? Thorax. 1985 Jul;40(7):497–500. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.7.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costabel U., Bross K. J., Guzman J., Nilles A., Rühle K. H., Matthys H. Predictive value of bronchoalveolar T cell subsets for the course of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;465:418–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb18518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniele R. P., Elias J. A., Epstein P. E., Rossman M. D. Bronchoalveolar lavage: role in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of interstitial lung disease. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Jan;102(1):93–108. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-1-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRemee R. A., Rohrbach M. S. Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in evaluating the clinical course of sarcoidosis. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Mar;92(3):361–365. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-3-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greening A. P., Nunn P., Dobson N., Rudolf M., Rees A. D. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: alterations in bronchoalveolar lymphocytes and T cell subsets. Thorax. 1985 Apr;40(4):278–283. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.4.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel-Biet D., Venet A., Chrétien J. Persistent high alveolar lymphocytosis as a predictive criterion of chronic pulmonary sarcoidosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;465:395–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb18516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. G., Neville E., Siltzbach L. E. A worldwide review of sarcoidosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;278:321–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLGREN J. H. Osteoarthrosis in patients and populations. Br Med J. 1961 Jul 1;2(5243):1–6. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5243.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogh B. A., Hunninghake G. W., Line B. R., Crystal R. G. The alveolitis of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Evaluation of natural history and alveolitis-dependent changes in lung function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Aug;128(2):256–265. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.2.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman J. Elevation of serum angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) level in sarcoidosis. Am J Med. 1975 Sep;59(3):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90395-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. H., Haslam P. L., Turner-Warwick M. Chronic pulmonary sarcoidosis: relationship between lung lavage cell counts, chest radiograph, and results of standard lung function tests. Thorax. 1985 Jul;40(7):501–507. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.7.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosal A., Schleissner L. A., Mishkin F. S., Lieberman J. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme and gallium scan in noninvasive evaluation of sarcoidosis. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Mar;90(3):328–331. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-3-328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Warwick M., McAllister W., Lawrence R., Britten A., Haslam P. L. Corticosteroid treatment in pulmonary sarcoidosis: do serial lavage lymphocyte counts, serum angiotensin converting enzyme measurements, and gallium-67 scans help management? Thorax. 1986 Dec;41(12):903–913. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.12.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward K., O'Connor C., Odlum C., Fitzgerald M. X. Prognostic value of bronchoalveolar lavage in sarcoidosis: the critical influence of disease presentation. Thorax. 1989 Jan;44(1):6–12. doi: 10.1136/thx.44.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeager H., Jr, Williams M. C., Beekman J. F., Bayly T. C., Beaman B. L. Sarcoidosis: analysis of cells obtained by bronchial lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Nov;116(5):951–954. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.5.951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


