Abstract
Glycoconjugates are important mediators of host-pathogen interactions and are usually very abundant in the surface of many protozoan parasites. However, in the particular case of Plasmodium species, previous works show that glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor modifications, and to an unknown extent, a severely truncated N-glycosylation are the only glycosylation processes taking place in the parasite. Nevertheless, a detailed analysis of the parasite genome and the recent identification of the sugar nucleotide precursors biosynthesized by Plasmodium falciparum support a picture in which several overlooked, albeit not very prominent glycosylations may be occurring during the parasite life cycle. In this work, the authors review recent developments in the characterization of the biosynthesis of glycosylation precursors in the parasite, focusing on the outline of the possible fates of these precursors.
keywords: Glycobiology, Malaria, Plasmodium falciparum, Sugar nucleotides
Background
The cell surfaces and endosomal/lysosomal systems of protozoan parasites are usually rich in glycoconjugates, some of which play essential roles in their survival, infectivity or virulence [1]. In Plasmodium falciparum, the only glycan structures described so far are limited to glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchors [2–5] and, recently, to unusual N-glycans composed of one or two GlcNAc residues [6, 7]. The glycan structures of P. falciparum GPI anchors are well characterized [3]. However, controversial questions regarding the glycobiology of P. falciparum, such as the presence of O-glycosylation or the extent and significance of N-glycosylation, remain open [8, 9].
In the blood stages, P. falciparum primarily relies upon glycolysis for its energetic requirements [10]. Due to the need of a large amount of glucose, P. falciparum increases the hexose permeability of the red blood cell (RBC) membrane by expressing an essential hexose transporter at the surface of the infected RBC [11, 12]. The presence of active sugar nucleotide biosynthetic routes in the parasite indicates that there is a flux of glucose for the synthesis of these various glycosylation precursors [13–16]. Sugar nucleotides can be synthetized, in general, through two main pathways: a de novo pathway, which involves inter-conversion of an existing sugar or sugar nucleotide, and a salvage pathway, which relies upon “activation” of the sugar by a kinase and a subsequent pyrophosphorylase to form a sugar nucleotide [15]. Thus, despite that evolution into a parasitic niche seems to have resulted in “paring down” of many Plasmodium metabolic pathways, the presence of sugar nucleotides suggests an involvement in the biosynthesis of different parasite glycans [10]. The biosynthesis of GDP-fucose and other sugar nucleotides not related to GPI anchors strongly suggests a role in the biosynthesis of glycans/glycolipids that are not yet characterized in the parasite [6, 8, 17–19].
GDP-mannose
GDP-mannose (GDP-Man), the activated form of mannose, is biosynthesized in a multistep process from mannose salvaging or via a de novo pathway from fructose-6-phosphate (Fru6P). Metabolic databases, based on the parasite genome sequence, predict the conservation of both biosynthetic routes (Fig. 1) [13]. In the de novo pathway a mannose-1-phosphate isomerase (MPI; EC 5.3.1.8) catalyzes the interconversion of Fru6P to mannose-6-phosphate (Man6P). Two more enzymes catalyze the conversion of Man6P into GDP-Man, firstly phosphomannomutase (PMM; EC 5.4.2.8) forms mannose-1-phosphate (Man1P), which is then converted into GDP-Man by a Man1P guanyltransferase (MPG; EC 2.7.7.13). The salvage pathway comprises the phosphorylation of mannose into Man6P by a hexokinase (HK; EC 2.7.1.1), after which the pathway follows the same route as the de novo pathway (see Table 1) [13, 15]. The presence of a mannose salvage pathway has been demonstrated through the incorporation of [3H]Man into GPI anchors by the blood stages of the parasite [2, 15, 20].
Fig. 1.
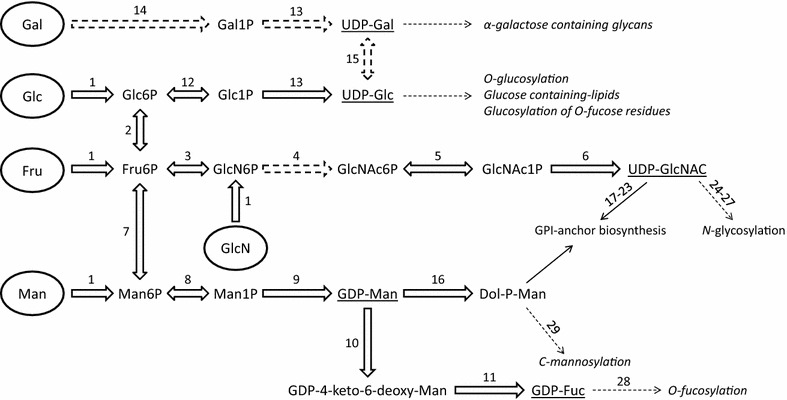
Sugar nucleotide biosynthesis pathways in Plasmodium falciparum. Activated sugars, used for glycoconjugate biosynthesis, are underlined. Carbohydrates, taken up from the medium or salvaged, are circled. Sugar nucleotide donor fates are indicated and they are in italics when glycosylations have not been proved to be present in the parasite. The numbers refer to the enzymatic activities summarized in Table 1. Discontinuous arrows depict enzymatic activities that could not be identified in P. falciparum genome
Table 1.
Enzymes involved in sugar nucleotide pathways, GPI-anchor and C-, N- and O-glycan biosynthesis of P. falciparum
| Step | Enzyme name | Enzyme number | P. falciparum homologuesa | Syntenic orthologsb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hexokinase (HK) | EC 2.7.1.1 | PF3D7_0624000 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 2 | Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (G6PI) | EC 5.3.1.9 | PF3D7_1436000 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 3 | Glucosamine-fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase (GFPT) | EC 2.6.1.16 | PF3D7_1025100 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 4 | Glucosamine-phosphate N- acetyltransferase (GNA) | EC 2.3.1.4 | No gene identified | |
| 5 | Phosphoacetylglucosamine mutase (PAGM) | EC 5.4.2.3 | PF3D7_1130000 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 6 | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase (UAP) | EC 2.7.7.23 | PF3D7_1343600 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 7 | Mannose-6-phosphate isomerase (MPI) | EC 5.3.1.8 | PF3D7_0801800 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 8 | Phosphomannomutase (PMM) | EC 5.4.2.8 | PF3D7_1017400 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 9 | Mannose-1-phosphate guanyltransferase (MPG) | EC 2.7.7.13 | PF3D7_1420900 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 10 | GDP-mannose 4,6-dehydratase (GMD) | EC 4.2.1.47 | PF3D7_0813800 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 11 | GDP-L-fucose synthase (FS) | EC 1.1.1.271 | PF3D7_1014000 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 12 | Phosphoglucomutase (PGM) | EC 5.4.2.2 | PF3D7_1012500 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 13 | UTP-glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase (UGP) or UDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase (USP) | EC 2.7.7.9 or EC 2.7.7.64 | PF3D7_0517500 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 14 | Galactokinase (GK) | EC 2.7.1.6 | No gene identified | |
| 15 | UDP-glucose 4-epimerase (GALE) | EC 5.1.3.2 | No gene identified | |
| 16 | Dolichol-phosphate mannosyltransferase polypeptide 1 (DPM1) | EC 2.4.1.83 | PF3D7_1141600 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| Enzymes involved in GPI-Anchor biosynthesis | ||||
| 17 | phosphatidylinositol n- acetylglucosaminyltransferase (PIG-A) | EC 2.4.1.198 | PF3D7_0618900.1 and PF3D7_0935300 and/or PF3D7_1032400 and/or PF3D7_1141400 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 18 | N-acetylglucosaminyl phosphatidylinositol deacetylase (PIG-L) | EC 3.5.1.89 | PF3D7_0624700 and/or PF3D7_0911000 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 19 | Inositol acyltransferase (PIG-W) | EC 2.3 | PF3D7_0615300 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 20 | GPI mannosyltransferase I (PIG-M) | EC 2.4.1 | PF3D7_1210900 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 21 | GPI mannosyltransferase II (PIG-V) | EC 2.4.1 | PF3D7_1247300 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 22 | GPI mannosyltransferase III (PIG-B) | EC 2.4.1 | PF3D7_1341600 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 23 | GPI mannosyltransferase IV | EC 2.4.1 | No gene identified | |
| Enzymes involved in N-glycans biosynthesis | ||||
| 24 | UDP-N-Acetyl-glucosamine-1-P transferase (ALG7) | EC 2.7.8.15 | PF3D7_0321200 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 25 | UDP-N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase subunit (ALG13) | EC 2.4.1.141 | PF3D7_0806400 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 26 | UDP-N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase subunit (ALG14) | EC 2.4.1.141 | PF3D7_0211600 | Pv, Pk, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| 27 | Catalytic subunit of the oligosaccharyltransferase complex (STT3) | EC 2.4.99.18 | PF3D7_1116600 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| Enzymes involved in O-fucosylation | ||||
| 28 | GDP-fucose protein O-fucosyltransferase 2 (PoFUT2) | EC 2.4.1.221 | PF3D7_0909200 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
| Enzymes involved in C-mannosylation | ||||
| 29 | C-mannosyltransferase | EC 2.4.1 | PF3D7_0806200 | Pv, Pk, Pc, Pr, Pb, Py, Pch |
aAll the gene ID numbers are identified and annotated in P. falciparum genome as putative candidates. The genes in italics (GMD and FS) are the only ones that have been functionally characterized [12]
bSyntenic orthologs identified in other Plasmodium species. Pv (P. vivax), Pk (P. knowlesii), Pc (P. cynomolgy), Pr (P. reichenowi), Pb (P. berghei), Py (P. yoelii) and Pch (P. chabaudi) [22]
In eukaryotes, Man is an important constituent of N-, O-linked glycans and glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchors. However, Man residues are absent in P. falciparum N-glycans, as the parasite synthesizes a severely truncated N-glycan precursor composed of one or two GlcNAc residues (Fig. 2) [2, 6, 7]. Nonetheless, Man residues are present in the P. falciparum major glycoconjugates, the GPI anchors that play an important role in the pathogenicity of the parasite. GPIs are attached to the C-terminus of many important surface proteins, such as MSP-1, and anchor them to the external leaflet of the plasma membrane. Besides, in the surface of the parasite there are also protein-free GPIs that function as malarial toxins and are involved in parasite-induced release of cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin 1 (IL-1) [3, 9, 21–24].
Fig. 2.
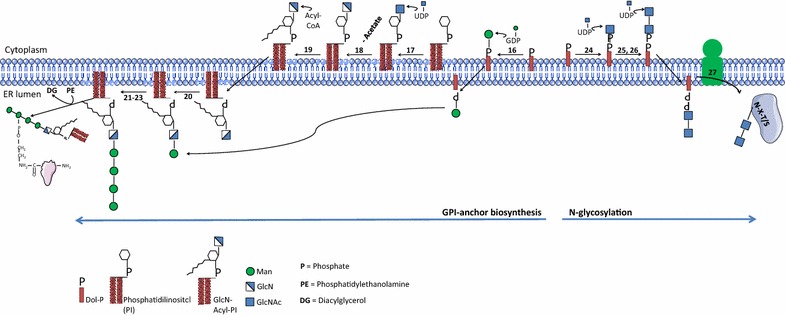
Biosynthetic scheme for GPI-anchor biosynthesis and N-glycosylation in Plasmodium falciparum. The numbers refer to the enzymes described in Table 1
Plasmodium falciparum GPIs consist of the conserved glycan core (Manα1-2Manα1-6Manα1-4GlcNH2α1-6myo-Ins) but have an extra/forth mannose and inositol-acylation. Thus, the complete P. falciparum GPI structure is defined as EtNP-6(Manα1-2)Manα1-2Manα1-6Manα1-4GlcNα1-6(acyl-2)myo-Ins-1-P-(sn1,2 diacyl)-glycerol (Figs. 2, 3) [2, 3, 20, 25]. The protein free GPI glycan core contains either 3 or 4 mannose residues since two structurally distinct GPI-anchor precursors (Pfα and Pfβ) are used by the parasite. Pfα presents an additional α1,2-mannose residue modifying the terminal mannose of the conserved trimannosyl core glycan [2, 3, 20, 21]. The biosynthesis of P. falciparum GPI anchors as with all other eukaryotes, starts with the preassembly of a GPI precursor in the cytoplasmic face of the ER membrane. Briefly, the addition of GlcNAc to phosphatidylinositol (PI) by phosphatidylinositol glycosyltransferase-A (PIG-A) gives rise to GlcNAc-PI (Fig. 2), which is then de-N-acetylated to form GlcN-PI by a de-N-acetylase (PIG-L)(steps are discussed in detail below). Prior to mannosylation at the 4 position of the GlcN, an inositol acyltransferase (PIG-W) transfers a fatty acid (usually myristate or palmitate) from acyl-CoA to the 2-OH group of the D-myo-inositol residue of GlcN-PI (Fig. 2). Subsequently, the GPI precursor is translocated from the cytoplasmic to the luminal face of the ER, where four Man residues are added sequentially by four different GPI-mannosyltransferases (Fig. 2). The Man donor for these mannosyltransferases is dolichol-phosphate-mannose (Dol-P-Man) formed by the action of dolichol-phosphate mannose polypeptide 1 (known as DPM1) alternatively known as Dol-P-Man synthase (DPMS). Interestingly, P. falciparum DPMS represents a unique class in the clade of DPMS enzymes [26] that has been genetically validated as essential (Williams and Smith, manuscript in preparation). Dol-P-Man is formed through the coupling of Man from GDP-Man to Dol-P to form Dol-P-Man and GDP as by-product. Three of the four mannosyltransferases required for GPI-biosynthesis, PIG-M, PIG-V and PIG-B encoding putative Man1, Man2 and Man3 transferases respectively, can be identified in the parasite genome [13, 27, 28]. However, no clear candidate genes for addition of Man4 (also performed in yeast by the Smp3 gene) are found [27]. Interestingly, a recent study suggests that P. falciparum PIG-B is responsible of adding the extra Man to the GPI precursor [29].
Fig. 3.
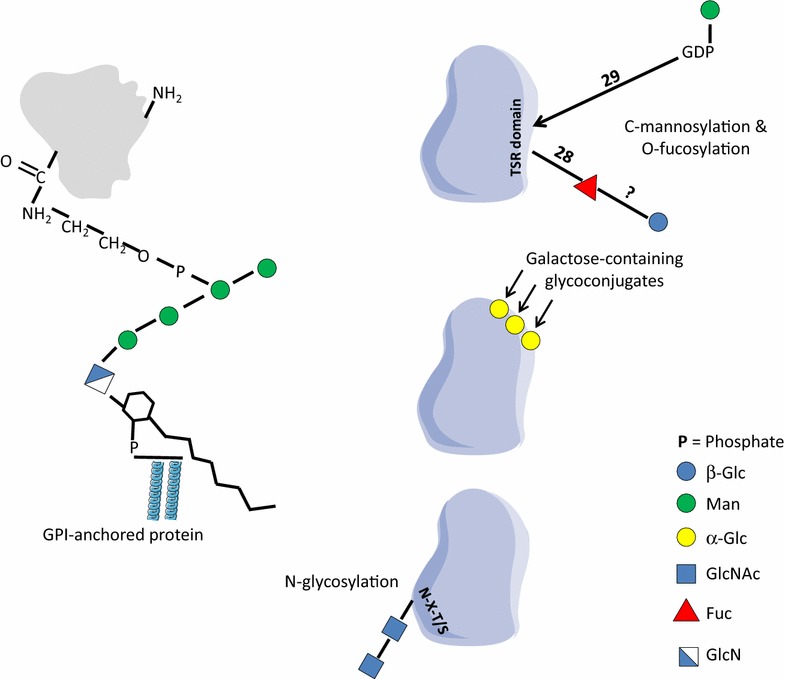
Schematic representation of described or putative glycosylations present in the surface of the malaria parasite. Enzymatic activities predicted to be involved in the glycosylation reactions described are indicated by numbers and summarized in Table 1
Several essential proteins present in the surface of various stages of the malaria life cycle, such as Pfs48/45 on gametes, Pfs25 on ookinetes, circumsporozoite (CS) on sporozoites and MSP-1 or MSP-2 on merozoites, are GPI-anchored proteins [30]. Therefore, GPI anchors play important roles in P. falciparum survival and pathogenicity. The essentiality of GPI-anchored proteins is supported by genetic studies. For instance, Pfs48/45 gene disruption prevents zygote development and transmission whereas mutant parasites lacking CS protein do not form sporozoites [31, 32]. In the blood stages, it was demonstrated that six proteins out of seven merozoite GPI-anchored proteins were refractory to genetic deletion, strongly suggesting an essential role in parasite survival [33].
Another possible fate for GDP-Man/Dol-P-Man is the C-mannosylation of proteins [34]. C-mannosylation is the attachment of a Man residue to tryptophan through a carbon–carbon bond. This type of glycosylation is found in WXXW sequences of secreted proteins and cell surface receptors containing thrombospondin type I repeat (TSR) domains [35]. Whereas TSR has been recognized as critical for protein adhesion and recognition in several organisms including Plasmodium [36, 37], the direct influence of C-mannosylation on protein function is not known. The enzyme responsible for C-mannosylation is a C-mannosyltransferase, which was first identified as DPY-19 in Caenorhabditis elegans [38]. In P. falciparum genome there is a DPY-19 homolog, which is present in all sequenced Plasmodium spp. genomes. Further investigations are required to confirm the presence/activity of this putative C-mannosyltransferase and the biological significance of this post-translational modification in P. falciparum.
GDP-fucose
Fucosylation is important in a wide variety of organisms, as it is associated with numerous types of recognition and adhesion events. GDP-fucose (GDP-Fuc), the precursor for all the fucosylation reactions, has been identified in the blood stages of P. falciparum at levels similar to the pools present in other protozoan parasites [15, 39]. The P. falciparum genome contains homologues of the enzymes involved in the de novo biosynthesis of GDP-Fuc from GDP-Man (Fig. 1 and Table 1) [13]. This pathway relies in a three-step conversion of GDP-Man to GDP-Fuc catalyzed by two enzymes: a GDP-Man dehydratase (GMD; EC 4.2.1.47) and a GDP-Fuc synthetase (FS; EC 1.1.1.271) also known as GDP-4-dehydro-6-deoxy-d-mannose epimerase/reductase. PfGMD and PfFS are expressed throughout the intraerythrocytic life cycle and have been shown to be active in in vitro studies [15]. In some organisms a salvage pathway for the biosynthesis of GDP-Fuc is also present. This pathway involves the phosphorylation of fucose by a fucose kinase (EC 2.7.1.52) followed by condensation with GTP catalyzed by a fucose-1-phosphate pyrophosphorylase (EC 2.7.7.30) [40]. However, P. falciparum genome lacks obvious candidate genes for these enzymatic activities and [3H]fucose is not significantly incorporated by the parasite, supporting the idea that most of the GDP-Fuc in the blood stages of P. falciparum is formed through the de novo biosynthetic pathway, i.e. conversion from GDP-Man (Fig. 1 and Table 1) [2, 13, 15]. Nevertheless, the utilization of GDP-[3H]Fuc by P. falciparum lysates suggests that the GDP-Fuc donor is used by the parasite in fucosylation reaction(s) as yet unidentified [15, 41].
Fucose has not yet been described in any glycoconjugates from P. falciparum. Hence, the fate and importance of GDP-Fuc for P. falciparum remains unknown [6, 9]. Our own preliminary data supports the presence of a fucose-containing glycan in the surface of the parasite, since a PfGMD null mutant shows a decreased labelling with fucose-binding Ulex europaeus agglutinin I (UEA-I) (Izquierdo and Samuelson, in preparation). Thus, despite the non-essentiality of GDP-Fuc for the growth/replication of the parasite in the blood-stage, it seems that P. falciparum presents, at least, a fucosyltransferase activity. The best candidate for a GDP-Fuc dependent glycosyltransferase activity in the parasite is a protein O-fucosyltransferase 2 (PoFUT2) homolog conserved in the genome (Table 1). In other organisms, PoFUT2 is involved in the O-fucosylation of TSR domains [42]. Remarkably, there are several TSR domain-containing proteins identified in P. falciparum with essential roles for infectivity and survival [37]. For instance, thrombospondin-related anonymous protein (TRAP) is crucial for sporozoite gliding motility and hepatocyte invasion, whereas merozoite TRAP (MTRAP) plays a role as putative adaptor between the merozoite invasion machinery and the surface proteins that mediate erythrocyte adhesion [43, 44]. CS protein, the main component of the RTS,S malaria vaccine, is involved in sporozoite infection and also contains an altered TSR domain [45]. The expression of TRAP and CS protein fragments in HEK293T cells showed that their TSR domains were modified with fucose residues, presumably by PoFUT2 present in HEK293T cells [17, 18]. Interestingly, peptides of PfGMD, PfFS and PoFUT2, the three principal components for GDP-Fuc metabolic route and O-fucosylation machinery, have been detected in the sporozoite stages of the parasite, when the surface of the cell is covered with CS and TRAP [46]. Altogether, the data strongly suggests the presence of an active PoFUT2 mediated O-fucosylation mechanism in sporozoites, which needs further exploration.
UDP-N-acetyl glucosamine
UDP-N-acetyl glucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc), the donor for all GlcNAc transferases, plays an important role in several eukaryotes. It is essential in Leishmania major and in Trypanosoma brucei for growth and survival in the mammalian host [47, 48]. There are two main active pathways for UDP-GlcNAc biosynthesis in P. falciparum: a conventional de novo pathway and a salvage pathway fed by glucosamine (GlcN) (Fig. 1). The de novo pathway (the amino-sugar pathway) starts with the conversion of Fructose-6P (Fru6P) into Glucosamine-6P (GlcN6P) through the glucosamine-fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase activity (GFPT; EC 2.6.1.16) [13, 15]. The next step, which is the acetylation of GlcN6P to generate N-acetyl-glucosamine-6P (GlcNAc6P), remains a mystery in P. falciparum since a candidate gene encoding for the glucosamine-phosphate-N-acetyltransferase (GNA) activity (EC 2.3.1.4) cannot be identified in the genome (Table 1). GNA enzymes have been characterized in several eukaryotes, including S. cerevisiae and T. brucei, but despite their well-conserved secondary structure, the amino acid sequences are often diverse [49, 50]. Besides, the presence of various histone-acetylases makes it challenging to unequivocally identify a P. falciparum GNA in the genome. After acetylation, GlcNAc6P is converted into N-acetyl-glucosamine-1P (GlcNAc1P) by a phosphoacetylglucosamine mutase (PAGM, EC 5.4.2.3). The last step is catalyzed by an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase (UAP, EC 2.7.7.23) which converts GlcNAc1P into UDP-GlcNAc [13, 15]. The salvage pathway for UDP-GlcNAc production exists possibly due to the action of hexokinase (HK; EC 2.7.1.1) which catalyzes the phosphorylation of glucosamine (GlcN) to GlcN-6-P which then feeds the same route as the de novo pathway (Fig. 1, Table 1) [15]. Several studies demonstrate the existence of this salvage pathway since GPI-anchors can be labelled with [3H]GlcN [2, 20, 51]. However, the contribution of this pathway in vivo seems to be minor, as GlcN is not an abundant sugar within the parasite hosts. As in the case of GDP-Man, the UDP-GlcNAc pathway is predicted to be essential in P. falciparum as it feeds GPI-anchor biosynthesis, required for survival and infectivity [9].
UDP-GlcNAc is used in P. falciparum N-glycosylation. Despite that the presence of N-glycans in parasite proteins was initially controversial [2, 52] recent work show evidences of the presence of short N-glycans on the surface of P. falciparum trophozoites and schizonts [6]. This agrees with the synthesis of Dolichol-PP (Dol-PP) linked GlcNAc and GlcNAc2 glycan precursors [7] and the conservation in the parasite’s genome of the genes involved in the biosynthesis of P. falciparum N-glycans: ALG7 (EC 2.7.8.15), ALG13/ALG14 (EC 2.4.1.141) and STT3 (EC 2.4.99.18) (Table 1). ALG7 transfers GlcNAc, from UDP-GlcNAc, to the ER-membrane Dol-PP forming Dol-PP-GlcNAc [7, 53]. ALG13/ALG14, a heterodimeric UDP-GlcNAc transferase complex, uses UDP-GlcNAc as donor substrate for the extension of Dol-PP-GlcNAc to Dol-PP-GlcNAc2. ALG14 acts as a scaffold, recruiting ALG13 (which retains a consensus UDP-sugar binding site such as ALG7) to the cytosolic face of ER where occurs the catalysis of Dol-PP-GlcNAc2 [54–56]. STT3, normally part of a 5 subunit complex, comprising of OST1, WBP1, STT3, OST4 and OST3, but OST4 seems to be missing from the complex [52], which catalyzes the transfer of GlcNAc and GlcNAc2 from Dol-PP-linked oligosaccharides to “sequon” Asparigine residues (N-X-T/S) in the nascent protein (Fig. 2) [7, 57, 58]. Interestingly, the N-linked glycosylation blocker tunicamycin is lethal for the parasite when it is exposed to the compound for two developmental cycles (more than 48 h), although the authors did not relate that effect to N-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis [59, 60]. Furthermore, if these short N-glycans elicit a specific immune response in the human host, they may be interesting as xenoantigens since these glycans are not expected to be present in the human glycome.
GlcN, the deacetylated form of GlcNAc, is an integral component of GPI-anchors (Fig. 2). To generate GlcN-PI, two reactions take place in the cytoplasmic side of the ER membrane: the transfer of GlcNAc from the UDP-GlcNAc donor to the phosphatidylinositol (PI) and the deacetylation of GlcNAc-PI to GlcN-PI (Fig. 2) [3, 13, 25, 27]. The first reaction is catalyzed by a phosphatidylinositol N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.198). In mammals this reaction is associated to a complex of six proteins [27, 61–64] and four subunits are conserved in the genome of the parasite [13]. N-acetylglucosaminyl phosphatidylinositol deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.89) is responsible for the deacetylation of GlcNAc-PI [13, 27]. Two candidate genes (Table 1) show certain homology to PIG-L that encodes for a de-N-acetylase in other organisms. However, the specific gene encoding for PIG-L in P. falciparum has not been functionally characterized [13, 65]. Once formed in the cytoplasmic side of the ER, the GlcN-PI GPI-precursor migrates to the luminal side for the addition of the mannose residues. GPI-anchored proteins are crucial for the parasite infectivity, virulence and survival. GPIs are also significant pro-inflammatory endotoxins of P. falciparum that, over their release after RBC rupture, induce cytokine and adhesin expression in macrophages and the vascular endothelium that correlates with severe malaria [22, 66, 67].
UDP-galactose
The incorporation of galactose into glycoproteins and glycolipids in eukaryotic cells is through the activated sugar precursor UDP-galactose (UDP-Gal). UDP-Gal was recently identified in the blood stages of the P. falciparum life cycle [15]. A candidate gene for a UDP-glucose 4-epimerase (EC 5.1.3.2) activity that produces UDP-Gal via the epimerization of UDP-glucose has yet to be identified (Table 1) [13]. Therefore, the production of this sugar nucleotide can be performed via activation of galactose 1 phosphate (Gal1P) by Gal1P uridylyltransferase (EC 2.7.7.12) which has also not been identified in the parasite’s genome. Other possibilities are enzymes with a UTP-glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase activity (UGP, EC 2.7.7.9) presenting also a weak galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase activity (EC 2.7.7.10), as occurs in mammals; or a broad substrate range UDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase (USP, EC 2.7.7.64) as described in plants and Leishmania major [68–71]. However, although galactose competes for PfHT1 hexose permease [72, 73], there is not a clear galactokinase (EC 2.7.1.6) candidate in the parasite genome. Furthermore, the biological relevance of the UDP-Gal pool is unknown (Fig. 1), and the presence of UDP-Gal and galactose-containing glycoconjugates (either glycolipids and/or glycoproteins) in the parasite remains a controversial issue.
The first evidences of the presence of galactosylated glycoconjugates in P. falciparum were reported by Ramasamy and Reese when they showed the reduction of the antigenicity of certain parasite proteins from infected red blood cells after a galactosidase treatment [74, 75]. Furthermore, it was observed that titers of anti-α-gal Abs were significantly elevated in sera collected from subjects living in malaria endemic areas or patients with acute P. falciparum malaria in Asia [76]. Maréchal et al. described the incorporation of radiolabelled UDP-Gal by late blood-stage P. falciparum lysates [77]. They also explored the presence of galactose-containing glycolipids in the apicoplast membranes, a common trait in plastids from plants and algae [78]. However, a recent lipidomic analysis of the parasite’s organelle confirmed the absence of galactoglycerolipids in P. falciparum apicoplast [79]. Ramasamy and Field also demonstrated that terminal α-galactosylation was minimal in P. falciparum late asexual blood stages, judging by α-galactose-specific lectin binding and UDP-[3H]Gal incorporation [80]. Nevertheless, recently Yilmaz et al. provided further evidences of the presence of α-galactose on the surface of P. falciparum sporozoites, based on α-galactose-binding Bandeiraea (Griffonia) simplicifolia-I isolectin IB4 labelling of sporozoite surfaces. Interestingly, they also demonstrated the protective effect against malaria associated to anti-α-galactose antibodies [19]. Thus, the UDP-galactose pool identified in the blood-stages of the parasite may possibly also be present in other life-stages and contribute to the biosynthesis of the proposed novel galactose-containing glycoconjugates [15]. This would also suggest the existence of at least one unidentified α-galactosyltransferase in the parasite genome.
UDP-glucose
In eukaryotes UDP-glucose (UDP-Glc) is synthetized through an isomerization between glucose-6-phosphate (Glc6P) and glucose-1-phosphate (Glc1P) catalyzed by a phosphoglucomutase (PGM; EC 5.4.2.2). Glc1P is further activated to the sugar nucleotide generally by UTP-glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase (UGP; EC 2.7.7.9) (Fig. 1). A homolog of PGM is present and expressed in the genome of P. falciparum, whereas the activation of Glc1P to UDP-Glc remains unknown as two enzymatic activities might be involved (see above): a UGP (EC 2.7.7.9), as in mammals [81] or a USP (EC 2.7.7.64), as in plants and L. major (Table 1) [15, 69, 82]. UDP-Glc levels in P. falciparum are relatively abundant in comparison to other sugar nucleotide pools identified on the blood stages [15]. The first evidences of UDP-Glc usage date back to 1994 when its incorporation/usage was detected in P. falciparum extracts [41].
A potential fate for UDP-Glc is the N-glycan-dependent quality control (QC) mechanism of glycoprotein folding. The mechanism consists of a UDP-Glc:glycoprotein glycosyltransferase (UGGT) and a Dol-P-Glc synthase, responsible for the biosynthesis of Dol-P-Glc precursors. UGGT normally glucosylates N-glycans of misfolded proteins in the ER in order to be recognized by the calreticulin/calnexin refolding system [83–87]. However, the N-glycan precursors synthetized by P. falciparum are constituted only by one or two GlcNAc residues missing the mannose residue that acts as UGGT acceptor. The parasite also lacks homologs for the components involved in this QC system [7, 88]. Another possible outcome for UDP-Glc may be the O-glucosylation of specific protein domains, such as epidermal growth factor (EGF) repeats [89] and/or the glucose substitution of O-fucose residues in TSR domains [90]. Interestingly, the crystal structures of HEK293T expressed recombinant CS and TRAP proteins shows both fucose and hexose residues attached to their TSR-domains [17, 18]. In any case, there are no clear candidates for glucosyltransferases in the parasite genome.
The UDP-Glc pool may also be related to the synthesis of glucose containing lipids. Glycolipids, as components of cellular membranes, play important roles in cell–cell contacts, membrane integrity and intracellular signaling [91–93]. In P. falciparum, glucose-containing lipids have been detected and an active glucosylceramide synthase activity (GCS; EC 2.4.1.80) has been identified in the parasite. This enzymatic activity adds glucose residues to dihydroceramide acceptors and is dependent on UDP-Glc [91, 94].
Concluding remarks
There are still many challenges for the community to tackle when studying the glycobiology of P. falciparum. Glycosylation has always been a controversial issue in this parasite due to several reasons such as difficulties concerning the isolation and culturing of parasites; complications due to the interconnected nature of P. falciparum and its mammalian host cell membranes and structures; technical limitations of metabolic tracing through classical methodologies; and the lack of appropriate tools for genetic manipulation and culture methods standardization [9]. It seems clear that, besides GPI-anchors proteins, there is a limited scope for other types of glycosylation processes in P. falciparum, as compared to other protozoan parasites such as Trypanosoma spp. and Leishmania spp., at least during the intracellular blood stages of the parasite. This may be due to the limited resources for P. falciparum within the relative biochemically inert red blood cell, including why there is a lack of sialyltransferase activities. Nonetheless, striking new pieces of evidence are emerging regarding overlooked glycosylation reactions that might be important for the parasite’s survival, infectivity and antigenicity. Furthermore, there is an obvious lack of knowledge about the presence and nature of parasite glycosylations during its extracellular stages.
Authors’ contributions
MC, LI and TKS conceived the review and all authors (MC, JR, LI and TKS) contributed to the writing of this review. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
Research in LI laboratory is supported by Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (SAF2010-21069 and SAF2013-43656-R) and National Institutes of Health (1R21AI115063-01) grants. TKS thanks previous funding from the Wellcome Trust (093228), SUSLA and BBSRC, and current funding from MRC (MR/M020118/1) and European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme under grant agreement No. 602773 (Project KINDRED). MC, JAR and LI are members of the GlycoPar-EU consortium (FP7 funded Marie Curie Initial Training Network), Grant Agreement Number GA. 608295.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Contributor Information
Marta Cova, Email: marta.cova@isglobal.org.
João A. Rodrigues, Email: j.rodrigues@medicina.ulisboa.pt
Terry K. Smith, Email: tks1@st-andrews.ac.uk
Luis Izquierdo, Email: luis.izquierdo@isglobal.org.
References
- 1.Guha-Niyogi A, Sullivan DR, Turco SJ. Glycoconjugate structures of parasitic protozoa. Glycobiology. 2001;11:45R–59R. doi: 10.1093/glycob/11.4.45R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gowda DC, Gupta P, Davidson EA. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchors represent the major carbohydrate modification in proteins of intraerythrocytic stage Plasmodium falciparum. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:6428–6439. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.10.6428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Naik RS, Branch OH, Woods AS, Vijaykumar M, Perkins DJ, Nahlen BL, et al. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchors of Plasmodium falciparum: molecular characterization and naturally elicited antibody response that may provide immunity to malaria pathogenesis. J Exp Med. 2000;192:1563–1576. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.11.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ferguson MA. The structure, biosynthesis and functions of glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchors, and the contributions of trypanosome research. J Cell Sci. 1999;112(Pt 1):2799–2809. doi: 10.1242/jcs.112.17.2799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Smith TK, Gerold P, Crossman A, Paterson MJ, Borissow CN, Brimacombe JS, et al. Substrate specificity of the Plasmodium falciparum glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthetic pathway and inhibition by species-specific suicide substrates. Biochemistry. 2002;41:12395–12406. doi: 10.1021/bi020351l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bushkin GG, Ratner DM, Cui J, Banerjee S, Duraisingh MT, Jennings CV, et al. Suggestive evidence for Darwinian selection against asparagine-linked glycans of Plasmodium falciparum and Toxoplasma gondii. Eukaryot Cell. 2010;9:228–241. doi: 10.1128/EC.00197-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Samuelson J, Banerjee S, Magnelli P, Cui J, Kelleher DJ, Gilmore R, et al. The diversity of dolichol-linked precursors to Asn-linked glycans likely results from secondary loss of sets of glycosyltransferases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:1548–1553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409460102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.de Macedo CS, Schwarz RT, Todeschini AR, Previato JO, Mendonça-Previato L. Overlooked post-translational modifications of proteins in Plasmodium falciparum: N- and O-glycosylation—a review. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2010;105:949–956. doi: 10.1590/S0074-02762010000800001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Von Itzstein M, Plebanski M, Cooke BM, Coppel RL. Hot, sweet and sticky: the glycobiology of Plasmodium falciparum. Trends Parasitol. 2008;24:210–218. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2008.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Olszewski KL, Llinás M. Central carbon metabolism of Plasmodium parasites. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2011;175:95–103. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2010.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kirk K, Horner HA, Kirk J. Glucose uptake in Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes is an equilibrative not an active process. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1996;82:195–205. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(96)02734-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Slavic K, Straschil U, Reininger L, Doerig C, Morin C, Tewari R, et al. Life cycle studies of the hexose transporter of Plasmodium species and genetic validation of their essentiality. Mol Microbiol. 2010;75:1402–1413. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07060.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ginsburg H. Progress in in silico functional genomics: the malaria metabolic pathways database. Trends Parasitol. 2006;22:238–240. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2006.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Aurrecoechea C, Brestelli J, Brunk BP, Dommer J, Fischer S, Gajria B, et al. PlasmoDB: a functional genomic database for malaria parasites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(Database issue):D539–43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Sanz S, Bandini G, Ospina D, Bernabeu M, Mariño K, Fernández-Becerra C, et al. Biosynthesis of GDP-fucose and other sugar nucleotides in the blood stages of Plasmodium falciparum. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:16506–16517. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.439828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dieckmann-Schuppert A, Bender S, Odenthal-Schnittler M, Bause E, Schwarz RT. Apparent lack of N-glycosylation in the asexual intraerythrocytic stage of Plasmodium falciparum. Eur J Biochem. 1992;205:815–825. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Doud MB, Koksal AC, Mi L-Z, Song G, Lu C, Springer TA. Unexpected fold in the circumsporozoite protein target of malaria vaccines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:7817–7822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1205737109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Song G, Koksal AC, Lu C, Springer TA. Shape change in the receptor for gliding motility in Plasmodium sporozoites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:21420–21425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218581109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yilmaz B, Portugal S, Tran TM, Gozzelino R, Ramos S, Gomes J, et al. Gut microbiota elicits a protective immune response against malaria transmission. Cell. 2014;159:1277–1289. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.10.053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gerold P, Dieckmann-Schuppert A, Schwarz RT. Glycosylphosphatidylinositols synthesized by asexual erythrocytic stages of the malarial parasite, Plasmodium falciparum. Candidates for plasmodial glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchor precursors and pathogenicity factors. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:2597–2606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Schmidt A, Schwarz RT, Gerold P. Plasmodium falciparum: asexual erythrocytic stages synthesize two structurally distinct free and protein-bound glycosylphosphatidylinositols in a maturation-dependent manner. Exp Parasitol. 1998;88:95–102. doi: 10.1006/expr.1998.4241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schofield L, Hewitt MC, Evans K, Siomos M-A, Seeberger PH. Synthetic GPI as a candidate anti-toxic vaccine in a model of malaria. Nature. 2002;418:785–789. doi: 10.1038/nature00937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Schofield L, Novakovic S, Gerold P, Schwarz RT, McConville MJ, Tachado SD. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol toxin of Plasmodium up-regulates intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, and E-selectin expression in vascular endothelial cells and increases leukocyte and parasite cytoadherence via tyrosine kinase-dependent signal transduction. J Immunol. 1996;156:1886–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tachado SD, Gerold P, McConville MJ, Baldwin T, Quilici D, Schwarz RT, et al. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol toxin of Plasmodium induces nitric oxide synthase expression in macrophages and vascular endothelial cells by a protein tyrosine kinase-dependent and protein kinase C-dependent signaling pathway. J Immunol. 1996;156:1897–1907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.McConville MJ, Ferguson MA. The structure, biosynthesis and function of glycosylated phosphatidylinositols in the parasitic protozoa and higher eukaryotes. Biochem J. 1993;294:305–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2940305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shams-Eldin H, de Macedo CS, Niehus S, Dorn C, Kimmel J, Azzouz N, et al. Plasmodium falciparum dolichol phosphate mannose synthase represents a novel clade. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;370:388–393. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.03.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Delorenzi M, Sexton A, Shams-Eldin H, Schwarz RT, Speed T, Schofield L. Genes for glycosylphosphatidylinositol toxin biosynthesis in Plasmodium falciparum. Infect Immun. 2002;70:4510–4522. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4510-4522.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Aurrecoechea C, Barreto A, Brestelli J, Brunk BP, Cade S, Doherty R, et al. EuPathDB: the eukaryotic pathogen database. Nucleic Acids Res 2013, 41(Database issue):D684–91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 29.Cortes LK, Scarcelli JJ, Taron CH. Complementation of essential yeast GPI mannosyltransferase mutations suggests a novel specificity for certain Trypanosoma and Plasmodium PigB proteins. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e87673. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gilson PR, Nebl T, Vukcevic D, Moritz RL, Sargeant T, Speed TP, et al. Identification and stoichiometry of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane proteins of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2006;5:1286–1299. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M600035-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang Q, Fujioka H, Nussenzweig V. Mutational analysis of the GPI-anchor addition sequence from the circumsporozoite protein of Plasmodium. Cell Microbiol. 2005;7:1616–1626. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00579.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Van Dijk MR, Janse CJ, Thompson J, Waters AP, Braks JA, Dodemont HJ, et al. A central role for P48/45 in malaria parasite male gamete fertility. Cell. 2001;104:153–164. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00199-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sanders PR, Kats LM, Drew DR, O’Donnell RA, O’Neill M, Maier AG, et al. A set of glycosylphosphatidyl inositol-anchored membrane proteins of Plasmodium falciparum is refractory to genetic deletion. Infect Immun. 2006;74:4330–4338. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00054-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Doucey MA, Hess D, Cacan R, Hofsteenge J. Protein C-mannosylation is enzyme-catalysed and uses dolichyl-phosphate-mannose as a precursor. Mol Biol Cell. 1998;9:291–300. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.2.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hofsteenge J, Huwiler KG, Macek B, Hess D, Lawler J, Mosher DF, et al. C-mannosylation and O-fucosylation of the thrombospondin type 1 module. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:6485–6498. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008073200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tucker RP. The thrombospondin type 1 repeat superfamily. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36:969–974. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2003.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Morahan BJ, Wang L, Coppel RL. No TRAP, no invasion. Trends Parasitol. 2009;25:77–84. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2008.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Buettner FFR, Ashikov A, Tiemann B, Lehle L, Bakker HC. Elegans DPY-19 is a C-mannosyltransferase glycosylating thrombospondin repeats. Mol Cell. 2013;50:295–302. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Turnock DC, Ferguson MAJ. Sugar nucleotide pools of Trypanosoma brucei, Trypanosoma cruzi, and Leishmania major. Eukaryot Cell. 2007;6:1450–1463. doi: 10.1128/EC.00175-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Becker DJ, Lowe JB. Fucose: biosynthesis and biological function in mammals. Glycobiology. 2003;13:41R–53R. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwg054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Dieckmann-Schuppert A, Bause E, Schwarz RT. Glycosylation reactions in Plasmodium falciparum, Toxoplasma gondii, and Trypanosoma brucei brucei probed by the use of synthetic peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1199:37–44. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(94)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Luo Y, Koles K, Vorndam W, Haltiwanger RS, Panin VM. Protein O-fucosyltransferase 2 adds O-fucose to thrombospondin type 1 repeats. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:9393–9399. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511975200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sultan AA, Thathy V, Frevert U, Robson KJ, Crisanti A, Nussenzweig V, et al. TRAP is necessary for gliding motility and infectivity of Plasmodium sporozoites. Cell. 1997;90:511–522. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80511-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Uchime O, Herrera R, Reiter K, Kotova S, Shimp RL, Miura K, et al. Analysis of the conformation and function of the Plasmodium falciparum merozoite proteins MTRAP and PTRAMP. Eukaryot Cell. 2012;11:615–625. doi: 10.1128/EC.00039-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Agnandji ST, Lell B, Soulanoudjingar SS, Fernandes JF, Abossolo BP, Conzelmann C, et al. First results of phase 3 trial of RTS, S/AS01 malaria vaccine in African children. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1863–1875. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1102287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lindner SE, Swearingen KE, Harupa A, Vaughan AM, Sinnis P, Moritz RL, et al. Total and putative surface proteomics of malaria parasite salivary gland sporozoites. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013;12:1127–1143. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M112.024505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Naderer T, Heng J, McConville MJ. Evidence that intracellular stages of Leishmania major utilize amino sugars as a major carbon source. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6:e1001245. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Stokes MJ, Güther MLS, Turnock DC, Prescott AR, Martin KL, Alphey MS, et al. The synthesis of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine is essential for bloodstream form Trypanosoma brucei in vitro and in vivo and UDP-N-acetylglucosamine starvation reveals a hierarchy in parasite protein glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:16147–16161. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709581200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Mariño K, Güther MLS, Wernimont AK, Qiu W, Hui R, Ferguson MAJ. Characterization, localization, essentiality, and high-resolution crystal structure of glucosamine 6-phosphate N-acetyltransferase from Trypanosoma brucei. Eukaryot Cell. 2011;10:985–997. doi: 10.1128/EC.05025-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Mio T, Yamada-Okabe T, Arisawa M, Yamada-Okabe H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae GNA1, an essential gene encoding a novel acetyltransferase involved in UDP-N-acetylglucosamine synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:424–429. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.1.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Gerold P, Jung N, Azzouz N, Freiberg N, Kobe S, Schwarz RT. Biosynthesis of glycosylphosphatidylinositols of Plasmodium falciparum in a cell-free incubation system: inositol acylation is needed for mannosylation of glycosylphosphatidylinositols. Biochem J. 1999;344:731–738. doi: 10.1042/bj3440731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kimura EA, Couto AS, Peres VJ, Casal OL, Katzin AM. N-linked glycoproteins are related to schizogony of the intraerythrocytic stage in Plasmodium falciparum. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:14452–14461. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.24.14452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kornfeld R, Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Gao X-D, Tachikawa H, Sato T, Jigami Y, Dean N. Alg14 recruits Alg13 to the cytoplasmic face of the endoplasmic reticulum to form a novel bipartite UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transferase required for the second step of N-linked glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:36254–36262. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M507569200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Lu J, Takahashi T, Ohoka A, Nakajima K, Hashimoto R, Miura N, et al. Alg14 organizes the formation of a multiglycosyltransferase complex involved in initiation of lipid-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis. Glycobiology. 2012;22:504–516. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwr162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Gao X-D, Moriyama S, Miura N, Dean N, Nishimura S-I. Interaction between the C termini of Alg13 and Alg14 mediates formation of the active UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transferase complex. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:32534–32541. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804060200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Silberstein S, Gilmore R. Biochemistry, molecular biology, and genetics of the oligosaccharyltransferase. FASEB J. 1996;10:849–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Yan Q, Lennarz WJ. Studies on the function of oligosaccharyl transferase subunits. Stt3p is directly involved in the glycosylation process. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:47692–47700. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208136200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Naik RS, Venkatesan M, Gowda DC. Plasmodium falciparum: the lethal effects of tunicamycin and mevastatin on the parasite are not mediated by the inhibition of N-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis. Exp Parasitol. 2001;98:110–114. doi: 10.1006/expr.2001.4616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Dieckmann-Schuppert A, Hensel J, Schwarz RT. Studies on the effect of tunicamycin on erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992;20:184S. doi: 10.1042/bst020184s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Watanabe R, Inoue N, Westfall B, Taron CH, Orlean P, Takeda J, et al. The first step of glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis is mediated by a complex of PIG-A, PIG-H, PIG-C and GPI1. EMBO J. 1998;17:877–885. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.4.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Miyata T, Takeda J, Iida Y, Yamada N, Inoue N, Takahashi M, et al. The cloning of PIG-A, a component in the early step of GPI-anchor biosynthesis. Science. 1993;259:1318–1320. doi: 10.1126/science.7680492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Inoue N, Watanabe R, Takeda J, Kinoshita T. PIG-C, one of the three human genes involved in the first step of glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis is a homologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae GPI2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;226:193–199. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Hong Y, Ohishi K, Watanabe R, Endo Y, Maeda Y, Kinoshita T. GPI1 stabilizes an enzyme essential in the first step of glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:18582–18588. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.26.18582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Watanabe R, Ohishi K, Maeda Y, Nakamura N, Kinoshita T. Mammalian PIG-L and its yeast homologue Gpi12p are N-acetylglucosaminylphosphatidylinositol de-N-acetylases essential in glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1999;339:185–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Arrighi RBG, Faye I. Plasmodium falciparum GPI toxin: a common foe for man and mosquito. Acta Trop. 2010;114:162–165. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2009.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Clark IA, Cowden WB. The pathophysiology of falciparum malaria. Pharmacol Ther. 2003;99:221–260. doi: 10.1016/S0163-7258(03)00060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Kleczkowski LA, Decker D, Wilczynska M. UDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase: a new old mechanism for sugar activation. Plant Physiol. 2011;156:3–10. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.174706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Damerow S, Lamerz A-C, Haselhorst T, Führing J, Zarnovican P, von Itzstein M, et al. Leishmania UDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase: the missing link in galactose salvage? J Biol Chem. 2010;285:878–887. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.067223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Coleman HD, Ellis DD, Gilbert M, Mansfield SD. Up-regulation of sucrose synthase and UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase impacts plant growth and metabolism. Plant Biotechnol J. 2006;4:87–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2005.00160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Dickmanns A, Damerow S, Neumann P, Schulz E-C, Lamerz A-C, Routier FH, et al. Structural basis for the broad substrate range of the UDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase from Leishmania major. J Mol Biol. 2011;405:461–478. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.10.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Woodrow CJ, Burchmore RJ, Krishna S. Hexose permeation pathways in Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:9931–9936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.170153097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Landfear SM. Glucose transporters in parasitic protozoa. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;637:245–262. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-700-6_13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ramasamy R, Reese RT. Terminal galactose residues and the antigenicity of Plasmodium falciparum glycoproteins. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986;19:91–101. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Ramasamy R, Reese RT. A role for carbohydrate moieties in the immune response to malaria. J Immunol. 1985;134:1952–1955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Ravindran B, Satapathy AK, Das MK. Naturally-occurring anti-alpha-galactosyl antibodies in human Plasmodium falciparum infections–a possible role for autoantibodies in malaria. Immunol Lett. 1988;19:137–141. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(88)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Maréchal E, Azzouz N, de Macedo CS, Block MA, Feagin JE, Schwarz RT, et al. Synthesis of chloroplast galactolipids in apicomplexan parasites. Eukaryot Cell. 2002;1:653–656. doi: 10.1128/EC.1.4.653-656.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Douce R. Site of biosynthesis of galactolipids in spinach chloroplasts. Science. 1974;183:852–853. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4127.852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Botté CY, Yamaryo-Botté Y, Rupasinghe TWT, Mullin KA, MacRae JI, Spurck TP, et al. Atypical lipid composition in the purified relict plastid (apicoplast) of malaria parasites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:7506–7511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301251110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Ramasamy R, Field MC. Terminal galactosylation of glycoconjugates in Plasmodium falciparum asexual blood stages and Trypanosoma brucei bloodstream trypomastigotes. Exp Parasitol. 2012;130:314–320. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2012.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Peng HL, Chang HY. Cloning of a human liver UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase cDNA by complementation of the bacterial galU mutation. FEBS Lett. 1993;329:153–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80213-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Litterer LA, Schnurr JA, Plaisance KL, Storey KK, Gronwald JW, Somers DA. Characterization and expression of Arabidopsis UDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2006;44:171–180. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2006.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Helenius A, Aebi M. Roles of N-linked glycans in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:1019–1049. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.073752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Moremen KW, Molinari M. N-linked glycan recognition and processing: the molecular basis of endoplasmic reticulum quality control. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006;16:592–599. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2006.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Schrag JD, Bergeron JJ, Li Y, Borisova S, Hahn M, Thomas DY, et al. The Structure of calnexin, an ER chaperone involved in quality control of protein folding. Mol Cell. 2001;8:633–644. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00318-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Trombetta ES, Parodi AJ. Quality control and protein folding in the secretory pathway. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2003;19:649–676. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.19.110701.153949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Izquierdo L, Atrih A, Rodrigues JA, Jones DC, Ferguson MAJ. Trypanosoma brucei UDP-glucose:glycoprotein glucosyltransferase has unusual substrate specificity and protects the parasite from stress. Eukaryot Cell. 2009;8:230–240. doi: 10.1128/EC.00361-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Banerjee S, Vishwanath P, Cui J, Kelleher DJ, Gilmore R, Robbins PW, et al. The evolution of N-glycan-dependent endoplasmic reticulum quality control factors for glycoprotein folding and degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:11676–11681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704862104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Takeuchi H, Kantharia J, Sethi MK, Bakker H, Haltiwanger RS. Site-specific O-glucosylation of the epidermal growth factor-like (EGF) repeats of notch: efficiency of glycosylation is affected by proper folding and amino acid sequence of individual EGF repeats. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:33934–33944. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.401315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Kozma K, Keusch JJ, Hegemann B, Luther KB, Klein D, Hess D, et al. Identification and characterization of abeta1,3-glucosyltransferase that synthesizes the Glc-beta1,3-Fuc disaccharide on thrombospondin type 1 repeats. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:36742–36751. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605912200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Gerold P, Schwarz RT. Biosynthesis of glycosphingolipids de-novo by the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2001;112:29–37. doi: 10.1016/S0166-6851(00)00336-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Merrill AH, Sullards MC, Wang E, Voss KA, Riley RT. Sphingolipid metabolism: roles in signal transduction and disruption by fumonisins. Environ Health Perspect. 2001;109(Suppl 2):283–289. doi: 10.1289/ehp.01109s2283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Simons K, Ikonen E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature. 1997;387:569–572. doi: 10.1038/42408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Couto AS, Caffaro C, Uhrig ML, Kimura E, Peres VJ, Merino EF, et al. Glycosphingolipids in Plasmodium falciparum. Presence of an active glucosylceramide synthase. Eur J Biochem. 2004;271:2204–2214. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


