Abstract
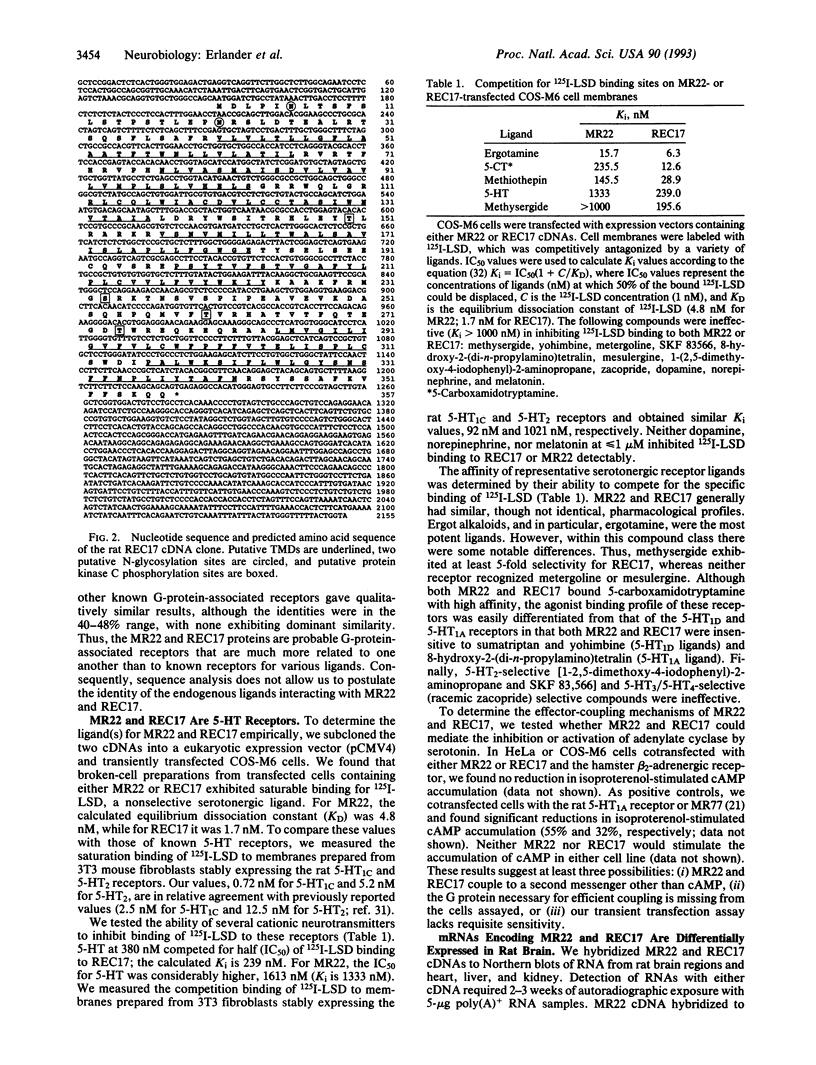
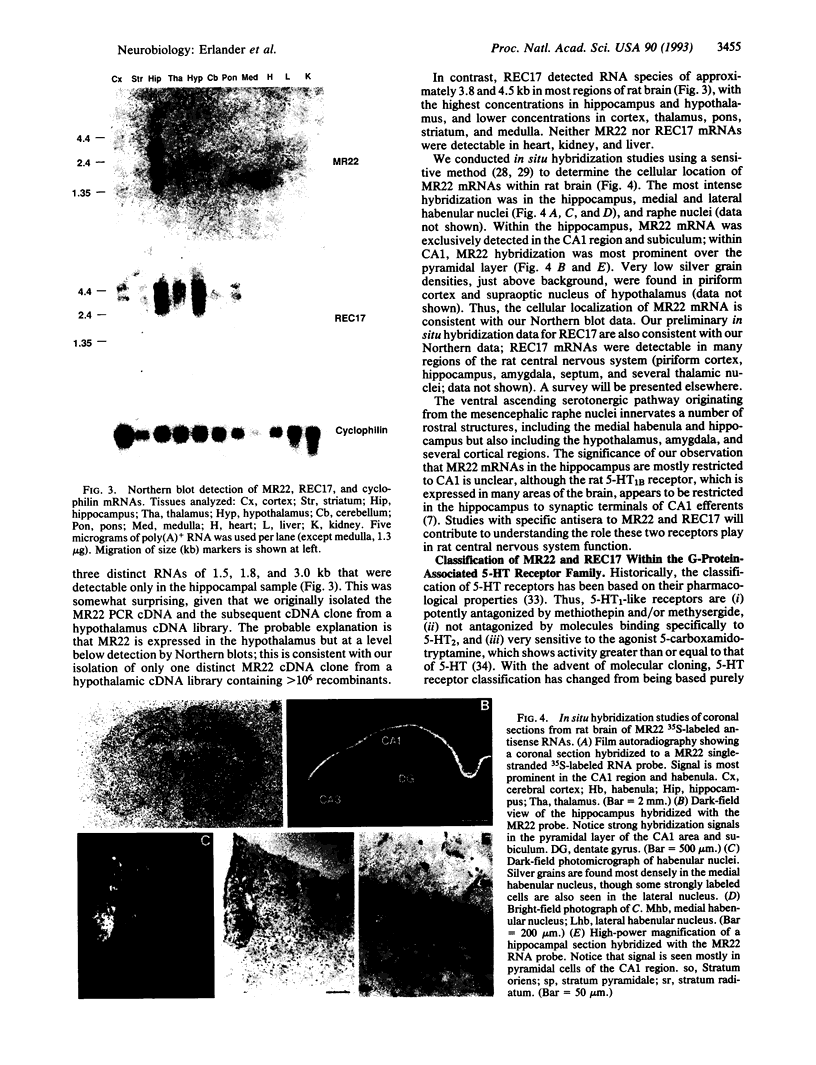
We report two serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) receptors, MR22 and REC17, that belong to the G-protein-associated receptor superfamily. MR22 and REC17 are 371 and 357 amino acids long, respectively, as deduced from nucleotide sequence and share 68% mutual amino acid identity and 30-35% identity with known catecholamine and 5-HT receptors. Saturable binding of 125I-labeled (+)-lysergic acid diethylamide to transiently expressed MR22 in COS-M6 cells was inhibited by ergotamine > methiothepin > 5-carboxamidotryptamine > 5-HT. For REC17, the rank of potency was ergotamine > 5-carboxamidotryptamine > methiothepin > methysergide > 5-HT. Both were insensitive to 5-HT1A, 5-HT1D or 5-HT2 serotonergic ligands [8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin, sumatriptan, and 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane]. The mRNAs encoding MR22 were detected in the CA1 region of hippocampus, the medial habenula, and raphe nuclei. In contrast, mRNAs encoding REC17 were found throughout the rat central nervous system. We propose that REC17 and MR22, designated as 5-HT5 alpha and 5-HT5 beta, represent a distinct subfamily of 5-HT receptors.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adham N., Romanienko P., Hartig P., Weinshank R. L., Branchek T. The rat 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptor is the species homologue of the human 5-hydroxytryptamine1D beta receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;41(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert P. R., Zhou Q. Y., Van Tol H. H., Bunzow J. R., Civelli O. Cloning, functional expression, and mRNA tissue distribution of the rat 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5825–5832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Engel G., Feniuk W., Fozard J. R., Humphrey P. P., Middlemiss D. N., Mylecharane E. J., Richardson B. P., Saxena P. R. Proposals for the classification and nomenclature of functional receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Jun;25(6):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowen P. J. Serotonin receptor subtypes: implications for psychopharmacology. Br J Psychiatry Suppl. 1991 Sep;(12):7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson P. E., Forss-Petter S., Brow M. A., Calavetta L., Douglass J., Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. p1B15: a cDNA clone of the rat mRNA encoding cyclophilin. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):261–267. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foguet M., Hoyer D., Pardo L. A., Parekh A., Kluxen F. W., Kalkman H. O., Stühmer W., Lübbert H. Cloning and functional characterization of the rat stomach fundus serotonin receptor. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3481–3487. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazer A., Maayani S., Wolfe B. B. Subtypes of receptors for serotonin. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:307–348. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall C. M., Isackson P. J. Limbic seizures increase neuronal production of messenger RNA for nerve growth factor. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):758–761. doi: 10.1126/science.2549634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamblin M. W., Metcalf M. A., McGuffin R. W., Karpells S. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a human 5-HT1B serotonin receptor: a homologue of the rat 5-HT1B receptor with 5-HT1D-like pharmacological specificity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 30;184(2):752–759. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90654-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamblin M. W., Metcalf M. A. Primary structure and functional characterization of a human 5-HT1D-type serotonin receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;40(2):143–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartig P. R. Molecular biology of 5-HT receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Feb;10(2):64–69. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin H., Oksenberg D., Ashkenazi A., Peroutka S. J., Duncan A. M., Rozmahel R., Yang Y., Mengod G., Palacios J. M., O'Dowd B. F. Characterization of the human 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5735–5738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., MacDermott A. B., Axel R., Jessell T. M. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA encoding the serotonin 1c receptor. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):558–564. doi: 10.1126/science.3399891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Dixon R. A., Frielle T., Dohlman H. G., Bolanowski M. A., Sigal I. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. cDNA for the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor: a protein with multiple membrane-spanning domains and encoded by a gene whose chromosomal location is shared with that of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):46–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Frielle T., Collins S., Yang-Feng T., Kobilka T. S., Francke U., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. An intronless gene encoding a potential member of the family of receptors coupled to guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):75–79. doi: 10.1038/329075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy F. O., Gudermann T., Perez-Reyes E., Birnbaumer M., Kaumann A. J., Birnbaumer L. Molecular cloning of a human serotonin receptor (S12) with a pharmacological profile resembling that of the 5-HT1D subtype. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7553–7562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert F., Parmentier M., Lefort A., Dinsart C., Van Sande J., Maenhaut C., Simons M. J., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Selective amplification and cloning of four new members of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):569–572. doi: 10.1126/science.2541503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovenberg T. W., Erlander M. G., Baron B. M., Racke M., Slone A. L., Siegel B. W., Craft C. M., Burns J. E., Danielson P. E., Sutcliffe J. G. Molecular cloning and functional expression of 5-HT1E-like rat and human 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2184–2188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucki I. 5-HT1 receptors and behavior. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1992 Spring;16(1):83–93. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(05)80055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbert H., Hoffman B. J., Snutch T. P., van Dyke T., Levine A. J., Hartig P. R., Lester H. A., Davidson N. cDNA cloning of a serotonin 5-HT1C receptor by electrophysiological assays of mRNA-injected Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4332–4336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maricq A. V., Peterson A. S., Brake A. J., Myers R. M., Julius D. Primary structure and functional expression of the 5HT3 receptor, a serotonin-gated ion channel. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.1718042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroteaux L., Saudou F., Amlaiky N., Boschert U., Plassat J. L., Hen R. Mouse 5HT1B serotonin receptor: cloning, functional expression, and localization in motor control centers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3020–3024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister G., Charlesworth A., Snodin C., Beer M. S., Noble A. J., Middlemiss D. N., Iversen L. L., Whiting P. Molecular cloning of a serotonin receptor from human brain (5HT1E): a fifth 5HT1-like subtype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5517–5521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlemiss D. N., Tricklebank M. D. Centrally active 5-HT receptor agonists and antagonists. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1992 Spring;16(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(05)80054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J. Phylogenetic tree analysis of G protein-coupled 5-HT receptors: implications for receptor nomenclature. Neuropharmacology. 1992 Jul;31(7):609–613. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(92)90138-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plassat J. L., Boschert U., Amlaiky N., Hen R. The mouse 5HT5 receptor reveals a remarkable heterogeneity within the 5HT1D receptor family. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4779–4786. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05583.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett D. B., Bach A. W., Wozny M., Taleb O., Dal Toso R., Shih J. C., Seeburg P. H. Structure and functional expression of cloned rat serotonin 5HT-2 receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4135–4140. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03308.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Dixon R. A. Structural basis of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J. 1989 May;3(7):1825–1832. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.7.2541037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt M. M., Laurie D. J., Seeburg P. H., Bach A. Molecular cloning and characterization of a rat brain cDNA encoding a 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4017–4023. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04977.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshank R. L., Zgombick J. M., Macchi M. J., Branchek T. A., Hartig P. R. Human serotonin 1D receptor is encoded by a subfamily of two distinct genes: 5-HT1D alpha and 5-HT1D beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3630–3634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zgombick J. M., Weinshank R. L., Macchi M., Schechter L. E., Branchek T. A., Hartig P. R. Expression and pharmacological characterization of a canine 5-hydroxytryptamine1D receptor subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):1036–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]