Abstract
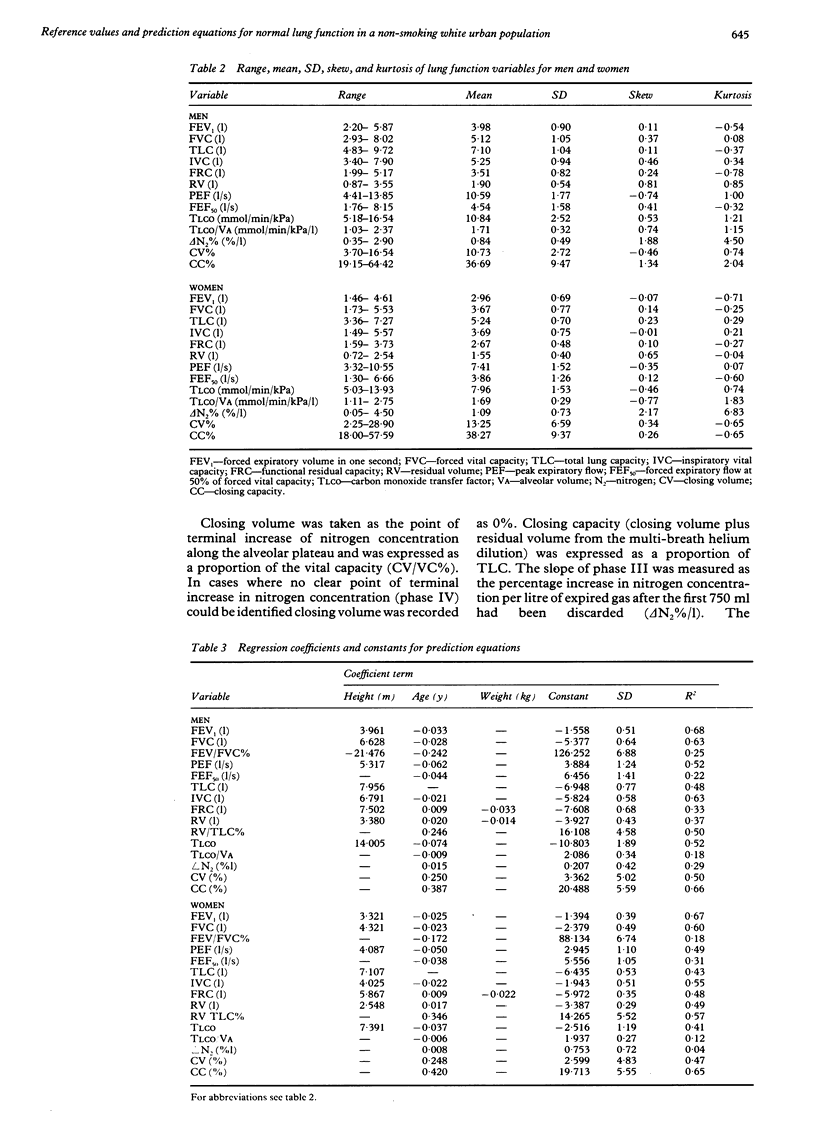
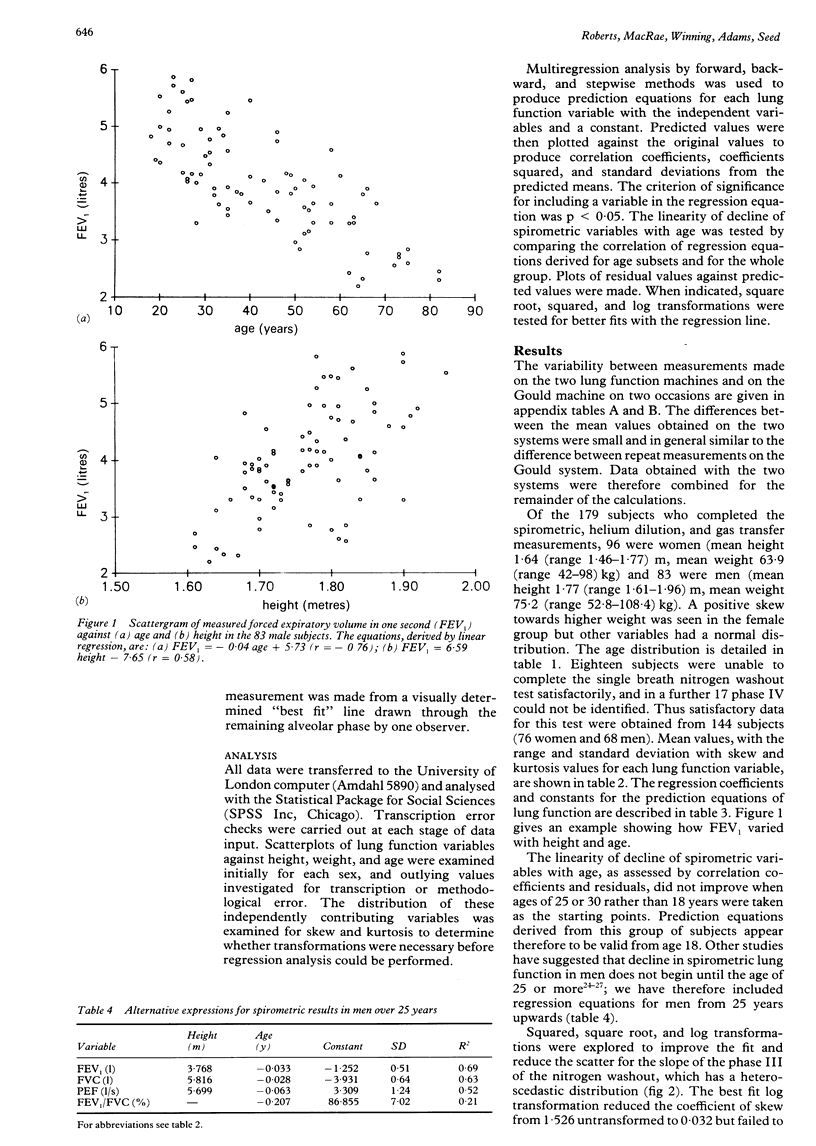
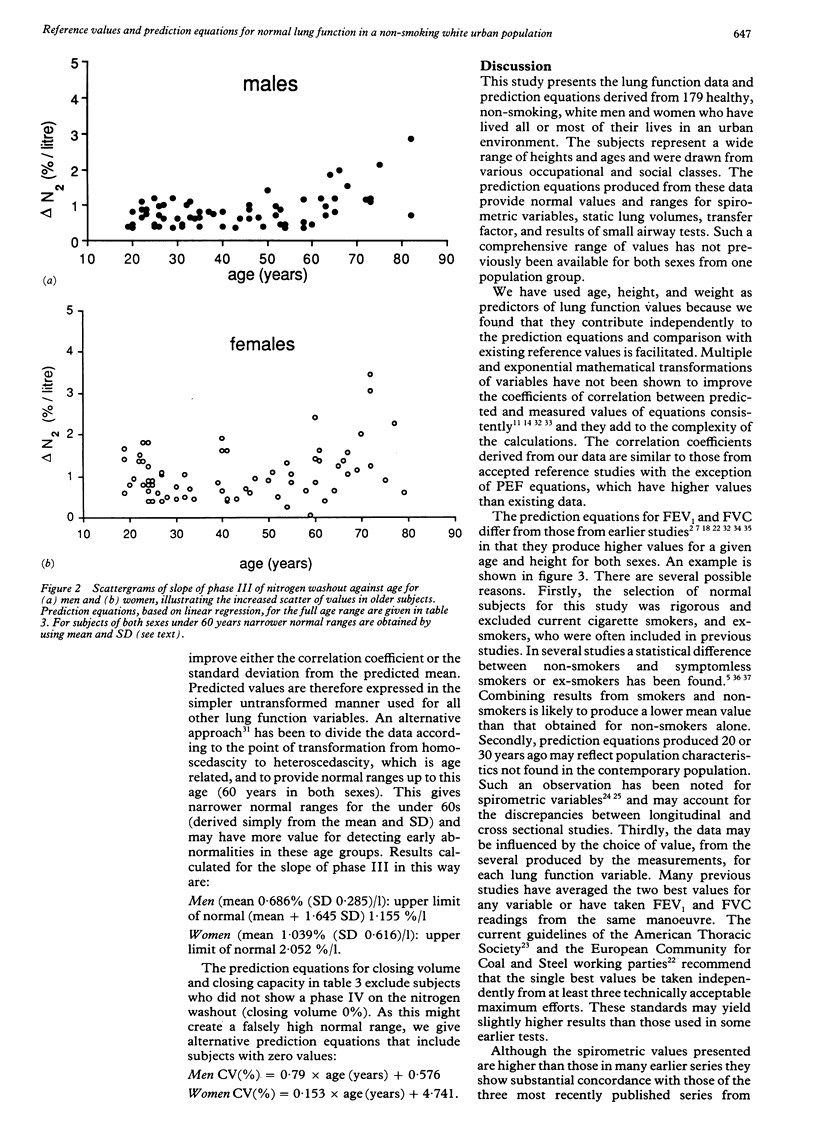
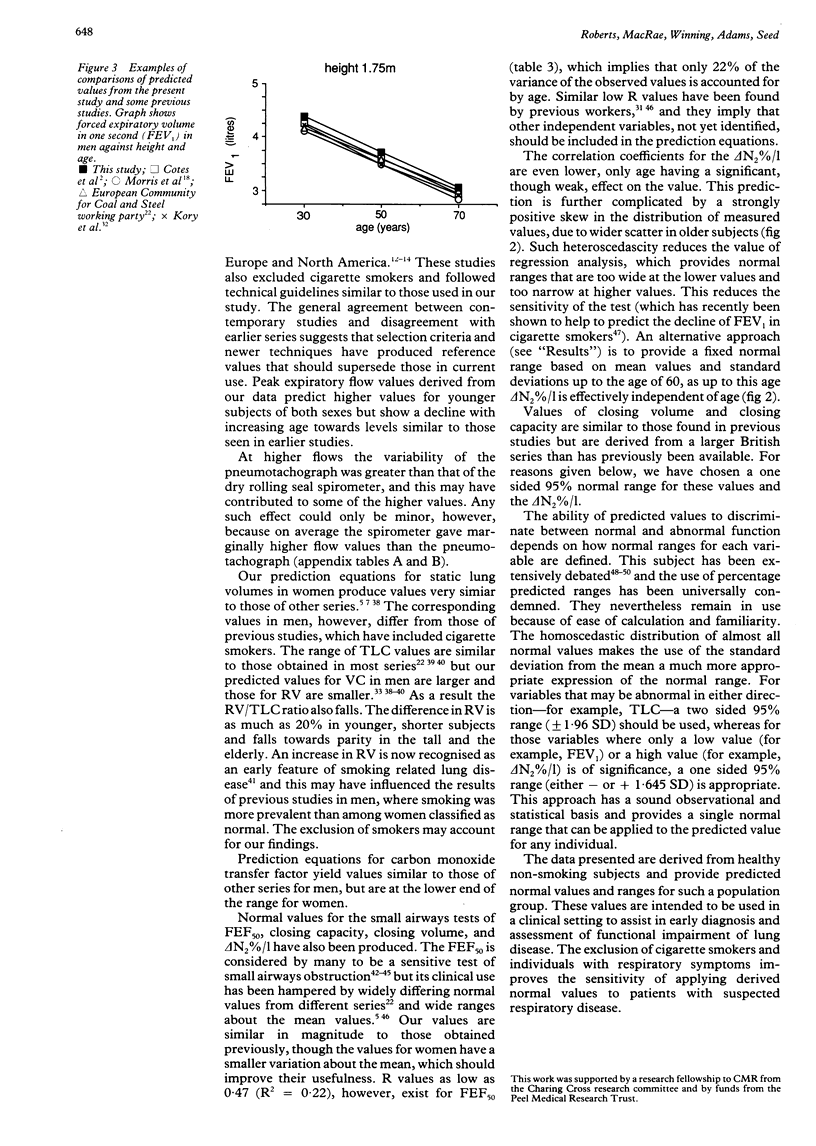
Prediction equations for normal lung function have been derived from tests on 179 healthy, non-smoking, white urban dwellers. The subjects, 96 women (height 1.46-1.77 m) and 83 men (height 1.61-1.96 m) aged 18-86 years, underwent measurements of spirometric flow and volume, multi-breath helium dilution lung volumes, and single breath carbon monoxide transfer factor and the single breath nitrogen washout test. Regression analysis using height, age, and weight as independent variables was used to provide predicted values for both sexes. Correlation coefficients were similar to those found in previous studies but normal ranges for spirometic measurements were narrower than in many previous studies, and spirometric flow and volume measurements were higher than those obtained in studies that included cigarette smokers, reflecting our more stringent criteria for selecting subjects and the newer standardised technical methods adopted. Multi-breath helium dilution values for total lung capacity were similar to those found in previous studies but the inspiratory vital capacity was larger and the residual volume reduced. Values for carbon monoxide transfer factor and the single breath nitrogen washout did not differ significantly from existing values. A complete set of lung function reference values and prediction equations for both sexes has been derived from a single population. The exclusion of cigarette smokers and subjects with respiratory symptoms has produced values that should have a greater sensitivity in the detection of mild lung disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams L., Lonsdale D., Robinson M., Rawbone R., Guz A. Respiratory impairment induced by smoking in children in secondary schools. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Mar 24;288(6421):891–895. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6421.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
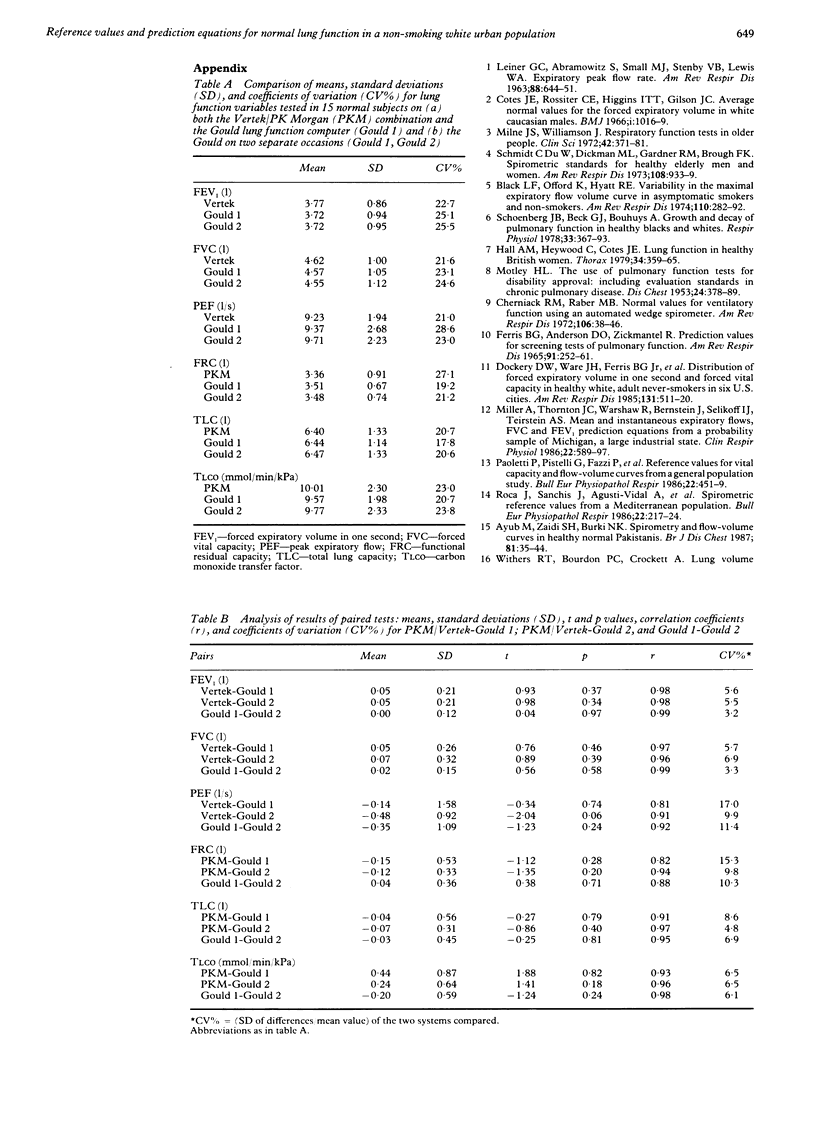
- Ayub M., Zaidi S. H., Burki N. K. Spirometry and flow-volume curves in healthy, normal Pakistanis. Br J Dis Chest. 1987 Jan;81(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(87)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGLUND E., BIRATH G., BJURE J., GRIMBY G., KJELLMER I., SANDQVIST L., SODERHOLM B. Spirometric studies in normal subjects. I. Forced expirograms in subjects between 7 and 70 years of age. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Feb;173:185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACKBURN H., BROZEK J., TAYLOR H. L. Lung volume in smokers and nonsmokers. Ann Intern Med. 1959 Jul;51(1):68–77. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-51-1-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAKEMORE W. S., FORSTER R. E., MORTON J. W., OGILVIE C. M. A standardized breath holding technique for the clinical measurement of the diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jan;36(1 Pt 1):1–17. doi: 10.1172/JCI103402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass H. The flow volume loop: normal standards and abnormalities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chest. 1973 Feb;63(2):171–176. doi: 10.1378/chest.63.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berend N., Woolcock A. J., Marlin G. E. Correlation between the function and structure of the lung in smokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 May;119(5):695–705. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.5.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black L. F., Offord K., Hyatt R. E. Variability in the maximal expiratory flow volume curve in asymptomatic smokers and in nonsmokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Sep;110(3):282–292. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.3.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buist A. S., Ross B. B. Predicted values for closing volumes using a modified single breath nitrogen test. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 May;107(5):744–752. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.107.5.744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buist A. S., Ross B. B. Quantitative analysis of the alveolar plateau in the diagnosis of early airway obstruction. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Nov;108(5):1078–1087. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.5.1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr M. L., Phillips K. M., Hurst D. N. Lung function in the elderly. Thorax. 1985 Jan;40(1):54–59. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows B., Lebowitz M. D., Camilli A. E., Knudson R. J. Longitudinal changes in forced expiratory volume in one second in adults. Methodologic considerations and findings in healthy nonsmokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Jun;133(6):974–980. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.6.974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherniack R. M., Raber M. B. Normal standards for ventilatory function using an automated wedge spirometer. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972 Jul;106(1):38–46. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1972.106.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotes J. E., Rossiter C. E., Higgins I. T., Gilson J. C. Average normal values for the forced expiratory volume in white Caucasian males. Br Med J. 1966 Apr 23;1(5494):1016–1019. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5494.1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo R. O., Morris A. H., Gardner R. M. Reference spirometric values using techniques and equipment that meet ATS recommendations. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jun;123(6):659–664. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.6.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockery D. W., Ware J. H., Ferris B. G., Jr, Glicksberg D. S., Fay M. E., Spiro A., 3rd, Speizer F. E. Distribution of forced expiratory volume in one second and forced vital capacity in healthy, white, adult never-smokers in six U.S. cities. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Apr;131(4):511–520. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.4.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERRIS B. G., Jr, ANDERSON D. O., ZICKMANTEL R. PREDICTION VALUES FOR SCREENING TESTS OF PULMONARY FUNCTION. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Feb;91:252–261. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.91.2.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler R. W., Pluck R. A., Hetzel M. R. Maximal expiratory flow-volume curves in Londoners aged 60 years and over. Thorax. 1987 Mar;42(3):173–182. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.3.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN H. I., BECKLAKE M. R. Respiratory function tests; normal values at median altitudes and the prediction of normal results. Am Rev Tuberc. 1959 Apr;79(4):457–467. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1959.79.4.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glindmeyer H. W., Diem J. E., Jones R. N., Weill H. Noncomparability of longitudinally and cross-sectionally determined annual change in spirometry. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 May;125(5):544–548. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.5.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg I., Nunn A. J. Peak expiratory flow in symptomless elderly smokers and ex-smokers. BMJ. 1989 Apr 22;298(6680):1071–1072. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6680.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. M., Heywood C., Cotes J. E. Lung function in healthy British women. Thorax. 1979 Jun;34(3):359–365. doi: 10.1136/thx.34.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORY R. C., CALLAHAN R., BOREN H. G., SYNER J. C. The Veterans Administration-Army cooperative study of pulmonary function. I. Clinical spirometry in normal men. Am J Med. 1961 Feb;30:243–258. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(61)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson R. J., Lebowitz M. D., Holberg C. J., Burrows B. Changes in the normal maximal expiratory flow-volume curve with growth and aging. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Jun;127(6):725–734. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.6.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson R. J., Slatin R. C., Lebowitz M. D., Burrows B. The maximal expiratory flow-volume curve. Normal standards, variability, and effects of age. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 May;113(5):587–600. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.5.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden E. R., Jr, Linden D. A. A reduction in maximum mid-expiratory flow rate. A spirographic manifestation of small airway disease. Am J Med. 1972 Jun;52(6):725–737. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Thornton J. C., Warshaw R., Anderson H., Teirstein A. S., Selikoff I. J. Single breath diffusing capacity in a representative sample of the population of Michigan, a large industrial state. Predicted values, lower limits of normal, and frequencies of abnormality by smoking history. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Mar;127(3):270–277. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.3.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Thornton J. C., Warshaw R., Bernstein J., Selikoff I. J., Teirstein A. S. Mean and instantaneous expiratory flows, FVC and FEV1: prediction equations from a probability sample of Michigan, a large industrial state. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1986 Nov-Dec;22(6):589–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. R., Pincock A. C. Predicted values: how should we use them? Thorax. 1988 Apr;43(4):265–267. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.4.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne J. S., Williamson J. Respiratory function tests in older people. Clin Sci. 1972 Mar;42(3):371–381. doi: 10.1042/cs0420371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. F., Koski A., Johnson L. C. Spirometric standards for healthy nonsmoking adults. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Jan;103(1):57–67. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEDHAM C. D., ROGAN M. C., McDONALD I. Normal standards for lung volumes, intrapulmonary gas-mixing, and maximum breathing capacity. Thorax. 1954 Dec;9(4):313–325. doi: 10.1136/thx.9.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn A. J., Gregg I. New regression equations for predicting peak expiratory flow in adults. BMJ. 1989 Apr 22;298(6680):1068–1070. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6680.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson J., Bake B., Svärdsudd K., Skoogh B. E. The single breath N2-test predicts the rate of decline in FEV1. The study of men born in 1913 and 1923. Eur J Respir Dis. 1986 Jul;69(1):46–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti P., Pistelli G., Fazzi P., Viegi G., Di Pede F., Giuliano G., Prediletto R., Carrozzi L., Polato R., Saetta M. Reference values for vital capacity and flow-volume curves from a general population study. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1986 Sep-Oct;22(5):451–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca J., Sanchis J., Agusti-Vidal A., Segarra F., Navajas D., Rodriguez-Roisin R., Casan P., Sans S. Spirometric reference values from a Mediterranean population. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1986 May-Jun;22(3):217–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C. D., Dickman M. L., Gardner R. M., Brough F. K. Spirometric standards for healthy elderly men and women. 532 subjects, ages 55 through 94 years. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Oct;108(4):933–939. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.4.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg J. B., Beck G. J., Bouhuys A. Growth and decay of pulmonary function in healthy blacks and whites. Respir Physiol. 1978 Jun;33(3):367–393. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(78)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobol B. J. Assessment of ventilatory abnormality in the asymptomatic subject: an exercise in futility. Thorax. 1966 Sep;21(5):445–449. doi: 10.1136/thx.21.5.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobol B. J. The early detection of airway obstruction: another perspective. Am J Med. 1976 May 10;60(5):619–624. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90495-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager I. B., Segal M. R., Speizer F. E., Weiss S. T. The natural history of forced expiratory volumes. Effect of cigarette smoking and respiratory symptoms. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Oct;138(4):837–849. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.4.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. L., Lawson L. M., Paré P. D., Kennedy S., Wiggs B., Hogg J. C. The detection of small airways disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Jun;129(6):989–994. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.6.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


