Abstract
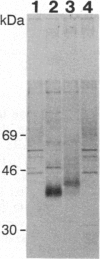
Because of their postmitotic nature, neurons are difficult subjects for gene transfer. To circumvent this, we have used a defective herpes simplex virus vector to overexpress the rat brain glucose transporter (GT) gene under the control of the human cytomegalovirus ie1 promoter. This vector, designated vIE1GT, was propagated using a herpes simplex virus type 1 temperature-sensitive mutant, ts756. GT expressed from vIE1GT was readily immunoprecipitated from membrane fractions of vIE1GT-infected Vero cells. By using indirect double immunofluorescence techniques, vIE1GT was shown to be capable of enhancing GT expression in cultured hippocampal neurons and glia. Glucose transport in such vIE1GT-infected cultures was increased approximately 2-fold relative to controls. The efficacy of this system in vivo was then tested by microinjection of vIE1GT into adult rat hippocampus. When examined 2 days later, GT expression from vIE1GT was demonstrated in hippocampal neurons by in situ hybridization; a small but significant increase in glucose transport was detected in tissue immediately surrounding the injection site by 2-deoxy[14C]glucose uptake and autoradiography. Such injections did not cause marked cytopathology. Thus, this approach can be used to alter central nervous system physiology in vitro and in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auer R. N., Siesjö B. K. Biological differences between ischemia, hypoglycemia, and epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 1988 Dec;24(6):699–707. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J., Haspel H. C., Rosen O. M. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the rat brain glucose-transporter protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5784–5788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington J. M., Mocarski E. S. Human cytomegalovirus ie1 transactivates the alpha promoter-enhancer via an 18-base-pair repeat element. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1435–1440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1435-1440.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiocca E. A., Choi B. B., Cai W. Z., DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A., DiFiglia M., Breakefield X. O., Martuza R. L. Transfer and expression of the lacZ gene in rat brain neurons mediated by herpes simplex virus mutants. New Biol. 1990 Aug;2(8):739–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson A. T., Margolis T. P., Sedarati F., Stevens J. G., Feldman L. T. A latent, nonpathogenic HSV-1-derived vector stably expresses beta-galactosidase in mouse neurons. Neuron. 1990 Sep;5(3):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90171-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dormitzer P. R., Ho D. Y., Mackow E. R., Mocarski E. S., Greenberg H. B. Neutralizing epitopes on herpes simplex virus-1-expressed rotavirus VP7 are dependent on coexpression of other rotavirus proteins. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):18–32. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90291-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutch R. E., Bruckner R. C., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex virus type 1 recombination: role of DNA replication and viral a sequences. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):277–285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.277-285.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., O'Donnell M. E., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. A DNA binding protein specific for an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6322–6326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federoff H. J., Geschwind M. D., Geller A. I., Kessler J. A. Expression of nerve growth factor in vivo from a defective herpes simplex virus 1 vector prevents effects of axotomy on sympathetic ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1636–1640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink D. J., Sternberg L. R., Weber P. C., Mata M., Goins W. F., Glorioso J. C. In vivo expression of beta-galactosidase in hippocampal neurons by HSV-mediated gene transfer. Hum Gene Ther. 1992 Feb;3(1):11–19. doi: 10.1089/hum.1992.3.1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller A. I., Breakefield X. O. A defective HSV-1 vector expresses Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase in cultured peripheral neurons. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1667–1669. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller A. I., Keyomarsi K., Bryan J., Pardee A. B. An efficient deletion mutant packaging system for defective herpes simplex virus vectors: potential applications to human gene therapy and neuronal physiology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8950–8954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel H. C., Birnbaum M. J., Wilk E. W., Rosen O. M. Biosynthetic precursors and in vitro translation products of the glucose transporter of human hepatocarcinoma cells, human fibroblasts, and murine preadipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7219–7225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. Y., Mocarski E. S. Beta-galactosidase as a marker in the peripheral and neural tissues of the herpes simplex virus-infected mouse. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. Y., Mocarski E. S. Herpes simplex virus latent RNA (LAT) is not required for latent infection in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7596–7600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horner H. C., Packan D. R., Sapolsky R. M. Glucocorticoids inhibit glucose transport in cultured hippocampal neurons and glia. Neuroendocrinology. 1990 Jul;52(1):57–64. doi: 10.1159/000125539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Q., Vonsattel J. P., Schaffer P. A., Martuza R. L., Breakefield X. O., DiFiglia M. Introduction of a foreign gene (Escherichia coli lacZ) into rat neostriatal neurons using herpes simplex virus mutants: a light and electron microscopic study. Exp Neurol. 1992 Mar;115(3):303–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(92)90196-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. G., Jr, Munyon W. H. Temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 defective in lysis but not in transformation. J Virol. 1975 Aug;16(2):275–283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.2.275-283.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong A. D., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon. IV. Efficient expression of a chimeric chicken ovalbumin gene amplified within defective virus genomes. Virology. 1985 Apr 30;142(2):421–425. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90351-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning W. C., Mocarski E. S. Insertional mutagenesis of the murine cytomegalovirus genome: one prominent alpha gene (ie2) is dispensable for growth. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):477–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palella T. D., Silverman L. J., Schroll C. T., Homa F. L., Levine M., Kelley W. N. Herpes simplex virus-mediated human hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase gene transfer into neuronal cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):457–460. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M., Boado R. J., Farrell C. R. Brain-type glucose transporter (GLUT-1) is selectively localized to the blood-brain barrier. Studies with quantitative western blotting and in situ hybridization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):18035–18040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rösen-Wolff A., Raab K., Zöller L., Darai G., Eberle J., Deinhardt F. Expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gag gene using genetically engineered herpes simplex virus type 1 recombinants. Virus Genes. 1990 Dec;4(4):325–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00570027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapolsky R. M. Glucocorticoids, hippocampal damage and the glutamatergic synapse. Prog Brain Res. 1990;86:13–23. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)63163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih M. F., Arsenakis M., Tiollais P., Roizman B. Expression of hepatitis B virus S gene by herpes simplex virus type 1 vectors carrying alpha- and beta-regulated gene chimeras. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5867–5870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. R., Smibert C., Everett R. D. Expression of a cellular gene cloned in herpes simplex virus: rabbit beta-globin is regulated as an early viral gene in infected fibroblasts. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2368–2377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2368-2377.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon: a new eucaryotic defective-virus cloning-amplifying vector. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutin E. L., Kilduff T. S. Circadian and light-induced expression of immediate early gene mRNAs in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Oct;15(3-4):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90119-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tackney C., Cachianes G., Silverstein S. Transduction of the Chinese hamster ovary aprt gene by herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):606–614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.606-614.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tombaugh G. C., Yang S. H., Swanson R. A., Sapolsky R. M. Glucocorticoids exacerbate hypoxic and hypoglycemic hippocampal injury in vitro: biochemical correlates and a role for astrocytes. J Neurochem. 1992 Jul;59(1):137–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb08884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmuza S. L., Smiley J. R. Signals for site-specific cleavage of HSV DNA: maturation involves two separate cleavage events at sites distal to the recognition sequences. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):793–802. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]