Abstract
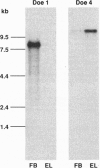
In many neurons, transmitter release from presynaptic terminals is triggered by Ca2+ entry via dihydropyridine-insensitive Ca2+ channels. We have looked for cDNAs for such channels in the nervous system of the marine ray Discopyge ommata. One cDNA (doe-2) is similar to dihydropyridine-sensitive L-type channels, and two cDNAs (doe-1 and doe-4) are similar to the subfamily of dihydropyridine-insensitive non-L-type channels. doe-4, which encodes a protein of 2326 aa, most closely resembles a previously cloned N-type channel. doe-1, which encodes a protein of 2223 aa, is a member of a separate branch of the non-L-type channels. Northern blot analysis reveals that doe-1 is abundant in the forebrain. doe-4 is more plentiful in the electric lobe and, therefore, may control neurotransmitter release in motor nerve terminals. These results show that the familial pattern of Ca(2+)-channel genes has been preserved from a stage in evolution before the divergence of higher and lower vertebrates > 400 million years ago. The cloning of these channels may be a useful starting point for elucidating the role of the Ca2+ channels in excitation-secretion coupling in nerve terminals.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad S. N., Miljanich G. P. The calcium channel antagonist, omega-conotoxin, and electric organ nerve terminals: binding and inhibition of transmitter release and calcium influx. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 21;453(1-2):247–256. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwyl R. Modulation of vertebrate neuronal calcium channels by transmitters. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1991 Sep-Dec;16(3):265–281. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(91)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:367–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Calakos N., Scheller R. H. Syntaxin: a synaptic protein implicated in docking of synaptic vesicles at presynaptic active zones. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):255–259. doi: 10.1126/science.1321498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biel M., Ruth P., Bosse E., Hullin R., Stühmer W., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. Primary structure and functional expression of a high voltage activated calcium channel from rabbit lung. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 3;269(2):409–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81205-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubel S. J., Starr T. V., Hell J., Ahlijanian M. K., Enyeart J. J., Catterall W. A., Snutch T. P. Molecular cloning of the alpha-1 subunit of an omega-conotoxin-sensitive calcium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5058–5062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds B., Klein M., Dale N., Kandel E. R. Contributions of two types of calcium channels to synaptic transmission and plasticity. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1142–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.2174573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabner M., Friedrich K., Knaus H. G., Striessnig J., Scheffauer F., Staudinger R., Koch W. J., Schwartz A., Glossmann H. Calcium channels from Cyprinus carpio skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne W. A., Hawrot E., Tsien R. W. omega-Conotoxin GVIA receptors of Discopyge electric organ. Characterization of omega-conotoxin binding to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13719–13725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui A., Ellinor P. T., Krizanova O., Wang J. J., Diebold R. J., Schwartz A. Molecular cloning of multiple subtypes of a novel rat brain isoform of the alpha 1 subunit of the voltage-dependent calcium channel. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W. J., Ellinor P. T., Schwartz A. cDNA cloning of a dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel from rat aorta. Evidence for the existence of alternatively spliced forms. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17786–17791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikami A., Imoto K., Tanabe T., Niidome T., Mori Y., Takeshima H., Narumiya S., Numa S. Primary structure and functional expression of the cardiac dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):230–233. doi: 10.1038/340230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori Y., Friedrich T., Kim M. S., Mikami A., Nakai J., Ruth P., Bosse E., Hofmann F., Flockerzi V., Furuichi T. Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of a brain calcium channel. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):398–402. doi: 10.1038/350398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niidome T., Kim M. S., Friedrich T., Mori Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel calcium channel from rabbit brain. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 10;308(1):7–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81038-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelzer S., Barhanin J., Pauron D., Trautwein W., Lazdunski M., Pelzer D. Diversity and novel pharmacological properties of Ca2+ channels in Drosophila brain membranes. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2365–2371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08365.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Reyes E., Wei X. Y., Castellano A., Birnbaumer L. Molecular diversity of L-type calcium channels. Evidence for alternative splicing of the transcripts of three non-allelic genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20430–20436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salkoff L., Baker K., Butler A., Covarrubias M., Pak M. D., Wei A. An essential 'set' of K+ channels conserved in flies, mice and humans. Trends Neurosci. 1992 May;15(5):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90165-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snutch T. P., Leonard J. P., Gilbert M. M., Lester H. A., Davidson N. Rat brain expresses a heterogeneous family of calcium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3391–3395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snutch T. P., Reiner P. B. Ca2+ channels: diversity of form and function. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Jun;2(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90111-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr T. V., Prystay W., Snutch T. P. Primary structure of a calcium channel that is highly expressed in the rat cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5621–5625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong M., Chandy K. G., Gutman G. A. Molecular evolution of voltage-sensitive ion channel genes: on the origins of electrical excitability. Mol Biol Evol. 1993 Jan;10(1):221–242. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a039986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Conti F., Suzuki H., Wang X. D., Noda M., Yahagi N., Kubo H., Numa S. Structural parts involved in activation and inactivation of the sodium channel. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):597–603. doi: 10.1038/339597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Beam K. G., Adams B. A., Niidome T., Numa S. Regions of the skeletal muscle dihydropyridine receptor critical for excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):567–569. doi: 10.1038/346567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Takeshima H., Mikami A., Flockerzi V., Takahashi H., Kangawa K., Kojima M., Matsuo H., Hirose T., Numa S. Primary structure of the receptor for calcium channel blockers from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):313–318. doi: 10.1038/328313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Ellinor P. T., Horne W. A. Molecular diversity of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Sep;12(9):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90595-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev P. M., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Identification of an intracellular peptide segment involved in sodium channel inactivation. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1658–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. E., Brust P. F., Feldman D. H., Patthi S., Simerson S., Maroufi A., McCue A. F., Veliçelebi G., Ellis S. B., Harpold M. M. Structure and functional expression of an omega-conotoxin-sensitive human N-type calcium channel. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):389–395. doi: 10.1126/science.1321501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. E., Feldman D. H., McCue A. F., Brenner R., Velicelebi G., Ellis S. B., Harpold M. M. Structure and functional expression of alpha 1, alpha 2, and beta subunits of a novel human neuronal calcium channel subtype. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):71–84. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90109-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]