Abstract
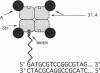
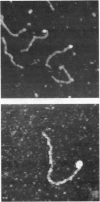
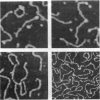
Small fragments of DNA of known length were made with the polymerase chain reaction. These fragments had biotin molecules covalently attached at their ends. They were subsequently labeled with a chimeric protein fusion between streptavidin and two immunoglobulin G-binding domains of staphylococcal protein A. This tetrameric species was expected to bind up to four DNA molecules via their attached biotin moieties. The DNA-protein complex was deposited on mica and imaged with an atomic force microscope. The images revealed the protein chimera at the expected location at the ends of the strands of DNA as well as the expected dimers, trimers, and tetramers of DNA bound to a single protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen M. J., Balooch M., Subbiah S., Tench R. J., Siekhaus W., Balhorn R. Scanning tunneling microscope images of adenine and thymine at atomic resolution. Scanning Microsc. 1991 Sep;5(3):625–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEER M., MOUDRIANAKISEN Determination of base sequence in nucleic acids with the electron microscope: visibility of a marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Mar 15;48:409–416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.3.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnig G, Quate CF, Gerber C. Atomic force microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 1986 Mar 3;56(9):930–933. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante C., Vesenka J., Tang C. L., Rees W., Guthold M., Keller R. Circular DNA molecules imaged in air by scanning force microscopy. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):22–26. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Jolly D. J., Rubin C. M., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Base sequence studies of 300 nucleotide renatured repeated human DNA clones. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Avidin. Adv Protein Chem. 1975;29:85–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G., Sinsheimer R. L., Li M. Q., Hansma P. K. Atomic force microscopy of single- and double-stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 25;20(14):3585–3590. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.14.3585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G., Vesenka J., Siegerist C., Kelderman G., Morrett H., Sinsheimer R. L., Elings V., Bustamante C., Hansma P. K. Reproducible imaging and dissection of plasmid DNA under liquid with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1180–1184. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highton P. J., Murr B. L., Shafa F., Beer M. Electron microscopic study of base sequence in nucleic acids. 8. Specific conversion of thymine into anionic osmate esters. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):825–833. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOUDRIANAKIS E. N., BEER M. BASE SEQUENCE DETERMINATION IN NUCLEIC ACIDS WITH THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE. 3. CHEMISTRY AND MICROSCOPY OF GUANINE-LABELED DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Mar;53:564–571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.3.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano T., Cantor C. R. A streptavidin-protein A chimera that allows one-step production of a variety of specific antibody conjugates. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Dec;9(12):1378–1381. doi: 10.1038/nbt1291-1378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R., Hirsh J. Electron microscopy of proteins bound to DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):885–896. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thundat T., Allison D. P., Warmack R. J., Ferrell T. L. Imaging isolated strands of DNA molecules by atomic force microscopy. Ultramicroscopy. 1992 Jul;42-44(Pt B):1101–1106. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90409-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesenka J., Guthold M., Tang C. L., Keller D., Delaine E., Bustamante C. Substrate preparation for reliable imaging of DNA molecules with the scanning force microscope. Ultramicroscopy. 1992 Jul;42-44(Pt B):1243–1249. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90430-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Davidson N. Use of gene 32 protein staining of single-strand polynucleotides for gene mapping by electron microscopy: application to the phi80d3ilvsu+7 system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4506–4510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenhausern F., Adrian M., ten Heggeler-Bordier B., Emch R., Jobin M., Taborelli M., Descouts P. Imaging of DNA by scanning force microscopy. J Struct Biol. 1992 Jan-Feb;108(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(92)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]