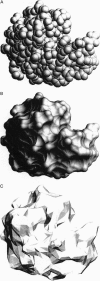
Abstract
Diffusion coefficients for proteins in water are predicted. The numerical method developed is general enough to be applied to a wide range of protein surface shapes, from rodlike to globular. Results are presented for lysozyme and tobacco mosaic virus, and they are compared with actual data and with predictions made by less general methods.
Full text
PDF

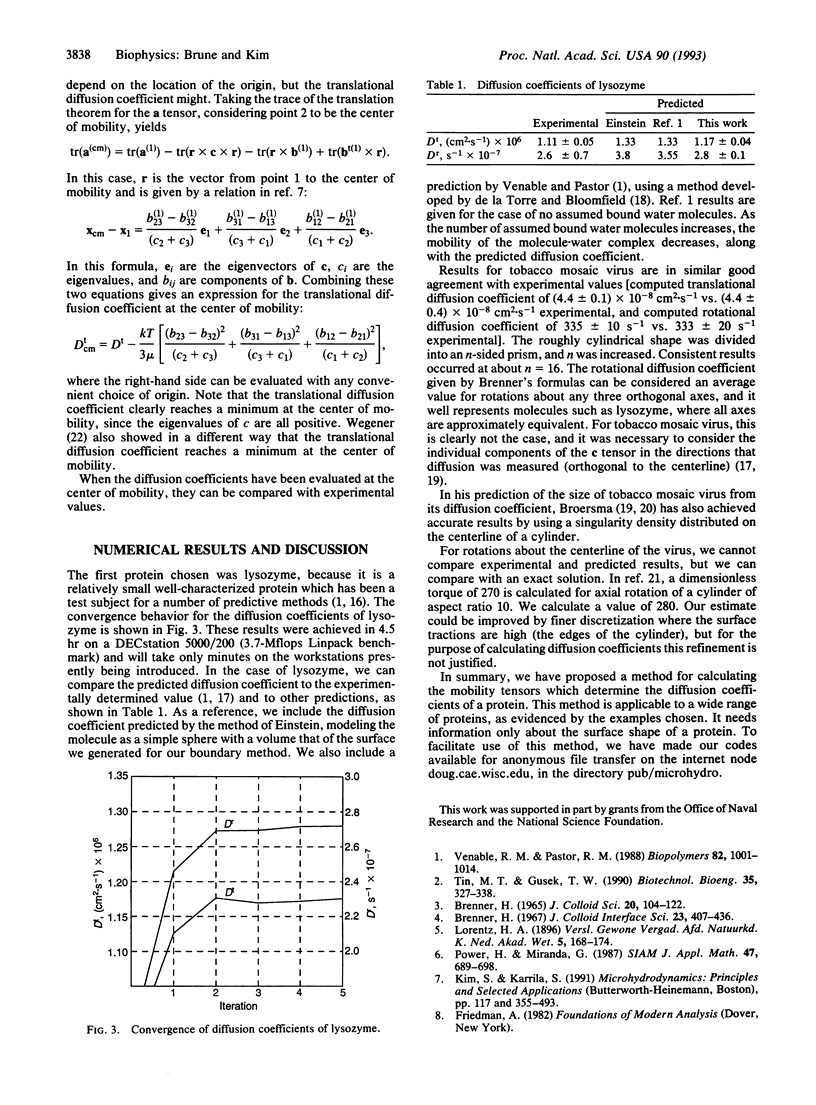

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Garcia de la Torre J. G., Bloomfield V. A. Hydrodynamic properties of complex, rigid, biological macromolecules: theory and applications. Q Rev Biophys. 1981 Feb;14(1):81–139. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntz I. D., Jr, Kauzmann W. Hydration of proteins and polypeptides. Adv Protein Chem. 1974;28:239–345. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venable R. M., Pastor R. W. Frictional models for stochastic simulations of proteins. Biopolymers. 1988 Jun;27(6):1001–1014. doi: 10.1002/bip.360270609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener W. A. On an exact starting expression for macromolecular hydrodynamic models. Biopolymers. 1986 Apr;25(4):627–637. doi: 10.1002/bip.360250408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]