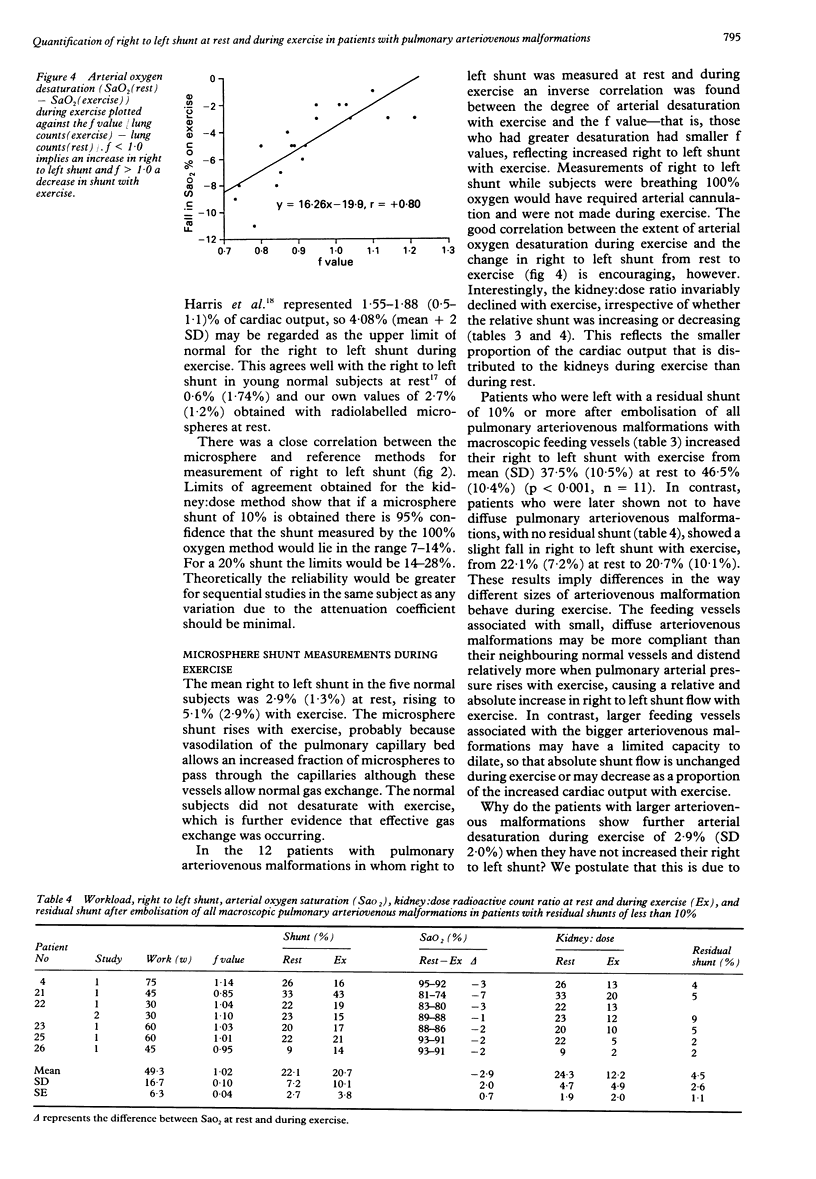
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Current treatment of patients with pulmonary arteriovenous malformations requires serial embolisations by means of steel coils or balloons. Measurement of right to left shunt is the most specific index of response to treatment. A new method of measuring shunt has been developed that is less invasive than traditional methods. METHODS: Right to left pulmonary shunt (expressed as percentage of cardiac output) was measured at rest in 19 patients with pulmonary arteriovenous malformations and six normal subjects by using intravenously injected albumin microspheres labelled with technetium-99m. The technique was compared with a simultaneous shunt measurement in subjects breathing 100% oxygen while they rested. The microsphere technique was adapted to measure the right to left shunt during exercise in 12 patients and five normal subjects with a new method of quantification. RESULTS: The mean (SD) shunt at rest as measured by the microsphere method was 23.2% (15.6%) in the patients and 2.7% (1.2%) in the normal subjects. When these values were compared with those of the 100% oxygen method the difference in mean values was 1% and the limits of agreement between the two methods -32% to +45%. The microsphere method is less invasive (arterial blood gas sampling is not required), quicker, and more comfortable for patients than the 100% oxygen method. In five of the normal subjects the mean (SD) 99mTc microsphere shunt increased from 2.9% (1.3%) at rest to 5.1% (2.9%) during exercise. In the 12 patients studied during exercise the shunt increased from 33.7% (12.7%) at rest to 41.7% (13.3%) during exercise in eight but decreased from 22.6% (2.4%) at rest to 17.6% (2.2%) during exercise in four. Arterial desaturation during exercise correlated with change in the size of the right to left shunt during exercise (r = +0.80). CONCLUSIONS: The microsphere method allows measurement of right to left shunt at rest and during exercise. Serial measurements at rest provide a simple, safe assessment of the physiological response to embolisation in patients with pulmonary arteriovenous malformations.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
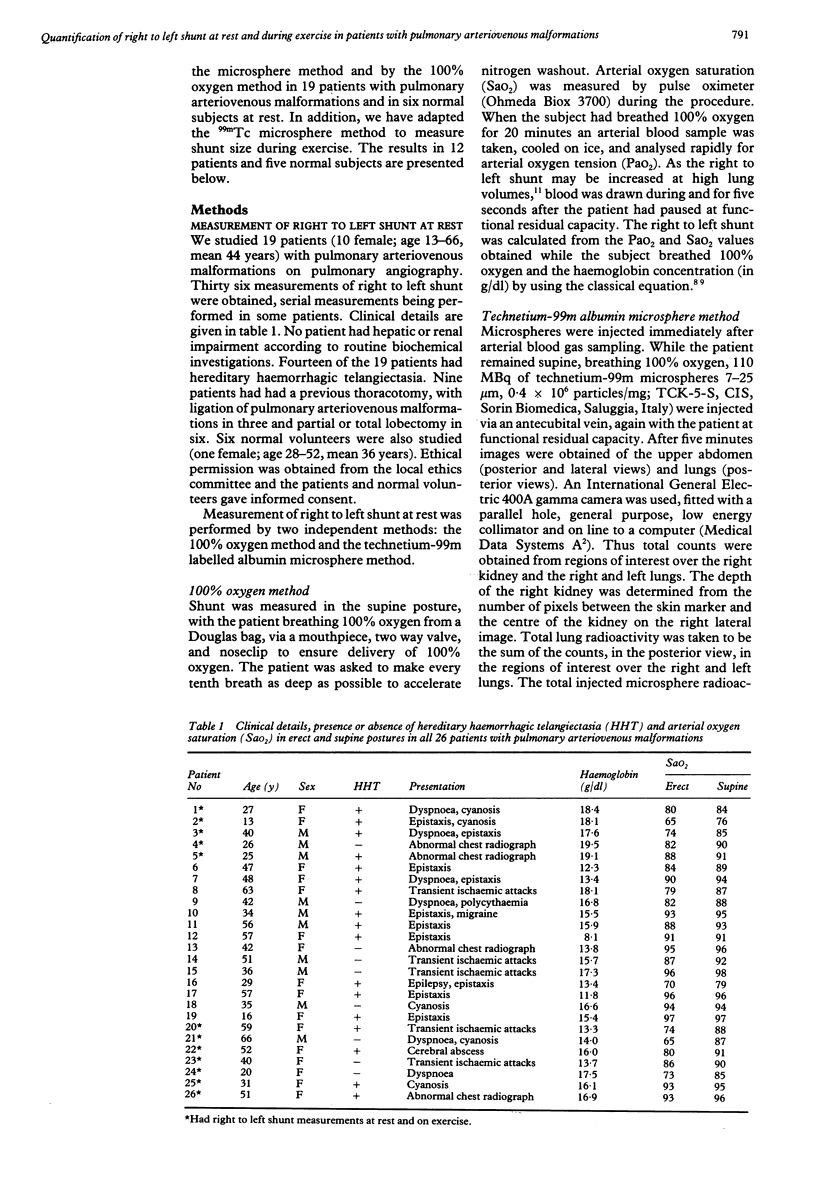
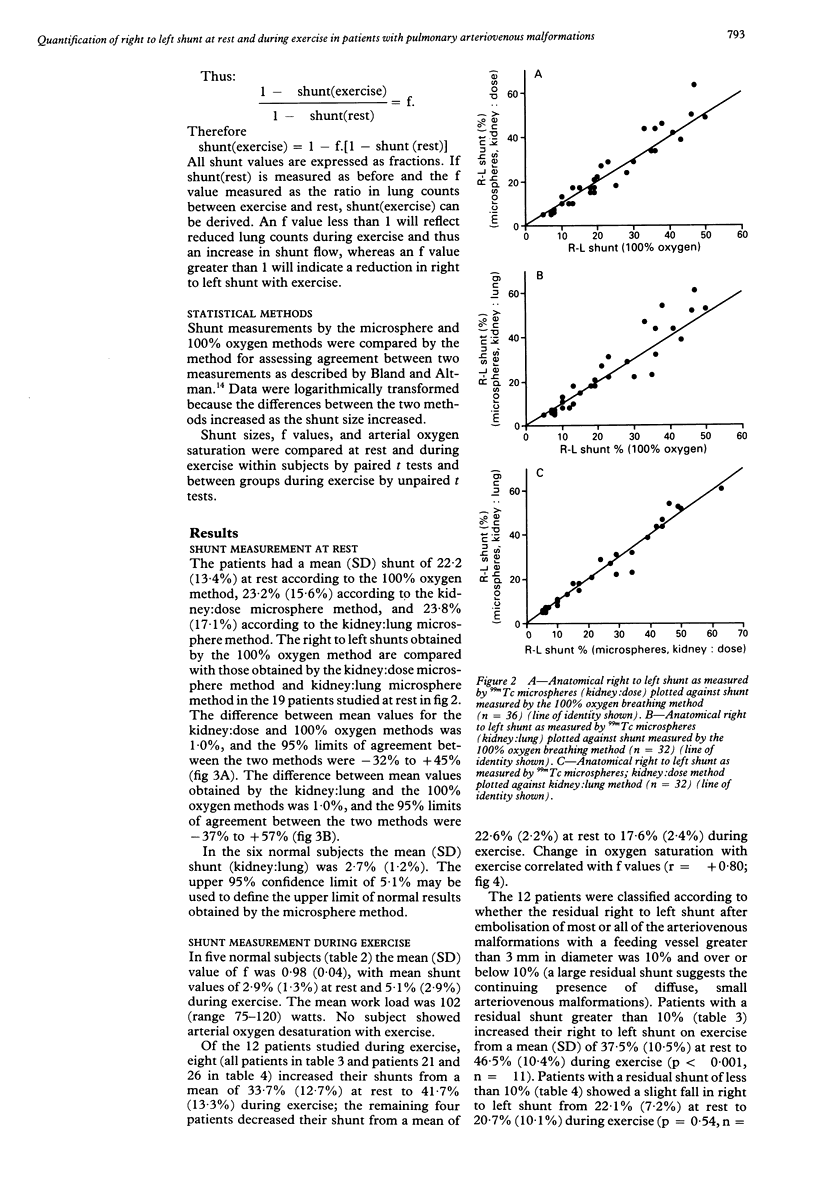
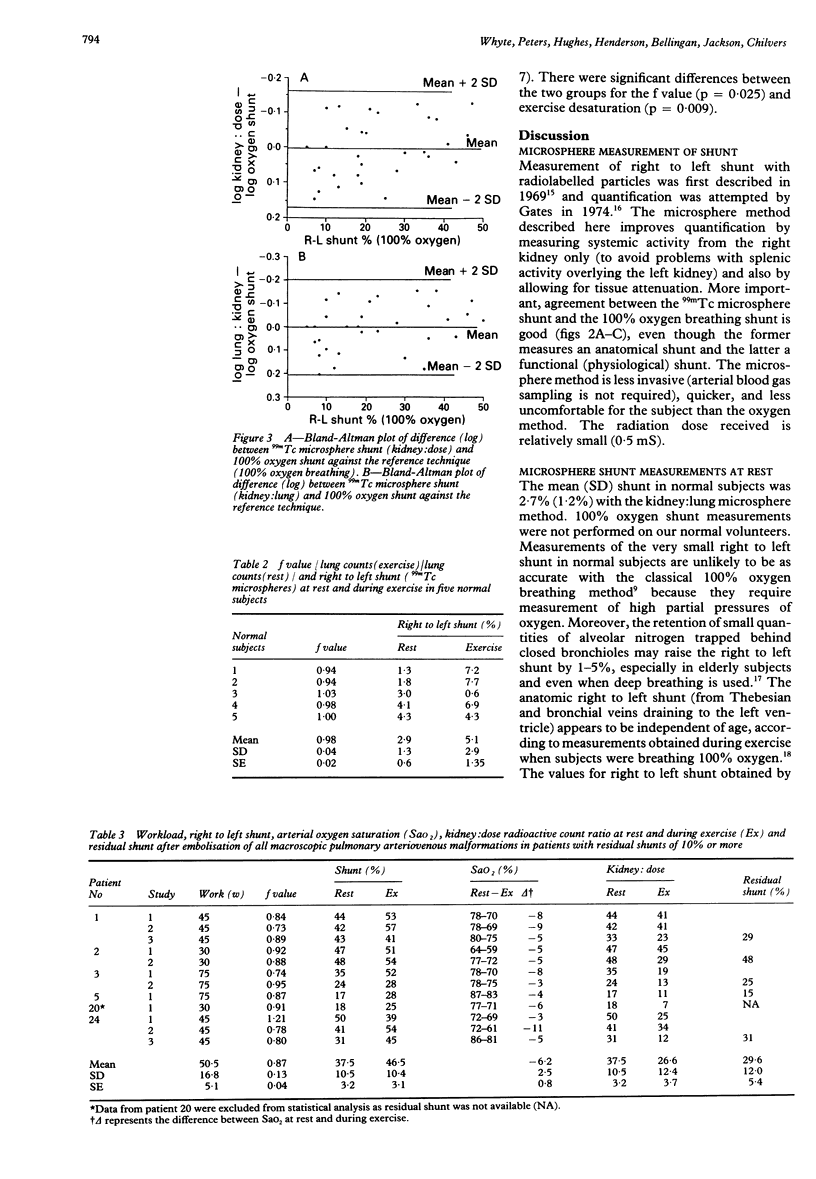
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke C. M., Safai C., Nelson D. P., Raffin T. A. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: a critical update. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Aug;134(2):334–339. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.2.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilvers E. R., Peters A. M., George P., Hughes J. M., Allison D. J. Quantification of right to left shunt through pulmonary arteriovenous malformations using 99Tcm albumin microspheres. Clin Radiol. 1988 Nov;39(6):611–614. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(88)80065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilvers E. R., Whyte M. K., Jackson J. E., Allison D. J., Hughes J. M. Effect of percutaneous transcatheter embolization on pulmonary function, right-to-left shunt, and arterial oxygenation in patients with pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Aug;142(2):420–425. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.2.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dines D. E., Arms R. A., Bernatz P. E., Gomes M. R. Pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas. Mayo Clin Proc. 1974 Jul;49(7):460–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dines D. E., Seward J. B., Bernatz P. E. Pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas. Mayo Clin Proc. 1983 Mar;58(3):176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gates G. F., Orme H. W., Dore E. K. Cardiac shunt assessment in children with macroaggregated albumin technetium-99m. Radiology. 1974 Sep;112(3):649–653. doi: 10.1148/112.3.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haroutunian L. M., Neill C. A., Wagner H. N., Jr Radioisotope scanning of the lung in cyanotic congenital heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 1969 Mar;23(3):387–395. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(69)90519-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. A., Seelye E. R., Whitlock R. M. Gas exchange during exercise in healthy people II. Venous admixture. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Oct;51(4):335–344. doi: 10.1042/cs0510335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartnell G. G., Allison D. J. Management of pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. Br J Hosp Med. 1988 Mar;39(3):197–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M., Allison D. J. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: the radiologist replaces the surgeon. Clin Radiol. 1990 May;41(5):297–298. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(05)81687-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huseby J. S., Culver B. H., Butler J. Pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas: increase in shunt at high lung volume. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Feb;115(2):229–232. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A. M., Brown J., Hartnell G. G., Myers M. J., Haskell C., Lavender J. P. Non-invasive measurement of renal blood flow with 99mTc DTPA: comparison with radiolabelled microspheres. Cardiovasc Res. 1987 Nov;21(11):830–834. doi: 10.1093/cvr/21.11.830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A. M., Gunasekera R. D., Henderson B. L., Brown J., Lavender J. P., De Souza M., Ash J. M., Gilday D. L. Noninvasive measurement of blood flow and extraction fraction. Nucl Med Commun. 1987 Oct;8(10):823–837. doi: 10.1097/00006231-198710000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea H. H., Withy S. J., Seelye E. R., Harris E. A. The effects of posture on venous admixture and respiratory dead space in health. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Apr;115(4):571–580. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.4.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry P. B., Barth K. H., Kaufman S. L., White R. I., Jr Balloon embolization for treatment of pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 22;302(21):1189–1190. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005223022107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. I., Jr, Lynch-Nyhan A., Terry P., Buescher P. C., Farmlett E. J., Charnas L., Shuman K., Kim W., Kinnison M., Mitchell S. E. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: techniques and long-term outcome of embolotherapy. Radiology. 1988 Dec;169(3):663–669. doi: 10.1148/radiology.169.3.3186989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]