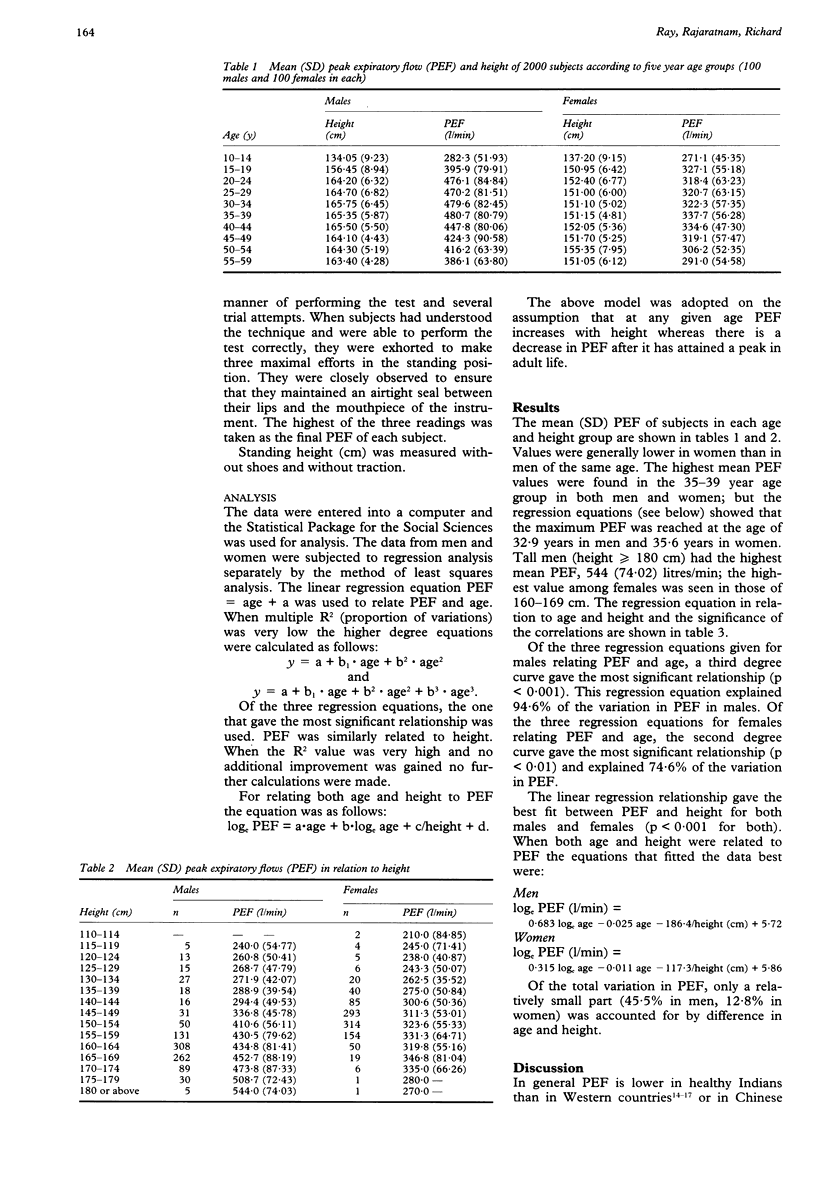
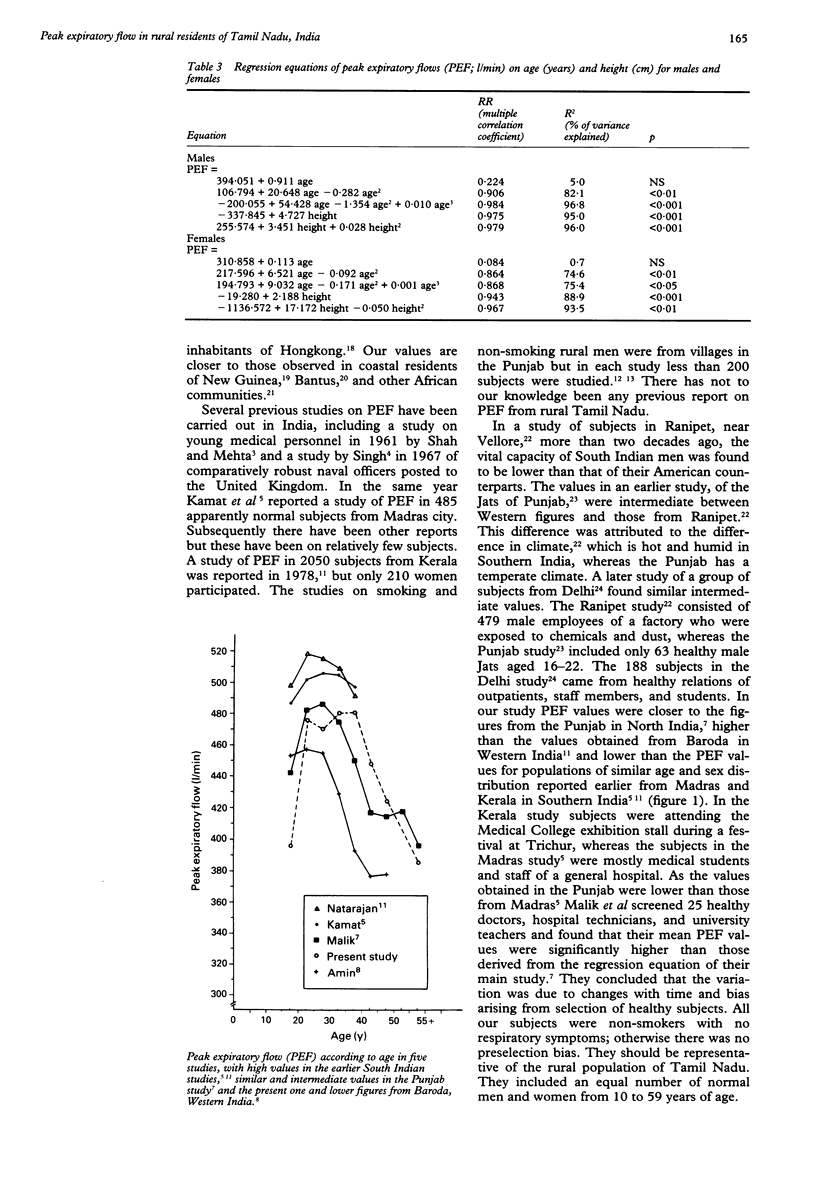
Abstract
BACKGROUND: In a country such as India that covers several latitudes, climatic zones, ethnic groups, and dietary habits lung function within the normal population would be expected to vary. Several studies have looked at normal values of peak expiratory flow (PEF) in different regions of urban India but none has looked at rural South India. A study of PEF has now been carried out in a rural population of Tamil Nadu. METHODS: All subjects were of Dravidian stock and lived at sea level with rice as their staple food. Ten five year age groups from 10 to 59 years with 100 males and 100 females in each were studied. Peak flow was measured by mini-Wright peak flow meter, and height was also measured. Regression equations for predicting normal PEF were calculated. RESULTS: Peak flow ranged from 150 to 680 l/min in males and from 150 to 500 l/min in females. Maximum values of PEF were attained at the age of 32.5 years in men and 35.6 years in women. There was a significant linear correlation between height and PEF and a curvilinear relation between age and PEF in both sexes. CONCLUSION: Regression equations are now available for PEF values in normal subjects from rural South India. PEF was related to age and height and values were greatest in the fourth decade.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin S. K., Pande R. S. Peak expiratory flow rate in normal subjects. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 1978 Apr;20(2):80–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BHATTACHARYA D. K. Vital capacity of the Jat males of Punjab: modification of the formulae existing for its computation. Indian J Med Res. 1963 Mar;51:361–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks A. G., Waller R. E. Peak flow measurements among visitors to a public health exhibition. Thorax. 1972 Sep;27(5):557–562. doi: 10.1136/thx.27.5.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERRIS B. G., Jr, ANDERSON D. O., ZICKMANTEL R. PREDICTION VALUES FOR SCREENING TESTS OF PULMONARY FUNCTION. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Feb;91:252–261. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.91.2.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg I., Nunn A. J. Peak expiratory flow in normal subjects. Br Med J. 1973 Aug 4;3(5874):282–284. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5874.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta C. K., Mathur N. Statistical models relating peak expiratory flow rates to age, height, and weight in men and women. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1982 Mar;36(1):64–67. doi: 10.1136/jech.36.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Puri M., Singh S. I. Pulmonary function tests in health. J Assoc Physicians India. 1975 Apr;23(4):247–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S. K., Ramiah T. J. Normal standards of pulmonary function tests for healthy Indian men 15-40 years old: comparison of different regression equations (prediction formulae). Indian J Med Res. 1969 Aug;57(8):1453–1466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johannsen Z. M., Erasmus L. D. Clinical spirometry in normal Bantu. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1968 Apr;97(4):585–597. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1968.97.4.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamat S. R., Thiruvengadam K. V., Rao T. L. A study of pulmonary function among Indians and assessment of the Wright peak flow meter in relation to spirometry for field use. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Oct;96(4):707–716. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.96.4.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEINER G. C., ABRAMOWITZ S., SMALL M. J., STENBY V. B., LEWIS W. A. EXPIRATORY PEAK FLOW RATE. STANDARD VALUES FOR NORMAL SUBJECTS. USE AS A CLINICAL TEST OF VENTILATORY FUNCTION. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1963 Nov;88:644–651. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1963.88.5.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. K., Pang S. C., Allan W. G., Hill L. E., Snell N. J., Fayers P. M., Nunn A. J., Prime F. J. Predictive nomograms for forced expiratory volume, forced vital capacity, and peak expiratory flow rate, in Chinese adults and children. Br J Dis Chest. 1983 Oct;77(4):390–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik S. K., Banga N. Peak expiratory flow rate in non-smoking rural males. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 1978 Oct;20(4):183–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik S. K., Jindal S. K., Jindal V., Bansal S. Peak expiratory flow rate in healthy adults. Indian J Chest Dis. 1975 Oct;17(4):166–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik S. K., Singh K. Smoking habits, chronic bronchitis and ventilatory function in rural males. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 1978 Apr;20(2):73–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milledge J. S. Vital capacity and forced expiratory volume one second in South Indian men. Indian J Chest Dis. 1965 Apr;7(2):97–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan S., Radha K. Peak expiratory flow rate in normal South Indians. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 1978 Oct;20(4):178–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn A. J., Gregg I. New regression equations for predicting peak expiratory flow in adults. BMJ. 1989 Apr 22;298(6680):1068–1070. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6680.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman M. A., Ullah M. B., Begum A. Lung function in teenage Bangladeshi boys and girls. Respir Med. 1990 Jan;84(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/s0954-6111(08)80094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H. D. Peak flow rate in Indians. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 1967 Jul;11(3):129–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT B. M., McKERROW C. B. Maximum forced expiratory flow rate as a measure of ventilatory capacity: with a description of a new portable instrument for measuring it. Br Med J. 1959 Nov 21;2(5159):1041–1046. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5159.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. E., Miller R. D., Taylor W. F. Pulmonary function studies in healthy Pakistani adults. Thorax. 1978 Apr;33(2):243–249. doi: 10.1136/thx.33.2.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock A. J., Colman M. H., Blackburn C. R. Factors affecting normal values for ventilatory lung function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972 Nov;106(5):692–709. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1972.106.5.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright B. M. A miniature Wright peak-flow meter. Br Med J. 1978 Dec 9;2(6152):1627–1628. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6152.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


