Abstract
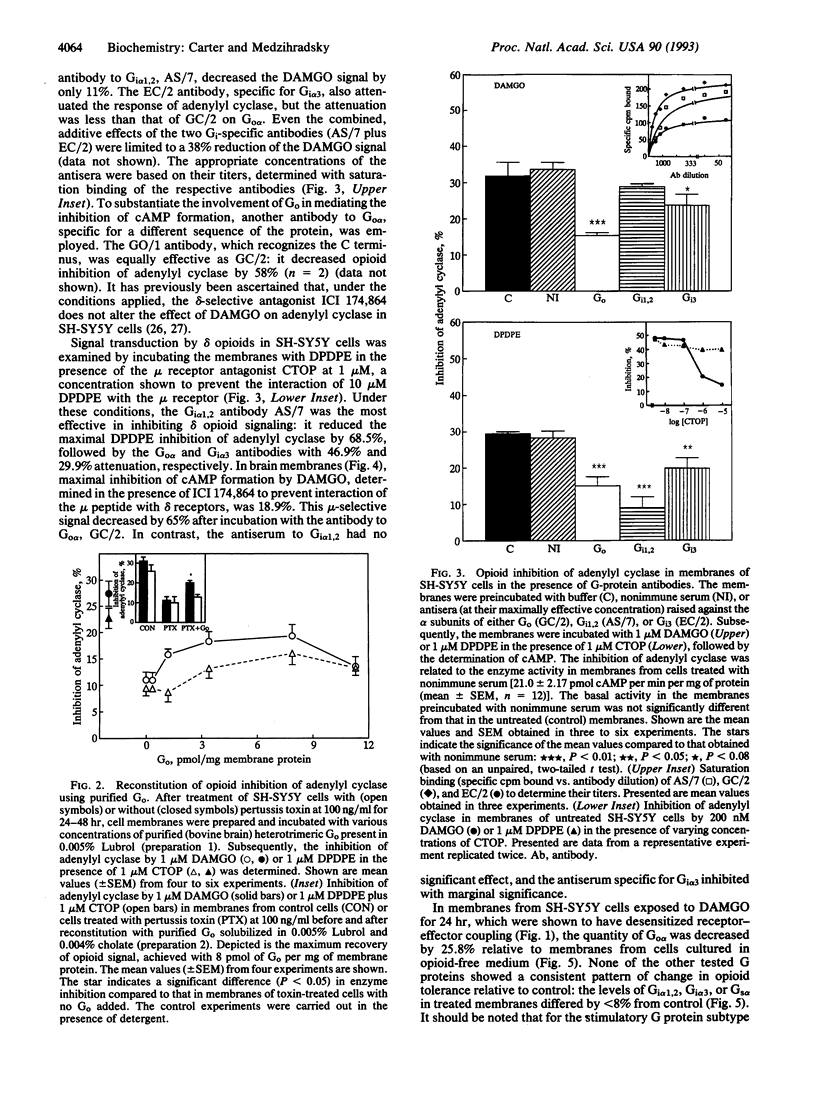
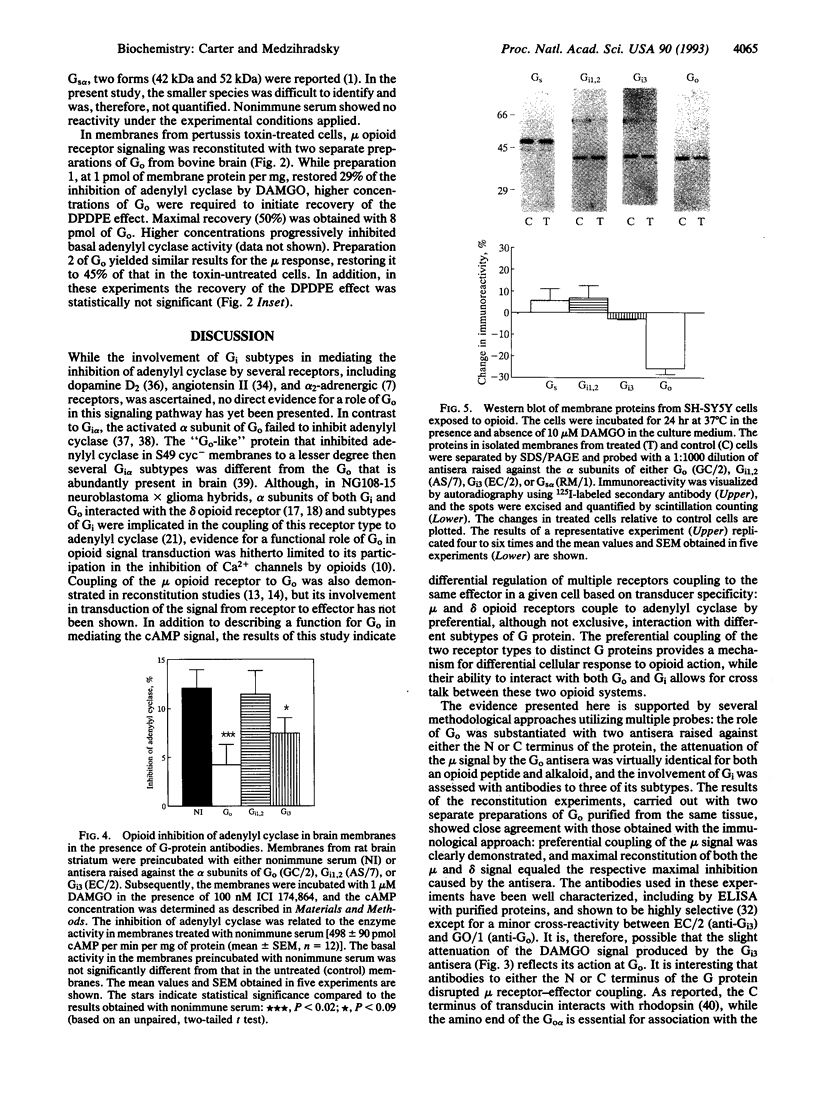
In membranes from SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells differentiated with retinoic acid, the mu-selective agonist Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-N-Me-Phe-Gly-ol (DAMGO) inhibited cAMP formation with an IC50 of 26 nM. Two separate antibodies raised against distinct regions of the Go alpha sequence attenuated the effect of DAMGO by 50-60%, whereas antibodies to Gi alpha 1,2 or Gi alpha 3 reduced the mu-opioid signal insignificantly or to a lesser extent. In contrast, inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by the delta-opioid agonist Tyr-D-Pen-Gly-Phe-D-Pen-OH (DPDPE; Pen = penicillamine) was very sensitive to the Gi alpha 1,2 antibody. In membranes from rat brain striatum, coupling of the mu opioid receptor to adenylyl cyclase was also maximally blocked by antibodies to Go alpha. After long-term treatment of the cells with DAMGO, the content of Go alpha was reduced by 26%, whereas the levels of Gi alpha 1,2, Gi alpha 3, and Gs alpha were unaltered. Addition of Go, purified from bovine brain, to membranes from pertussis toxin-treated SH-SY5Y cells restored the inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by DAMGO to 70% of that in toxin-untreated cells. To comparably restore the effect of DPDPE, much higher concentrations of Go were required. By demonstrating mediation of cAMP-dependent signal transduction by Go, these results describe (i) an additional role for this G protein present at a high concentration in brain, (ii) preferential, although not exclusive, interaction of mu and delta opioid receptors with different G protein subtypes in coupling to adenylyl cyclase, and (iii) reduced levels of Go following chronic opioid treatment of SH-SY5Y cells with mu opioids.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carter B. D., Medzihradsky F. Opioid signal transduction in intact and fragmented SH-SY5Y neural cells. J Neurochem. 1992 May;58(5):1611–1619. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter B. D., Medzihradsky F. Receptor mechanisms of opioid tolerance in SH-SY5Y human neural cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;43(3):465–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childers S. R. Opioid receptor-coupled second messenger systems. Life Sci. 1991;48(21):1991–2003. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. J., Carter B. D., Medzihradsky F. Selectivity of ligand binding to opioid receptors in brain membranes from the rat, monkey and guinea pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 13;148(3):343–351. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. J., Medzihradsky F. Coupling of multiple opioid receptors to GTPase following selective receptor alkylation in brain membranes. Neuropharmacology. 1987 Dec;26(12):1763–1770. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. J., Nordby G. L., Medzihradsky F. Relationship between opioid-receptor occupancy and stimulation of low-Km GTPase in brain membranes. J Neurochem. 1989 Apr;52(4):1162–1169. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb01862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denker B. M., Neer E. J., Schmidt C. J. Mutagenesis of the amino terminus of the alpha subunit of the G protein Go. In vitro characterization of alpha o beta gamma interactions. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6272–6277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic D., Hamm H. E. Topographic analysis of antigenic determinants recognized by monoclonal antibodies to the photoreceptor guanyl nucleotide-binding protein, transducin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10839–10847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhardt M. A., Neubig R. R. Multiple Gi protein subtypes regulate a single effector mechanism. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):707–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins K. N., Knapp R. J., Lui G. K., Gulya K., Kazmierski W., Wan Y. P., Pelton J. T., Hruby V. J., Yamamura H. I. [3H]-[H-D-Phe-Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Orn-Thr-Pen-Thr-NH2] ([3H]CTOP), a potent and highly selective peptide for mu opioid receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jan;248(1):73–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Rosenthal W., Trautwein W., Schultz G. The GTP-binding protein, Go, regulates neuronal calcium channels. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):445–447. doi: 10.1038/325445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inanobe A., Shibasaki H., Takahashi K., Kobayashi I., Tomita U., Ui M., Katada T. Characterization of four G0-type proteins purified from bovine brain membranes. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 24;263(2):369–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81416-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Ui M. Mechanisms for inhibition of the catalytic activity of adenylate cyclase by the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins serving as the substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5215–5221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M. H., Neubig R. R. Membrane reconstitution of high-affinity alpha 2 adrenergic agonist binding with guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3664–3672. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinz F. J., Yu V. C., Sadée W., Costa T. Differential expression of alpha-subunits of G-proteins in human neuroblastoma-derived cell clones. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80419-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi I., Shibasaki H., Takahashi K., Tohyama K., Kurachi Y., Ito H., Ui M., Katada T. Purification and characterization of five different alpha subunits of guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins in bovine brain membranes. Their physiological properties concerning the activities of adenylate cyclase and atrial muscarinic K+ channels. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 31;191(2):499–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laugwitz K. L., Offermanns S., Spicher K., Schultz G. mu and delta opioid receptors differentially couple to G protein subtypes in membranes of human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90314-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matesic D. F., Manning D. R., Luthin G. R. Tissue-dependent association of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors with guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;40(3):347–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Milligan G. Delta-opioid-receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase is transduced specifically by the guanine-nucleotide-binding protein Gi2. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):391–398. doi: 10.1042/bj2670391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Carr C., Gould G. W., Mullaney I., Lavan B. E. Agonist-dependent, cholera toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation of pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins following transfection of the human alpha 2-C10 adrenergic receptor into rat 1 fibroblasts. Evidence for the direct interaction of a single receptor with two pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins, Gi2 and Gi3. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6447–6455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochly-Rosen D., Gordon A. S. GTP-binding proteins are restricted to signal transduction sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 30;173(1):388–395. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty T. M., Padrell E., Carty D. J., Omri G., Landau E. M., Iyengar R. Go protein as signal transducer in the pertussis toxin-sensitive phosphatidylinositol pathway. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):79–82. doi: 10.1038/343079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offermanns S., Schultz G., Rosenthal W. Evidence for opioid receptor-mediated activation of the G-proteins, Go and Gi2, in membranes of neuroblastoma x glioma (NG108-15) hybrid cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3365–3368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott S., Costa T., Herz A. Opioid receptors of neuroblastoma cells are in two domains of the plasma membrane that differ in content of G proteins. J Neurochem. 1989 Feb;52(2):619–626. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pobiner B. F., Northup J. K., Bauer P. H., Fraser E. D., Garrison J. C. Inhibitory GTP-binding regulatory protein Gi3 can couple angiotensin II receptors to inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in hepatocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;40(2):156–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remmers A. E., Medzihradsky F. Reconstitution of high-affinity opioid agonist binding in brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2171–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roerig S. C., Loh H. H., Law P. Y. Identification of three separate guanine nucleotide-binding proteins that interact with the delta-opioid receptor in NG108-15 neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 May;41(5):822–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof D. J., Applebury M. L., Sternweis P. C. Relationships within the family of GTP-binding proteins isolated from bovine central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16242–16249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senogles S. E., Spiegel A. M., Padrell E., Iyengar R., Caron M. G. Specificity of receptor-G protein interactions. Discrimination of Gi subtypes by the D2 dopamine receptor in a reconstituted system. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4507–4514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Nirenberg M., Klee W. A. Morphine receptors as regulators of adenylate cyclase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Goldsmith P. K., Codina J., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. Gi2 mediates alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in platelet membranes: in situ identification with G alpha C-terminal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suki W. N., Abramowitz J., Mattera R., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. The human genome encodes at least three non-allellic G proteins with alpha i-type subunits. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 10;220(1):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80900-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. J., Gilman A. G. Type-specific regulation of adenylyl cyclase by G protein beta gamma subunits. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1500–1503. doi: 10.1126/science.1962211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger R. Z., Beitner-Johnson D., Sevarino K. A., Crain S. M., Nestler E. J. A general role for adaptations in G-proteins and the cyclic AMP system in mediating the chronic actions of morphine and cocaine on neuronal function. Brain Res. 1991 May 10;548(1-2):100–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91111-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Harada H., Nozaki M., Katada T., Ui M., Satoh M., Takagi H. Reconstitution of rat brain mu opioid receptors with purified guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins, Gi and Go. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):7013–7017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.7013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Misawa H., Katada T., Ui M., Takagi H., Satoh M. Functional reconstruction of purified Gi and Go with mu-opioid receptors in guinea pig striatal membranes pretreated with micromolar concentrations of N-ethylmaleimide. J Neurochem. 1990 Mar;54(3):841–848. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb02328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Uno S., Harada J., Kobayashi I., Katada T., Ui M., Satoh M. Evidence for receptor-mediated inhibition of intrinsic activity of GTP-binding protein, Gi1 and Gi2, but not G0 in reconstitution experiments. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 18;266(1-2):178–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81534-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanDongen A. M., Codina J., Olate J., Mattera R., Joho R., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. Newly identified brain potassium channels gated by the guanine nucleotide binding protein Go. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1433–1437. doi: 10.1126/science.3144040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Barg J., Attali B., Simantov R. Differential effect of mu, delta, and kappa ligands on G protein alpha subunits in cultured brain cells. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Sep;27(1):106–111. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490270116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Y. H., Conklin B. R., Bourne H. R. Gz-mediated hormonal inhibition of cyclic AMP accumulation. Science. 1992 Jan 17;255(5042):339–342. doi: 10.1126/science.1347957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Y. H., Demoliou-Mason C. D., Barnard E. A. Opioid receptors in magnesium-digitonin-solubilized rat brain membranes are tightly coupled to a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding protein. J Neurochem. 1989 Apr;52(4):999–1009. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb01840.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Mattera R., Codina J., Graf R., Okabe K., Padrell E., Iyengar R., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. The G protein-gated atrial K+ channel is stimulated by three distinct Gi alpha-subunits. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):680–682. doi: 10.1038/336680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Eiger S., Duan D. S., Lameh J., Sadée W. Regulation of cyclic AMP by the mu-opioid receptor in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurochem. 1990 Oct;55(4):1390–1396. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb03151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Sadée W. Efficacy and tolerance of narcotic analgesics at the mu opioid receptor in differentiated human neuroblastoma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Apr;245(1):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



