Abstract
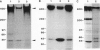
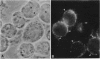
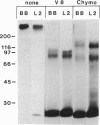
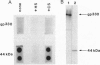
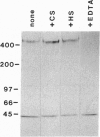
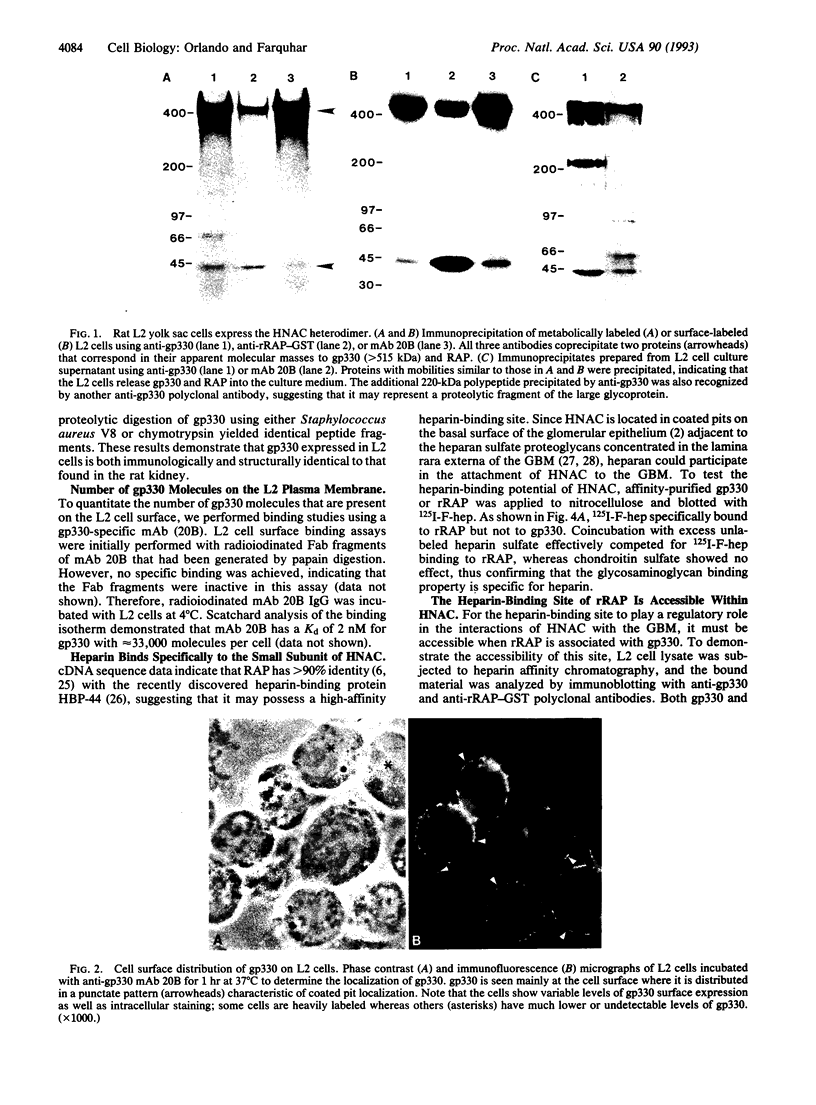
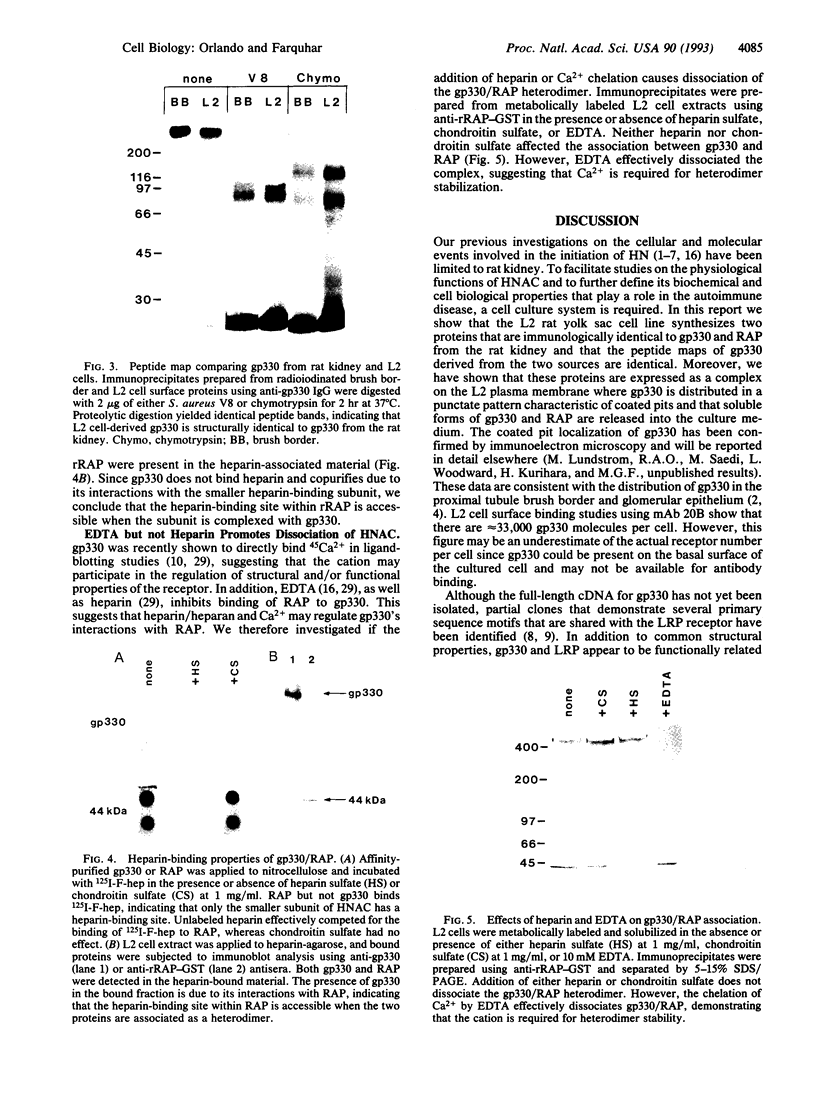
gp330 is a large glycoprotein located in clathrin-coated pits at the surface of the glomerular and proximal tubule epithelia in the rat kidney. It was originally identified as the target of autoimmune antibodies in Heymann nephritis (HN) and has since been shown to be a member of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene family and to form a stable association with receptor-associated protein (RAP), which together constitute the HN antigen complex (HNAC). Progress in defining the normal functions of gp330 as well as the molecular mechanisms of HN has been hampered by the lack of an available kidney cell line that expresses this protein. We here report the identification of a rat yolk sac carcinoma cell line (L2) that synthesizes HNAC and expresses it in coated pits at the cell surface. gp330 and RAP from L2 cells are immunologically identical to their kidney counterparts, and peptide maps of gp330 yielded identical peptide fragments. Characterization of the cell line revealed that there are 3.3 x 10(4) gp330 molecules per L2 cell and that the cells produce a soluble form of gp330 that is released into the medium. Heparin ligand blot analysis demonstrated that RAP but not gp330 binds heparin. By heparin affinity chromatography, gp330 and RAP copurify, indicating that the glycosaminoglycan binding site within RAP is accessible when the subunit is complexed with gp330. These results indicate that the L2 cell line provides a valid and useful model for studies on the function of HNAC and the pathogenesis of HN.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cardin A. D., Weintraub H. J. Molecular modeling of protein-glycosaminoglycan interactions. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Jan-Feb;9(1):21–32. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatelet F., Brianti E., Ronco P., Roland J., Verroust P. Ultrastructural localization by monoclonal antibodies of brush border antigens expressed by glomeruli. I. Renal distribution. Am J Pathol. 1986 Mar;122(3):500–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheresh D. A., Smith J. W., Cooper H. M., Quaranta V. A novel vitronectin receptor integrin (alpha v beta x) is responsible for distinct adhesive properties of carcinoma cells. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen E. I., Gliemann J., Moestrup S. K. Renal tubule gp330 is a calcium binding receptor for endocytic uptake of protein. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Oct;40(10):1481–1490. doi: 10.1177/40.10.1382088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Ozawa M., Huang R. P., Muramatsu T. A heparin binding protein whose expression increases during differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells to parietal endoderm cells: cDNA cloning and sequence analysis. J Biochem. 1990 Aug;108(2):297–302. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glabe C. G., Harty P. K., Rosen S. D. Preparation and properties of fluorescent polysaccharides. Anal Biochem. 1983 Apr 15;130(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90590-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Goldstein J. L., Strickland D. K., Ho Y. K., Brown M. S. 39-kDa protein modulates binding of ligands to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21232–21238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobman T. C., Woodward L., Farquhar M. G. The rubella virus E1 glycoprotein is arrested in a novel post-ER, pre-Golgi compartment. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(4):795–811. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.4.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthöfer H., Sainio K., Miettinen A. Rat glomerular cells do not express podocytic markers when cultured in vitro. Lab Invest. 1991 Nov;65(5):548–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. Immunocytochemical localization of the Heymann nephritis antigen (GP330) in glomerular epithelial cells of normal Lewis rats. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):667–686. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. The pathogenic antigen of Heymann nephritis is a membrane glycoprotein of the renal proximal tubule brush border. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5557–5561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Miettinen A., Farquhar M. G. Initial events in the formation of immune deposits in passive Heymann nephritis. gp330-anti-gp330 immune complexes form in epithelial coated pits and rapidly become attached to the glomerular basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):109–128. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Ullrich R., Diem K., Pietromonaco S., Orlando R. A., Farquhar M. G. Identification of a pathogenic epitope involved in initiation of Heymann nephritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11179–11183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung C. C., Cheewatrakoolpong B., O'Mara T., Black M. Passive Heymann nephritis induced by rabbit antiserum to membrane antigens isolated from rat visceral yolk-sac microvilli. Am J Anat. 1987 Jun;179(2):169–174. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001790209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen A., Dekan G., Farquhar M. G. Monoclonal antibodies against membrane proteins of the rat glomerulus. Immunochemical specificity and immunofluorescence distribution of the antigens. Am J Pathol. 1990 Oct;137(4):929–944. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moestrup S. K., Gliemann J., Pallesen G. Distribution of the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in human tissues. Cell Tissue Res. 1992 Sep;269(3):375–382. doi: 10.1007/BF00353892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlando R. A., Kerjaschki D., Kurihara H., Biemesderfer D., Farquhar M. G. gp330 associates with a 44-kDa protein in the rat kidney to form the Heymann nephritis antigenic complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6698–6702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietromonaco S., Kerjaschki D., Binder S., Ullrich R., Farquhar M. G. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding a major pathogenic domain of the Heymann nephritis antigen gp330. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1811–1815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychowdhury R., Niles J. L., McCluskey R. T., Smith J. A. Autoimmune target in Heymann nephritis is a glycoprotein with homology to the LDL receptor. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1163–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2786251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahali D., Mulliez N., Chatelet F., Dupuis R., Ronco P., Verroust P. Characterization of a 280-kD protein restricted to the coated pits of the renal brush border and the epithelial cells of the yolk sac. Teratogenic effect of the specific monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):213–218. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow J. L., Sawada H., Farquhar M. G. Basement membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans are concentrated in the laminae rarae and in podocytes of the rat renal glomerulus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3296–3300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland D. K., Ashcom J. D., Williams S., Battey F., Behre E., McTigue K., Battey J. F., Argraves W. S. Primary structure of alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor-associated protein. Human homologue of a Heymann nephritis antigen. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13364–13369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewer U. Characterization of a rat yolk sac carcinoma cell line. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):416–421. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willnow T. E., Goldstein J. L., Orth K., Brown M. S., Herz J. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein and gp330 bind similar ligands, including plasminogen activator-inhibitor complexes and lactoferrin, an inhibitor of chylomicron remnant clearance. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):26172–26180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]