Abstract
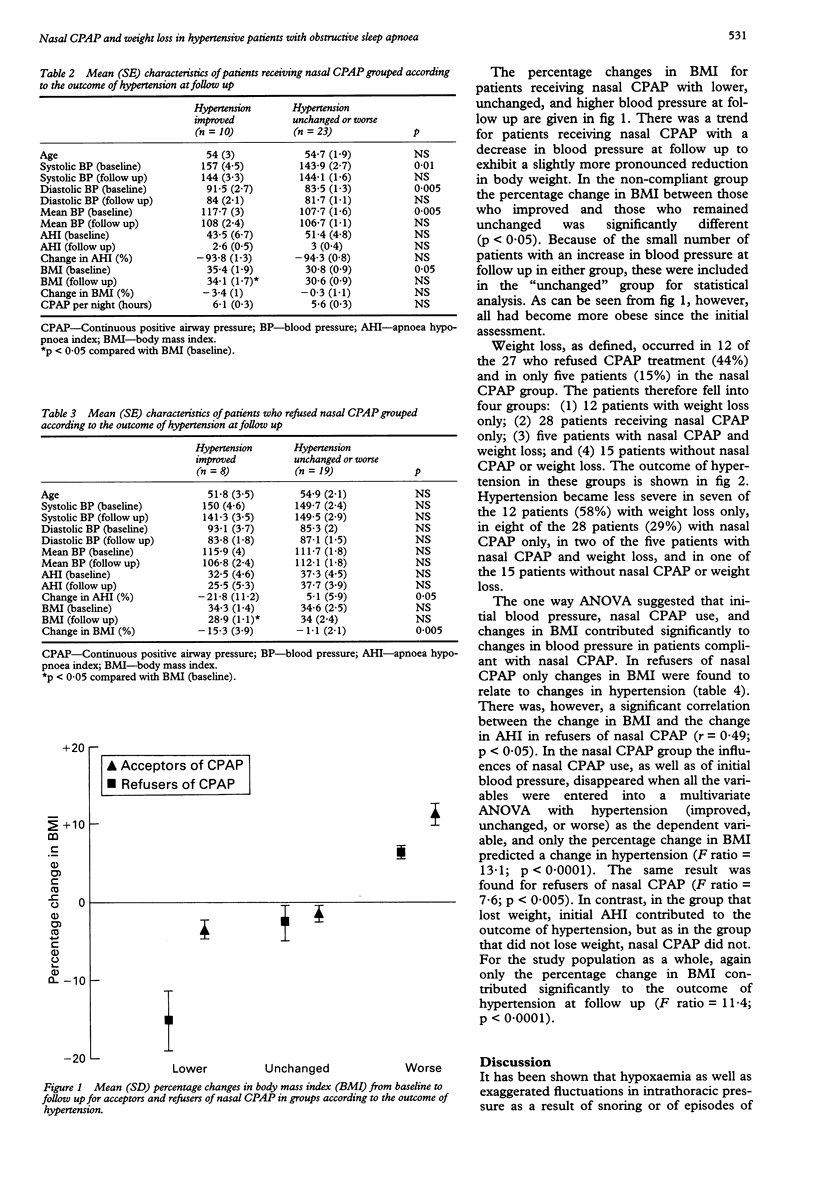
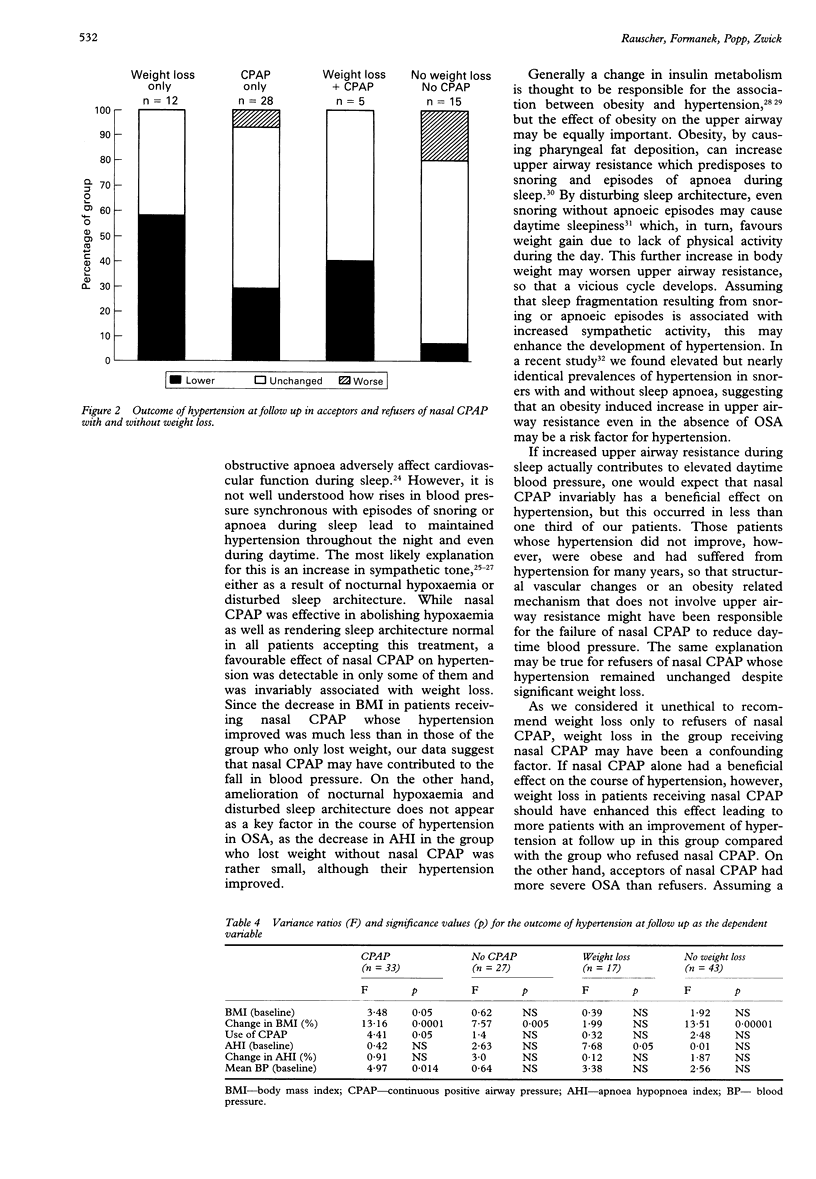
BACKGROUND--The high prevalence of obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) in patients with systemic hypertension and of hypertension in patients with OSA suggests a causal link between the two disorders. This study was carried out to determine whether nasal continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and weight loss affect daytime hypertension in OSA. METHODS--Sixty hypertensive patients with OSA took part in the study; 33 accepted nasal CPAP and used their machine for 5.7 (0.2) hours per night, and the remaining 27 patients refused nasal CPAP and upper airway surgery so the only therapeutic intervention was a recommendation of weight loss. A significant change in hypertension during follow up was defined as either a change in mean blood pressure of at least 10 mm Hg (or more than 8%) without a change in drug treatment, or a reduction in drug dosage with mean blood pressure within these limits. Weight loss was defined as a body mass index of at least 5% below the baseline value. RESULTS--After 512 (41) days, hypertension had become less severe in seven of 12 patients (58%) treated with weight loss only, in eight of 28 patients (29%) with nasal CPAP only, in two of five patients with nasal CPAP and weight loss, and in one of 15 patients without nasal CPAP or weight loss. Multivariate analysis of variance with the outcome of hypertension at follow up as the dependent variable revealed that only the percentage change in body mass index significantly contributed to the course of hypertension. CONCLUSION--The course of hypertension in OSA is more closely linked to weight loss than to elimination of sleep apnoea by nasal CPAP.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubert-Tulkens G., Culée C., Rodenstein D. O. Cure of sleep apnea syndrome after long-term nasal continuous positive airway pressure therapy and weight loss. Sleep. 1989 Jun;12(3):216–222. doi: 10.1093/sleep/12.3.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry D. T., Webb W. B., Block A. J. Sleep apnea syndrome. A critical review of the apnea index as a diagnostic criterion. Chest. 1984 Oct;86(4):529–531. doi: 10.1378/chest.86.4.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charuzi I., Peiser J., Ovnat A., Lavie P. Removal of tracheostomy in a morbidly obese sleep apneic patient after gastric bypass. Sleep. 1986;9(3):449–450. doi: 10.1093/sleep/9.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher E. C., DeBehnke R. D., Lovoi M. S., Gorin A. B. Undiagnosed sleep apnea in patients with essential hypertension. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Aug;103(2):190–195. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-2-190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. S. Plasma catecholamines and essential hypertension. An analytical review. Hypertension. 1983 Jan-Feb;5(1):86–99. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.5.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Stoohs R., Duncan S. Snoring (I). Daytime sleepiness in regular heavy snorers. Chest. 1991 Jan;99(1):40–48. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halverson J. D., Kramer J., Cave A., Permutt A., Santiago J. Altered glucose tolerance, insulin response, and insulin sensitivity after massive weight reduction subsequent to gastric bypass. Surgery. 1982 Aug;92(2):235–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harman E. M., Wynne J. W., Block A. J. The effect of weight loss on sleep-disordered breathing and oxygen desaturation in morbidly obese men. Chest. 1982 Sep;82(3):291–294. doi: 10.1378/chest.82.3.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harman E., Wynne J. W., Block A. J., Malloy-Fisher L. Sleep-disordered breathing and oxygen desaturation in obese patients. Chest. 1981 Mar;79(3):256–260. doi: 10.1378/chest.79.3.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffstein V., Rubinstein I., Mateika S., Slutsky A. S. Determinants of blood pressure in snorers. Lancet. 1988 Oct 29;2(8618):992–994. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90744-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovell M. F. The experimental evidence for weight-loss treatment of essential hypertension: a critical review. Am J Public Health. 1982 Apr;72(4):359–368. doi: 10.2105/ajph.72.4.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kales A., Bixler E. O., Cadieux R. J., Schneck D. W., Shaw L. C., 3rd, Locke T. W., Vela-Bueno A., Soldatos C. R. Sleep apnoea in a hypertensive population. Lancet. 1984 Nov 3;2(8410):1005–1008. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannel W. B., Brand N., Skinner J. J., Jr, Dawber T. R., McNamara P. M. The relation of adiposity to blood pressure and development of hypertension. The Framingham study. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Jul;67(1):48–59. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-1-48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz I., Stradling J., Slutsky A. S., Zamel N., Hoffstein V. Do patients with obstructive sleep apnea have thick necks? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 May;141(5 Pt 1):1228–1231. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.5_Pt_1.1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie P., Ben-Yosef R., Rubin A. E. Prevalence of sleep apnea syndrome among patients with essential hypertension. Am Heart J. 1984 Aug;108(2):373–376. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90628-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugaresi E., Coccagna G., Cirignotta F., Farneti P., Gallassi R., Di Donato G., Verucchi P. Breathing during sleep in man in normal and pathological conditions. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;99:35–45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4009-6_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miall W. E., Lovell H. G. Relation between change of blood pressure and age. Br Med J. 1967 Jun 10;2(5553):660–664. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5553.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modan M., Halkin H., Almog S., Lusky A., Eshkol A., Shefi M., Shitrit A., Fuchs Z. Hyperinsulinemia. A link between hypertension obesity and glucose intolerance. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):809–817. doi: 10.1172/JCI111776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motta J., Guilleminault C., Schroeder J. S., Dement W. C. Tracheostomy and hemodynamic changes in sleep-inducing apnea. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Oct;89(4):454–458. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-4-454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oparil S. The sympathetic nervous system in clinical and experimental hypertension. Kidney Int. 1986 Sep;30(3):437–452. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher H., Popp W., Zwick H. Systemic hypertension in snorers with and without sleep apnea. Chest. 1992 Aug;102(2):367–371. doi: 10.1378/chest.102.2.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. L., Gold A. R., Meyers D. A., Haponik E. F., Bleecker E. R. Weight loss in mildly to moderately obese patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Dec;103(6 ):850–855. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-6-850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugerman H. J., Fairman R. P., Lindeman A. K., Mathers J. A., Greenfield L. J. Gastroplasty for respiratory insufficiency of obesity. Ann Surg. 1981 Jun;193(6):677–685. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198106000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suratt P. M., McTier R. F., Findley L. J., Pohl S. L., Wilhoit S. C. Changes in breathing and the pharynx after weight loss in obstructive sleep apnea. Chest. 1987 Oct;92(4):631–637. doi: 10.1378/chest.92.4.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilkian A. G., Guilleminault C., Schroeder J. S., Lehrman K. L., Simmons F. B., Dement W. C. Hemodynamics in sleep-induced apnea. Studies during wakefulness and sleep. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Dec;85(6):714–719. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-6-714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilkian A. G., Guilleminault C., Schroeder J. S., Lehrman K. L., Simmons F. B., Dement W. C. Hemodynamics in sleep-induced apnea. Studies during wakefulness and sleep. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Dec;85(6):714–719. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-6-714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor D. W., Jr, Sarmiento C. F., Yanta M., Halverson J. D. Obstructive sleep apnea in the morbidly obese. An indication for gastric bypass. Arch Surg. 1984 Aug;119(8):970–972. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1984.01390200086020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. J., Houston D., Finberg S., Lam C., Kinney J. L., Santiago S. Sleep apnea syndrome and essential hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 1985 Apr 1;55(8):1019–1022. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(85)90738-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


