A binuclear bis(carboxylato)dirhenium(III) complex is reported. The compound is a representative of a small class of alkylcarboxylate complexes involving a quadruple metal–metal bonds
Keywords: crystal structure, rhenium(III), cluster, alkylcarboxylate complex, quadruple metal–metal bond, hydrogen bonding
Abstract
The title compound, [Re2(C3H7COO)2Cl4{(CH3)2SO}2], comprises binuclear complex molecules [Re—Re = 2.24502 (13) Å] involving cis-oriented double carboxylate bridges, four equatorial chloride ions and two weakly bonded O atoms from dimethyl sulfoxide ligands in the axial positions at the ReIII atoms. In the crystal, molecules are linked into corrugated layers parallel to (101) by very weak C—H⋯Cl and C—H⋯O hydrogen-bonding interactions. C—H⋯Cl hydrogen bonding provides the links between layers to consolidate a three-dimensional framework.
Chemical context
Binuclear rhenium(III) clusters are classical complexes with a unique quadruple metal–metal bond (Cotton et al., 2005 ▸, Golichenko & Shtemenko, 2006 ▸). In our previous work we have shown that such compounds with chloride and alkylcarboxylate equatorial ligands exhibit antitumor, antiradical and hepato- and nephroprotective biological activity with low toxicity (Dimitrov et al., 1978 ▸, Shtemenko et al., 2007 ▸, 2008 ▸, 2009 ▸, 2013 ▸).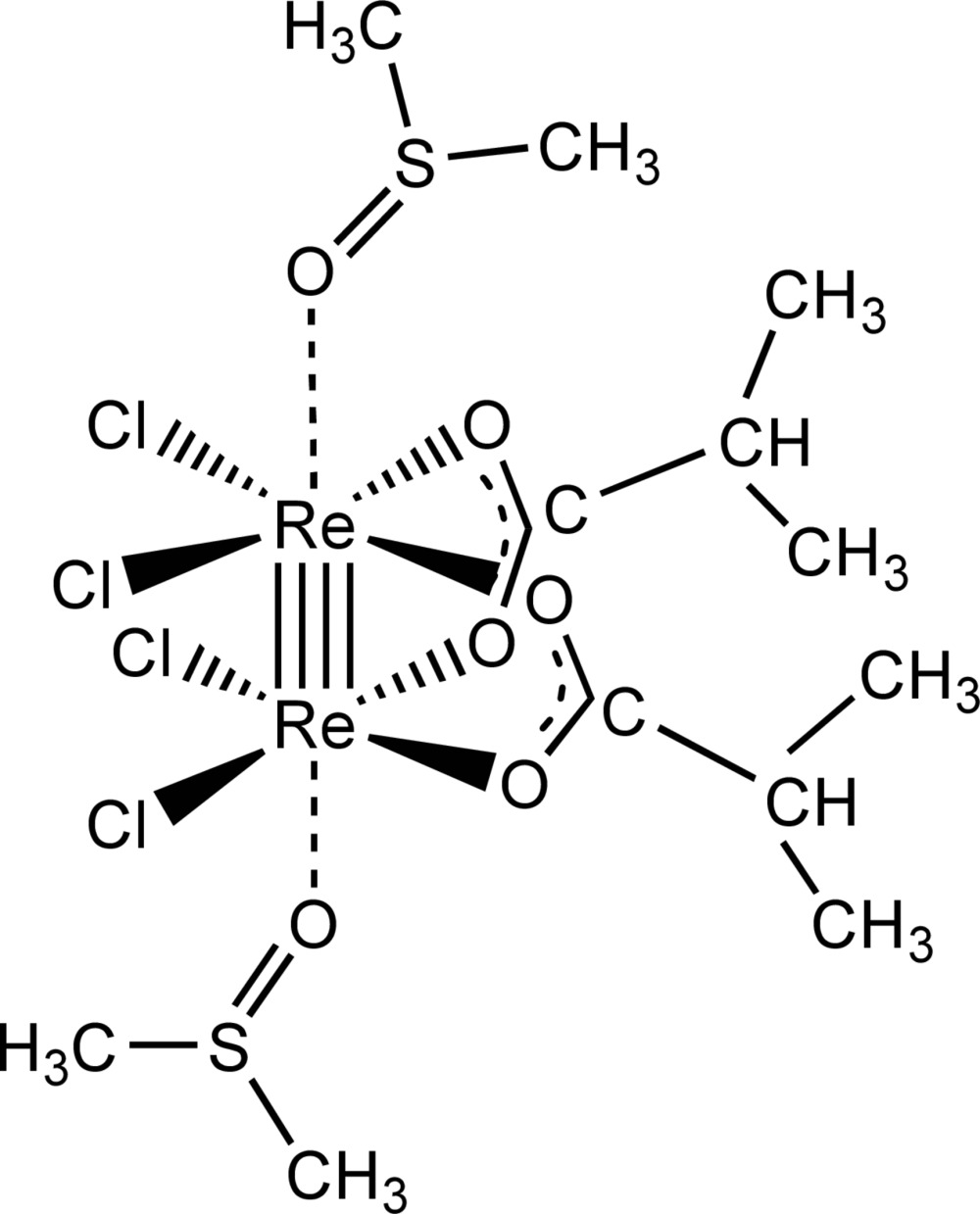
Labile axial ligands and equatorial chloride groups are the reactive centers in interactions with other chemical compounds and biological macromolecules in vitro and in vivo (Shtemenko et al., 2013 ▸). In this context, we present the synthesis and the structure of the title dirhenium(III) complex with isobutyrate equatorial ligands as biologically active groups, which can exhibit antitumor activity in the tetracarboxylate compound Re2(i-C3H7COO)4Cl2 (Shtemenko et al., 2007 ▸).
Structural commentary
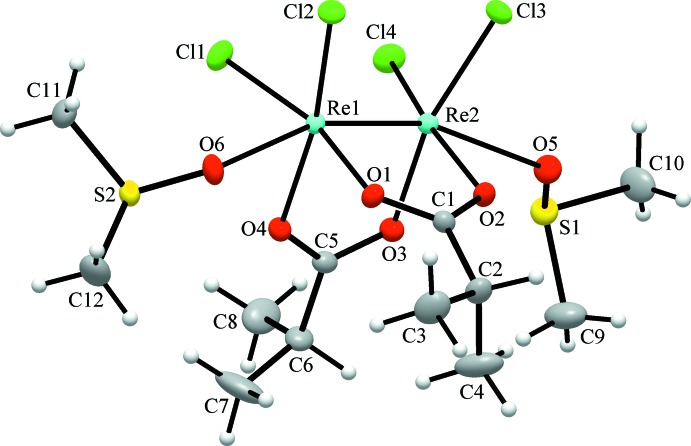
The quadruple Re—Re bond [2.24502 (13) Å] is typical for related dicarboxylato clusters (Cotton et al., 2005 ▸, Shtemenko et al., 2009 ▸) and the coordination of each of the rhenium ions also comprises two chlorides and two oxygen atoms of carboxylate ligands (Fig. 1 ▸). The distorted octahedral coordination geometry of Re1 and Re2 is completed by weakly bonded oxygen atoms from dimethyl sulfoxide ligands [Re1—O6 = 2.3282 (15) and Re2—O5 = 2.3938 (15) Å], in trans-positions to the Re—Re bond. This may be compared with a similar weak binding of N- or O-donors, which is characteristic of dicarboxylatodirhenium compounds (Bera et al., 2003 ▸, Shtemenko et al., 2009 ▸, Golichenko et al., 2015 ▸).
Figure 1.
The structure of cis-Re2Cl4{i-C3H7COO}2·2(CH3)2SO, showing displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are shown as small spheres of arbitrary radii.
Supramolecular features
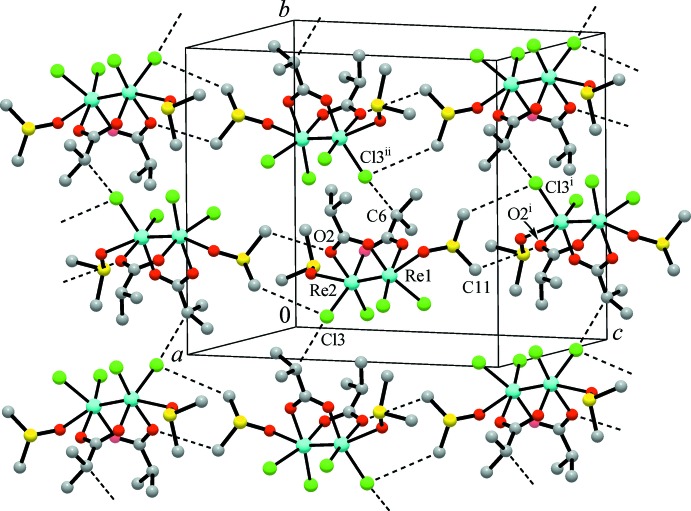
Intermolecular bonding is only very weak: it comprises distal, though relatively directional, C—H⋯O and C—H⋯Cl hydrogen-bond interactions between the methine- and methyl-H of the carboxylate and DMSO ligands (Table 1 ▸). The shortest bonds found for the chloride acceptors are C6—H6⋯Cl3ii [C6⋯Cl3ii = 3.519 (2) Å; symmetry code (ii):  − x,
− x,  + y,
+ y,  − z], which unite the molecules into chains along the b axis (Fig. 2 ▸). The hydrogen bonds adopted by two methyl groups of DMSO molecules (referenced by a sulfur atoms S2) assemble these chains into corrugated layers parallel to (101). A very weak bond of this type is found also between adjacent layers: C12⋯Cl2iii = 3.751 (3) Å; symmetry code (iii): −
− z], which unite the molecules into chains along the b axis (Fig. 2 ▸). The hydrogen bonds adopted by two methyl groups of DMSO molecules (referenced by a sulfur atoms S2) assemble these chains into corrugated layers parallel to (101). A very weak bond of this type is found also between adjacent layers: C12⋯Cl2iii = 3.751 (3) Å; symmetry code (iii): − − x,
− x,  + y,
+ y,  − z] (Table 1 ▸). The latter extends the structure into a third direction and provides the formation of a hydrogen-bonded framework.
− z] (Table 1 ▸). The latter extends the structure into a third direction and provides the formation of a hydrogen-bonded framework.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C11H11BO2i | 0.98 | 2.40 | 3.324(3) | 156 |
| C6H6Cl3ii | 1.00 | 2.73 | 3.519(2) | 136 |
| C12H12ACl2iii | 0.98 | 2.82 | 3.751(3) | 159 |
| C12H12BCl3i | 0.98 | 2.82 | 3.760(3) | 161 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 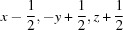 ; (ii)
; (ii) 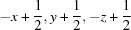 ; (iii)
; (iii) 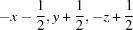 .
.
Figure 2.
A fragment of the structure, showing weak C—H⋯O and C—H⋯Cl hydrogen-bond interactions (dashed lines), which assemble the molecules into corrugated layers parallel to (101). [Symmetry codes: (i) − + x,
+ x,  − y,
− y,  + z; (ii)
+ z; (ii)  − x,
− x,  + y,
+ y,  − z.]
− z.]
Synthesis and crystallization
[NBu4]2[Re2Cl8] (0.2 g, 0.175 mmol) was added to isobutyric acid (10 ml). The mixture was heated for 3 h in a water bath under an inert atmosphere. DMSO (0.5 ml) was then added to the resulting blue solution at room temperature. A dark-blue crystalline product (0.12 g, yield 81%) was obtained after 12 h, was collected by filtration and dried in air.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. All H were refined using a riding-model approximation, with C—H = 0.98–1.00 Å, and with U
iso(H) = 1.2U
eq(C) or 1.5U
eq(C) for methyl H atoms. A rotating model was used for the methyl groups. Six outliers (2 6 1, 3 3 3, 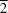 4 3, 0 1 1,
4 3, 0 1 1, 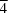 3 4, 3 3 7) were omitted in the last cycles of refinement.
3 4, 3 3 7) were omitted in the last cycles of refinement.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Re2(C4H7O2)2Cl4(C2H6OS)2] |
| M r | 844.65 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 110 |
| a, b, c () | 10.5581(4), 14.7406(5), 15.6088(6) |
| () | 100.794(2) |
| V (3) | 2386.26(15) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo K |
| (mm1) | 10.78 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.22 0.18 0.09 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Siemens SMART CCD area-detector |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.133, 0.478 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2(I)] reflections | 93039, 14497, 11921 |
| R int | 0.040 |
| (sin /)max (1) | 0.909 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.025, 0.049, 1.00 |
| No. of reflections | 14497 |
| No. of parameters | 243 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| max, min (e 3) | 1.71, 1.14 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017429/rz5165sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017429/rz5165Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1425634
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the fund Grant for Science Research (No. 0111U000111) from the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine. We also thank COST Action CM 1105 for supporting this study. We thank Joseph H. Reibenspies (Texas A&M University, College Station, USA) and Professor Konstantin V. Domasevitch (National Taras Shevchenko University of Kyiv, Ukraine) for providing facilities for a portion of these studies, and helpful discussions.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| [Re2(C4H7O2)2Cl4(C2H6OS)2] | F(000) = 1584 |
| Mr = 844.65 | Dx = 2.351 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 10.5581 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 9919 reflections |
| b = 14.7406 (5) Å | θ = 2.4–39.0° |
| c = 15.6088 (6) Å | µ = 10.78 mm−1 |
| β = 100.794 (2)° | T = 110 K |
| V = 2386.26 (15) Å3 | Plate, blue |
| Z = 4 | 0.22 × 0.18 × 0.09 mm |
Data collection
| Siemens SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 11921 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.040 |
| phi and ω scans | θmax = 40.2°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | h = −19→18 |
| Tmin = 0.133, Tmax = 0.478 | k = −25→26 |
| 93039 measured reflections | l = −28→27 |
| 14497 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.025 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.049 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0183P)2 + 1.7981P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.00 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 14497 reflections | Δρmax = 1.71 e Å−3 |
| 243 parameters | Δρmin = −1.14 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Re1 | −0.06723 (2) | 0.17363 (2) | 0.27880 (2) | 0.01130 (2) | |
| Re2 | 0.10986 (2) | 0.16371 (2) | 0.21905 (2) | 0.01147 (2) | |
| Cl1 | −0.01954 (5) | 0.08982 (4) | 0.40554 (3) | 0.02107 (9) | |
| Cl2 | −0.19965 (5) | 0.05974 (3) | 0.21084 (3) | 0.01810 (8) | |
| Cl3 | 0.06421 (5) | 0.04494 (3) | 0.12210 (3) | 0.01726 (8) | |
| Cl4 | 0.25202 (5) | 0.07759 (3) | 0.31739 (3) | 0.02151 (9) | |
| S1 | 0.41251 (5) | 0.24240 (4) | 0.20176 (3) | 0.01935 (9) | |
| S2 | −0.23871 (5) | 0.25929 (3) | 0.42297 (3) | 0.01756 (9) | |
| O1 | −0.14493 (13) | 0.26371 (9) | 0.18365 (9) | 0.0142 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.02927 (14) | 0.25241 (9) | 0.12399 (9) | 0.0145 (2) | |
| O3 | 0.18421 (14) | 0.27603 (9) | 0.28722 (9) | 0.0159 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.01121 (14) | 0.28533 (9) | 0.34802 (9) | 0.0158 (3) | |
| O5 | 0.28531 (14) | 0.20575 (10) | 0.14988 (10) | 0.0189 (3) | |
| O6 | −0.24413 (14) | 0.23612 (10) | 0.32675 (9) | 0.0189 (3) | |
| C1 | −0.07803 (18) | 0.29012 (12) | 0.12848 (12) | 0.0133 (3) | |
| C2 | −0.1181 (2) | 0.37225 (13) | 0.07331 (14) | 0.0181 (4) | |
| H2 | −0.1090 | 0.3585 | 0.0120 | 0.022* | |
| C3 | −0.2560 (2) | 0.40050 (17) | 0.07314 (17) | 0.0274 (5) | |
| H3A | −0.2788 | 0.4516 | 0.0330 | 0.041* | |
| H3B | −0.2647 | 0.4188 | 0.1321 | 0.041* | |
| H3C | −0.3138 | 0.3494 | 0.0542 | 0.041* | |
| C4 | −0.0227 (3) | 0.44808 (16) | 0.1087 (2) | 0.0354 (6) | |
| H4A | 0.0658 | 0.4260 | 0.1125 | 0.053* | |
| H4B | −0.0358 | 0.4662 | 0.1668 | 0.053* | |
| H4C | −0.0371 | 0.5004 | 0.0694 | 0.053* | |
| C5 | 0.1204 (2) | 0.31512 (13) | 0.33854 (12) | 0.0152 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.1796 (2) | 0.39547 (14) | 0.38935 (14) | 0.0197 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.2283 | 0.4313 | 0.3518 | 0.024* | |
| C7 | 0.0785 (3) | 0.4565 (2) | 0.4167 (2) | 0.0469 (8) | |
| H7A | 0.0176 | 0.4764 | 0.3649 | 0.070* | |
| H7B | 0.1206 | 0.5095 | 0.4476 | 0.070* | |
| H7C | 0.0321 | 0.4229 | 0.4554 | 0.070* | |
| C8 | 0.2750 (3) | 0.36103 (19) | 0.46883 (17) | 0.0337 (6) | |
| H8A | 0.3380 | 0.3207 | 0.4495 | 0.051* | |
| H8B | 0.2282 | 0.3276 | 0.5074 | 0.051* | |
| H8C | 0.3200 | 0.4127 | 0.5004 | 0.051* | |
| C9 | 0.4146 (3) | 0.36054 (17) | 0.1775 (2) | 0.0360 (6) | |
| H9A | 0.4047 | 0.3689 | 0.1143 | 0.054* | |
| H9B | 0.4968 | 0.3868 | 0.2065 | 0.054* | |
| H9C | 0.3435 | 0.3908 | 0.1984 | 0.054* | |
| C10 | 0.5306 (2) | 0.20667 (18) | 0.14113 (18) | 0.0291 (5) | |
| H10A | 0.5367 | 0.1403 | 0.1425 | 0.044* | |
| H10B | 0.6144 | 0.2329 | 0.1669 | 0.044* | |
| H10C | 0.5057 | 0.2272 | 0.0806 | 0.044* | |
| C11 | −0.3361 (3) | 0.17496 (16) | 0.46035 (17) | 0.0286 (5) | |
| H11A | −0.4191 | 0.1709 | 0.4200 | 0.043* | |
| H11B | −0.3508 | 0.1913 | 0.5186 | 0.043* | |
| H11C | −0.2922 | 0.1162 | 0.4631 | 0.043* | |
| C12 | −0.3441 (3) | 0.35344 (17) | 0.42132 (18) | 0.0338 (6) | |
| H12A | −0.3087 | 0.4057 | 0.3950 | 0.051* | |
| H12B | −0.3529 | 0.3685 | 0.4811 | 0.051* | |
| H12C | −0.4289 | 0.3381 | 0.3870 | 0.051* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Re1 | 0.01040 (3) | 0.01222 (3) | 0.01171 (3) | −0.00114 (2) | 0.00320 (2) | 0.00002 (2) |
| Re2 | 0.00953 (3) | 0.01154 (3) | 0.01360 (3) | 0.00081 (2) | 0.00288 (2) | 0.00041 (2) |
| Cl1 | 0.0222 (2) | 0.0241 (2) | 0.0166 (2) | −0.00111 (18) | 0.00305 (17) | 0.00674 (16) |
| Cl2 | 0.0161 (2) | 0.01640 (19) | 0.0219 (2) | −0.00426 (15) | 0.00380 (17) | −0.00305 (15) |
| Cl3 | 0.0169 (2) | 0.01521 (19) | 0.0201 (2) | 0.00138 (15) | 0.00460 (16) | −0.00402 (14) |
| Cl4 | 0.0167 (2) | 0.0215 (2) | 0.0244 (2) | 0.00463 (17) | −0.00088 (18) | 0.00541 (17) |
| S1 | 0.0130 (2) | 0.0223 (2) | 0.0230 (2) | −0.00283 (17) | 0.00407 (18) | −0.00136 (17) |
| S2 | 0.0194 (2) | 0.0189 (2) | 0.0162 (2) | −0.00284 (17) | 0.00824 (17) | −0.00281 (15) |
| O1 | 0.0120 (6) | 0.0153 (6) | 0.0159 (6) | 0.0000 (5) | 0.0041 (5) | 0.0022 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0133 (6) | 0.0153 (6) | 0.0157 (6) | 0.0025 (5) | 0.0048 (5) | 0.0026 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0136 (6) | 0.0161 (6) | 0.0186 (6) | −0.0023 (5) | 0.0044 (5) | −0.0023 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0156 (7) | 0.0163 (6) | 0.0162 (6) | −0.0038 (5) | 0.0050 (5) | −0.0034 (5) |
| O5 | 0.0108 (6) | 0.0225 (7) | 0.0238 (7) | −0.0020 (5) | 0.0040 (5) | −0.0011 (5) |
| O6 | 0.0164 (7) | 0.0255 (7) | 0.0167 (7) | −0.0009 (5) | 0.0076 (5) | −0.0038 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0134 (8) | 0.0128 (7) | 0.0135 (8) | 0.0015 (6) | 0.0022 (6) | −0.0002 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0175 (9) | 0.0170 (8) | 0.0199 (9) | 0.0037 (7) | 0.0034 (7) | 0.0046 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0184 (10) | 0.0275 (11) | 0.0353 (13) | 0.0065 (8) | 0.0025 (9) | 0.0084 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0254 (12) | 0.0162 (10) | 0.0617 (18) | −0.0007 (8) | 0.0004 (12) | 0.0048 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0161 (9) | 0.0132 (8) | 0.0155 (8) | −0.0013 (6) | 0.0015 (7) | −0.0012 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0206 (10) | 0.0179 (9) | 0.0204 (9) | −0.0062 (7) | 0.0028 (7) | −0.0044 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0375 (16) | 0.0298 (14) | 0.072 (2) | −0.0008 (11) | 0.0079 (15) | −0.0319 (14) |
| C8 | 0.0341 (14) | 0.0370 (14) | 0.0254 (12) | −0.0122 (11) | −0.0065 (10) | −0.0026 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0340 (14) | 0.0203 (11) | 0.0549 (17) | −0.0051 (10) | 0.0113 (13) | −0.0022 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0134 (9) | 0.0340 (13) | 0.0412 (14) | 0.0010 (8) | 0.0083 (9) | −0.0067 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0379 (14) | 0.0239 (11) | 0.0294 (12) | −0.0072 (9) | 0.0206 (11) | −0.0015 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0494 (17) | 0.0237 (11) | 0.0322 (13) | 0.0104 (11) | 0.0172 (12) | −0.0002 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Re1—O1 | 2.0459 (13) | C3—H3C | 0.9800 |
| Re1—O4 | 2.0565 (13) | C4—H4A | 0.9800 |
| Re1—Re2 | 2.2450 (1) | C4—H4B | 0.9800 |
| Re1—Cl1 | 2.3065 (5) | C4—H4C | 0.9800 |
| Re1—Cl2 | 2.3115 (5) | C5—C6 | 1.495 (3) |
| Re1—O6 | 2.3282 (15) | C6—C7 | 1.517 (4) |
| Re2—O2 | 2.0401 (13) | C6—C8 | 1.531 (3) |
| Re2—O3 | 2.0437 (14) | C6—H6 | 1.0000 |
| Re2—Cl3 | 2.3052 (5) | C7—H7A | 0.9800 |
| Re2—Cl4 | 2.3147 (5) | C7—H7B | 0.9800 |
| Re2—O5 | 2.3938 (15) | C7—H7C | 0.9800 |
| S1—O5 | 1.5310 (15) | C8—H8A | 0.9800 |
| S1—C10 | 1.780 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.9800 |
| S1—C9 | 1.783 (3) | C8—H8C | 0.9800 |
| S2—O6 | 1.5308 (15) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| S2—C12 | 1.776 (3) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| S2—C11 | 1.780 (2) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| O1—C1 | 1.273 (2) | C10—H10A | 0.9800 |
| O2—C1 | 1.276 (2) | C10—H10B | 0.9800 |
| O3—C5 | 1.276 (2) | C10—H10C | 0.9800 |
| O4—C5 | 1.268 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.500 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.514 (3) | C11—H11C | 0.9800 |
| C2—C4 | 1.536 (3) | C12—H12A | 0.9800 |
| C2—H2 | 1.0000 | C12—H12B | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9800 | C12—H12C | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3B | 0.9800 | ||
| O1—Re1—O4 | 85.93 (6) | C2—C3—H3C | 109.5 |
| O1—Re1—Re2 | 89.58 (4) | H3A—C3—H3C | 109.5 |
| O4—Re1—Re2 | 89.18 (4) | H3B—C3—H3C | 109.5 |
| O1—Re1—Cl1 | 164.51 (4) | C2—C4—H4A | 109.5 |
| O4—Re1—Cl1 | 88.65 (4) | C2—C4—H4B | 109.5 |
| Re2—Re1—Cl1 | 104.857 (14) | H4A—C4—H4B | 109.5 |
| O1—Re1—Cl2 | 90.71 (4) | C2—C4—H4C | 109.5 |
| O4—Re1—Cl2 | 166.43 (4) | H4A—C4—H4C | 109.5 |
| Re2—Re1—Cl2 | 103.960 (13) | H4B—C4—H4C | 109.5 |
| Cl1—Re1—Cl2 | 91.189 (19) | O4—C5—O3 | 121.00 (17) |
| O1—Re1—O6 | 74.92 (5) | O4—C5—C6 | 120.74 (18) |
| O4—Re1—O6 | 77.45 (6) | O3—C5—C6 | 118.24 (18) |
| Re2—Re1—O6 | 160.04 (4) | C5—C6—C7 | 111.87 (19) |
| Cl1—Re1—O6 | 89.75 (4) | C5—C6—C8 | 108.26 (18) |
| Cl2—Re1—O6 | 88.98 (4) | C7—C6—C8 | 111.1 (2) |
| O2—Re2—O3 | 85.80 (6) | C5—C6—H6 | 108.5 |
| O2—Re2—Re1 | 89.66 (4) | C7—C6—H6 | 108.5 |
| O3—Re2—Re1 | 89.97 (4) | C8—C6—H6 | 108.5 |
| O2—Re2—Cl3 | 90.11 (4) | C6—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| O3—Re2—Cl3 | 165.87 (4) | C6—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| Re1—Re2—Cl3 | 103.544 (13) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| O2—Re2—Cl4 | 164.60 (4) | C6—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| O3—Re2—Cl4 | 87.76 (4) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| Re1—Re2—Cl4 | 104.318 (15) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| Cl3—Re2—Cl4 | 92.789 (18) | C6—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| O2—Re2—O5 | 76.03 (5) | C6—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| O3—Re2—O5 | 76.76 (5) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| Re1—Re2—O5 | 161.00 (4) | C6—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| Cl3—Re2—O5 | 89.13 (4) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| Cl4—Re2—O5 | 88.89 (4) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| O5—S1—C10 | 104.28 (10) | S1—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| O5—S1—C9 | 106.08 (12) | S1—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C10—S1—C9 | 97.94 (14) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| O6—S2—C12 | 104.59 (11) | S1—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| O6—S2—C11 | 104.36 (10) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C12—S2—C11 | 98.71 (14) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C1—O1—Re1 | 119.46 (12) | S1—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C1—O2—Re2 | 119.54 (12) | S1—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C5—O3—Re2 | 119.74 (13) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C5—O4—Re1 | 120.10 (13) | S1—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| S1—O5—Re2 | 121.94 (8) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| S2—O6—Re1 | 121.25 (8) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| O1—C1—O2 | 121.00 (17) | S2—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 120.20 (17) | S2—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 118.55 (17) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 112.98 (18) | S2—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C4 | 106.60 (17) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C4 | 111.48 (19) | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 108.6 | S2—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 108.6 | S2—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C4—C2—H2 | 108.6 | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 109.5 | S2—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3B | 109.5 | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 109.5 | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C11—H11B···O2i | 0.98 | 2.40 | 3.324 (3) | 156 |
| C6—H6···Cl3ii | 1.00 | 2.73 | 3.519 (2) | 136 |
| C12—H12A···Cl2iii | 0.98 | 2.82 | 3.751 (3) | 159 |
| C12—H12B···Cl3i | 0.98 | 2.82 | 3.760 (3) | 161 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ii) −x+1/2, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) −x−1/2, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
References
- Bera, J. K., Vo, T.-T., Walton, R. A. & Dunbar, K. R. (2003). Polyhedron, 22, 3009–3014.
- Brandenburg, K. (1999). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2008). SADABS, APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cotton, F. A., Murillo, C. A. & Walton, R. A. (2005). Multiple Bonds between Metal Atoms, 3rd ed., pp. 271–376. New York: Springer Science and Business Media Inc.
- Dimitrov, N. V. & Eastland, G. W. (1978). Current Chemotherapy, edited by W. Siegenthaler & R. Luthy, Vol. 2, pp. 1319–1321. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology Publishing.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Golichenko, A. A., Domasevitch, K. V., Kytova, D. E. & Shtemenko, A. V. (2015). Acta Cryst. E71, 45–47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Golichenko, A. A. & Shtemenko, A. V. (2006). Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 32, 242–249.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Shtemenko, N. I., Chifotides, H. T., Domasevitch, K. V., Golichenko, A. A., Babiy, S. A., Li, Z., Paramonova, K. V., Shtemenko, A. V. & Dunbar, K. R. (2013). J. Inorg. Biochem. 129, 127–134. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shtemenko, N., Collery, P. & Shtemenko, A. (2007). Anticancer Res. 27, 2487–2492. [PubMed]
- Shtemenko, A. V., Collery, P., Shtemenko, N. I., Domasevitch, K. V., Zabitskaya, E. D. & Golichenko, A. A. (2009). Dalton Trans. pp. 5132–5136. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shtemenko, A., Golichenko, A., Tretyak, S., Shtemenko, N. & Randarevich, M. (2008). Metal Ions in Biology and Medicine, Vol. 10, pp. 229–234. Paris: John Libbey Eurotext.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017429/rz5165sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017429/rz5165Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1425634
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report