Abstract
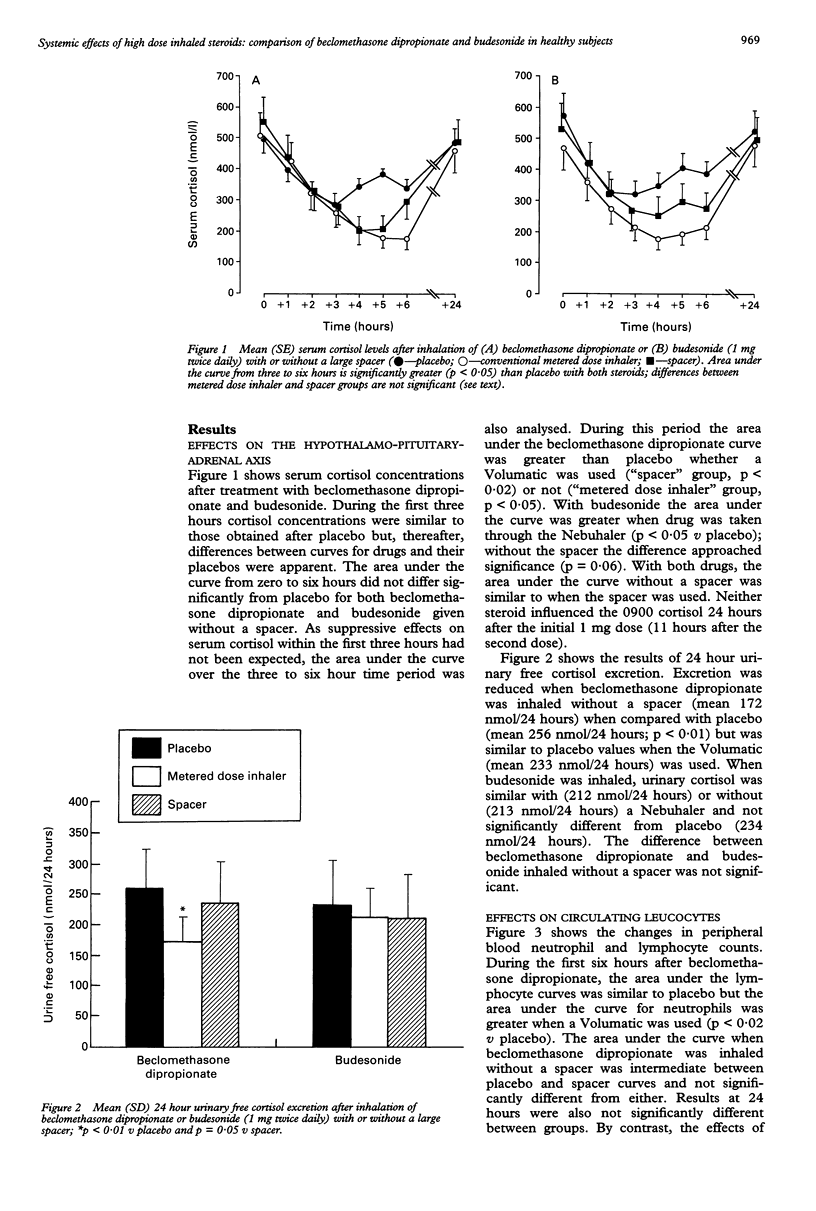
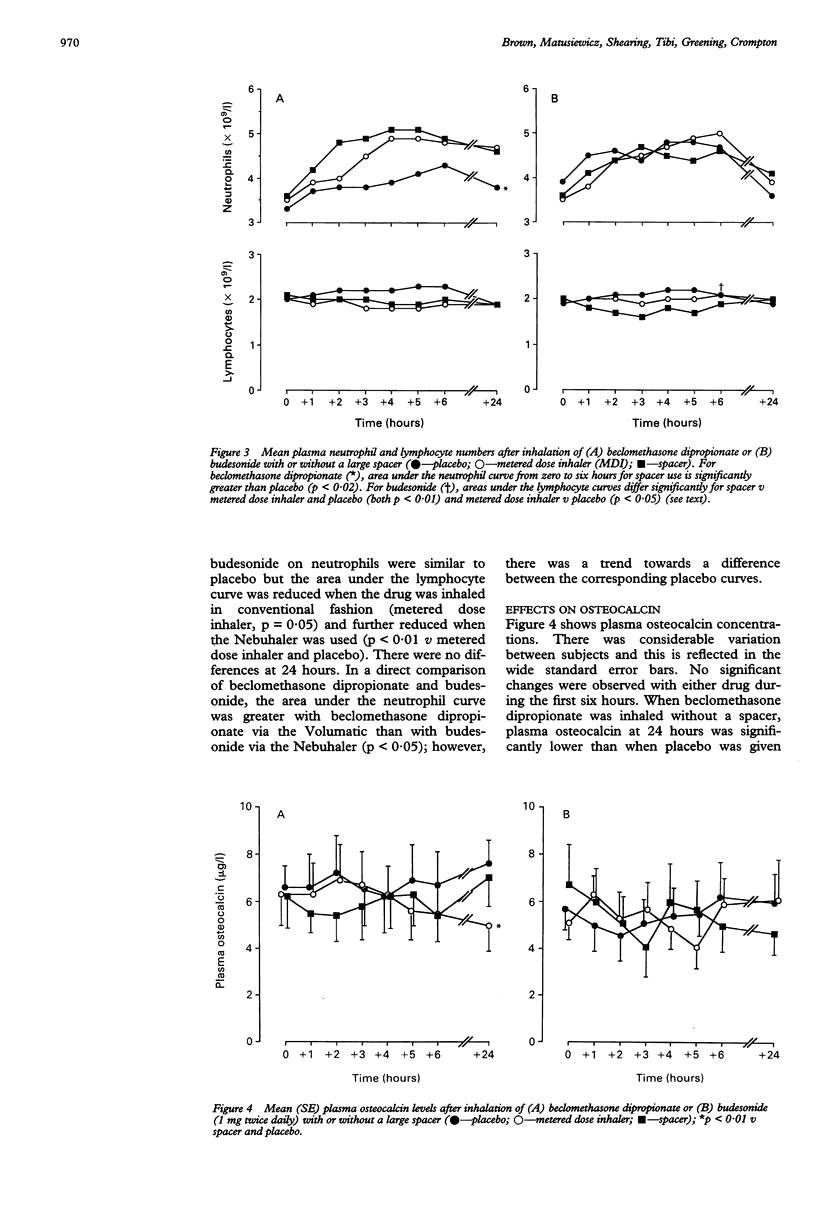
ACKGROUND--Systemic absorption of inhaled corticosteroids may adversely influence the function of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis, bone metabolism, and circulating leucocytes. These changes can be used to assess the safety of different types and modes of administration of these drugs. METHODS--The study was a randomised, double dummy, crossover design with nine healthy adults. It compared the effects of beclomethasone dipropionate and budesonide (given by metered dose aerosols with and without their respective large volume spacers (Volumatic and Nebuhaler) attached) on serum cortisol, 24 hour urinary free cortisol, and plasma osteocalcin concentrations, and circulating neutrophils and lymphocytes. Subjects inhaled the drug (1 mg) and matching placebo at 0900 and 2200 hours on each of six study days. Blood samples were taken hourly for six hours after the morning dose and at the end of the study period. RESULTS--All results were within the reference ranges. Both drugs caused similar reductions in serum cortisol four to six hours after inhalation. These changes were not affected by the use of a large spacer and did not persist at 24 hours. Use of spacers tended to increase the haematological effects of the steroids. Beclomethasone dipropionate inhaled through a Volumatic provoked a rise in circulating neutrophils compared with placebo although lymphocyte numbers were unaffected. Budesonide did not influence neutrophil numbers but did reduce circulating lymphocytes, numbers of which were further reduced when the Nebuhaler was used. There were no significant changes in plasma osteocalcin concentration or 24 hour urinary free cortisol excretion with budesonide, with or without a spacer. Beclomethasone dipropionate inhaled without a spacer reduced urinary cortisol and plasma osteocalcin at 24 hours; however, use of the Volumatic protected against these effects. CONCLUSIONS--Attaching a Volumatic reduces the systemic effects of 2 mg aerosol beclomethasone dipropionate on the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis and circulating osteocalcin concentrations. This study did not establish whether the Nebuhaler reduces the systemic effects of budesonide. When large spacers are used, 2 mg per day of beclomethasone dipropionate and budesonide seem to be equivalent in terms of unwanted effects.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali N. J., Capewell S., Ward M. J. Bone turnover during high dose inhaled corticosteroid treatment. Thorax. 1991 Mar;46(3):160–164. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.3.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. P., Delmas P. D., Malaval L., Edouard C., Chapuy M. C., Meunier P. J. Serum bone Gla-protein: a specific marker for bone formation in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Lancet. 1984 May 19;1(8386):1091–1093. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92506-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. H., Blundell G., Greening A. P., Crompton G. K. Do large volume spacer devices reduce the systemic effects of high dose inhaled corticosteroids? Thorax. 1990 Oct;45(10):736–739. doi: 10.1136/thx.45.10.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. H., Blundell G., Greening A. P., Crompton G. K. High dose inhaled steroid therapy and the cortisol stress response to acute severe asthma. Respir Med. 1992 Nov;86(6):495–497. doi: 10.1016/s0954-6111(96)80009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. H., Blundell G., Greening A. P., Crompton G. K. Screening for hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression in asthmatics taking high dose inhaled corticosteroids. Respir Med. 1991 Nov;85(6):511–516. doi: 10.1016/s0954-6111(06)80269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. H., Greening A. P., Crompton G. K. Large volume spacer devices and the influence of high dose beclomethasone dipropionate on hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis function. Thorax. 1993 Mar;48(3):233–238. doi: 10.1136/thx.48.3.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmas P. D., Malaval L., Arlot M. E., Meunier P. J. Serum bone Gla-protein compared to bone histomorphometry in endocrine diseases. Bone. 1985;6(5):339–341. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(85)90326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebden P., Jenkins A., Houston G., Davies B. H. Comparison of two high dose corticosteroid aerosol treatments, beclomethasone dipropionate (1500 micrograms/day) and budesonide (1600 micrograms/day), for chronic asthma. Thorax. 1986 Nov;41(11):869–874. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.11.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer M., Francis A. J., Pearce S. J. Morning serum cortisol concentrations after 2 mg inhaled beclomethasone dipropionate in normal subjects: effect of a 750 ml spacing device. Thorax. 1990 Oct;45(10):740–742. doi: 10.1136/thx.45.10.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Carrasco M., Gruson M., de Vernejoul M. C., Denne M. A., Miravet L. Osteocalcin and bone morphometric parameters in adults without bone disease. Calcif Tissue Int. 1988 Jan;42(1):13–17. doi: 10.1007/BF02555833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes D. M. Inhaled corticosteroids: benefits and risks. Thorax. 1992 Jun;47(6):404–407. doi: 10.1136/thx.47.6.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundberg C. M., Markowitz M. E., Mizruchi M., Rosen J. F. Osteocalcin in human serum: a circadian rhythm. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Apr;60(4):736–739. doi: 10.1210/jcem-60-4-736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodsman A. B., Toogood J. H., Jennings B., Fraher L. J., Baskerville J. C. Differential effects of inhaled budesonide and oral prednisolone on serum osteocalcin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Mar;72(3):530–540. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-3-530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings B. H., Andersson K. E., Johansson S. A. Assessment of systemic effects of inhaled glucocorticosteroids: comparison of the effects of inhaled budesonide and oral prednisolone on adrenal function and markers of bone turnover. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1991;40(1):77–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00315143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S. A., Andersson K. E., Brattsand R., Gruvstad E., Hedner P. Topical and systemic glucocorticoid potencies of budesonide and beclomethasone dipropionate in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1982;22(6):523–529. doi: 10.1007/BF00609625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S. A., Andersson K. E., Brattsand R., Gruvstad E., Hedner P. Topical and systemic glucocorticoid potencies of budesonide and beclomethasone dipropionate in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1982;22(6):523–529. doi: 10.1007/BF00609625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfdahl C. G., Mellstrand T., Svedmyr N. Glucocorticoids and asthma. Studies of resistance and systemic effects of glucocorticoids. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1984;136:69–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen H. K., Laurberg P., Brixen K., Mosekilde L. Relations between diurnal variations in serum osteocalcin, cortisol, parathyroid hormone, and ionized calcium in normal individuals. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1991 Apr;124(4):391–398. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1240391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packe G. E., Douglas J. G., McDonald A. F., Robins S. P., Reid D. M. Bone density in asthmatic patients taking high dose inhaled beclomethasone dipropionate and intermittent systemic corticosteroids. Thorax. 1992 Jun;47(6):414–417. doi: 10.1136/thx.47.6.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S., Fuglsang G. Urine cortisol excretion in children treated with high doses of inhaled corticosteroids: a comparison of budesonide and beclomethasone. Eur Respir J. 1988 May;1(5):433–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peretz A., Praet J. P., Bosson D., Rozenberg S., Bourdoux P. Serum osteocalcin in the assessment of corticosteroid induced osteoporosis. Effect of long and short term corticosteroid treatment. J Rheumatol. 1989 Mar;16(3):363–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouw E. M., Prummel M. F., Oosting H., Roos C. M., Endert E. Beclomethasone inhalation decreases serum osteocalcin concentrations. BMJ. 1991 Mar 16;302(6777):627–628. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6777.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prahl P. Adrenocortical suppression following treatment with beclomethasone and budesonide. Clin Exp Allergy. 1991 Jan;21(1):145–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1991.tb00817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prahl P., Jensen T. Decreased adreno-cortical suppression utilizing the Nebuhaler for inhalation of steroid aerosols. Clin Allergy. 1987 Sep;17(5):393–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1987.tb02031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prummel M. F., Wiersinga W. M., Lips P., Sanders G. T., Sauerwein H. P. The course of biochemical parameters of bone turnover during treatment with corticosteroids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Feb;72(2):382–386. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-2-382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid I. R., Chapman G. E., Fraser T. R., Davies A. D., Surus A. S., Meyer J., Huq N. L., Ibbertson H. K. Low serum osteocalcin levels in glucocorticoid-treated asthmatics. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Feb;62(2):379–383. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-2-379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selroos O., Halme M. Effect of a volumatic spacer and mouth rinsing on systemic absorption of inhaled corticosteroids from a metered dose inhaler and dry powder inhaler. Thorax. 1991 Dec;46(12):891–894. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.12.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teelucksingh S., Padfield P. L., Tibi L., Gough K. J., Holt P. R. Inhaled corticosteroids, bone formation, and osteocalcin. Lancet. 1991 Jul 6;338(8758):60–61. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90058-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toogood J. H., Baskerville J., Jennings B., Lefcoe N. M., Johansson S. A. Use of spacers to facilitate inhaled corticosteroid treatment of asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 May;129(5):723–729. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.5.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toogood J. H., Jennings B., Hodsman A. B., Baskerville J., Fraher L. J. Effects of dose and dosing schedule of inhaled budesonide on bone turnover. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Oct;88(4):572–580. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90150-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


