Abstract
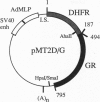
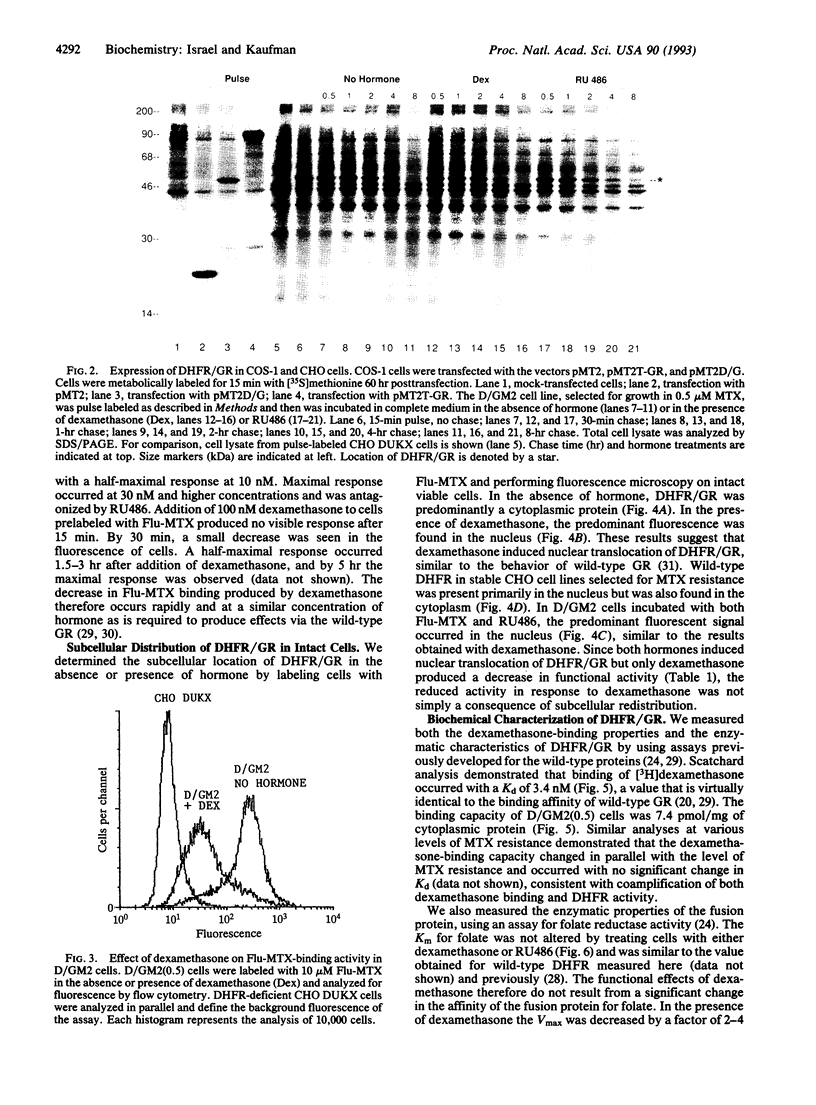
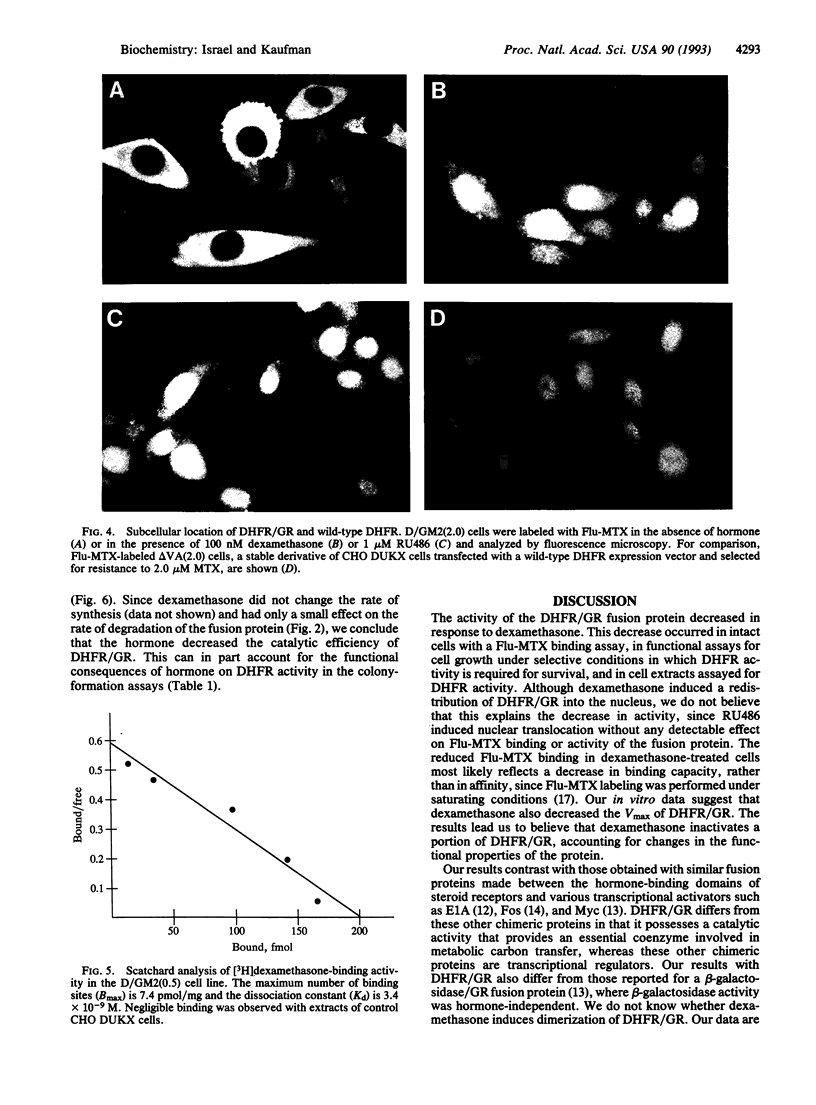
A chimeric gene was constructed encoding the entire murine dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) protein with a carboxyl-terminal extension encompassing amino acids 494-795 of the rat glucocorticoid receptor (GR). The chimeric DHFR/GR gene encoded a functional DHFR protein, as measured by the ability to transform DHFR-deficient Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells to a DHFR-positive phenotype. The DHFR/GR protein bound [3H]dexamethasone with a similar affinity as wild-type GR. Selection of stable CHO transformants in increasing concentrations of methotrexate resulted in increased expression of DHFR/GR. Addition of dexamethasone, a synthetic glucocorticoid agonist, decreased the activity of the chimeric protein, as measured by colony formation in selective medium, binding of fluoresceinated methotrexate, and direct enzymatic assay for DHFR. Addition of RU486, a glucocorticoid antagonist, antagonized the effect of dexamethasone. In the absence of dexamethasone, the chimeric protein was primarily localized to the cytoplasm. In the presence of dexamethasone or RU486, DHFR/GR translocated into the nucleus. However, RU486 did not decrease DHFR activity, distinguishing subcellular location from functional activity. These results demonstrate that glucocorticoids negatively affect the function of DHFR/GR.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Kellems R. E., Schimke R. T. Synthesis and degradation of folate reductase in sensitive and methotrexate-resistant lines of S-180 cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):3063–3074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. D., Tomkins G. M. Specific cytoplasmic glucocorticoid hormone receptors in hepatoma tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):932–937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. D., Tomkins G. M. The relationship between glucocorticoid binding and tyrosine aminotransferase induction in hepatoma tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):709–715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadepond F., Schweizer-Groyer G., Segard-Maurel I., Jibard N., Hollenberg S. M., Giguère V., Evans R. M., Baulieu E. E. Heat shock protein 90 as a critical factor in maintaining glucocorticosteroid receptor in a nonfunctional state. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5834–5841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. S., Kokontis J., Liao S. T. Molecular cloning of human and rat complementary DNA encoding androgen receptors. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):324–326. doi: 10.1126/science.3353726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneely O. M., Sullivan W. P., Toft D. O., Birnbaumer M., Cook R. G., Maxwell B. L., Zarucki-Schulz T., Greene G. L., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Molecular cloning of the chicken progesterone receptor. Science. 1986 Aug 15;233(4765):767–770. doi: 10.1126/science.2426779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M. The mouse glucocorticoid receptor: mapping of functional domains by cloning, sequencing and expression of wild-type and mutant receptor proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2513–2522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04529.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A. The molybdate-stabilized nonactivated glucocorticoid receptor contains a dimer of Mr 90,000 non-hormone-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11803–11806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Picard D., Yamamoto K. R., Bishop J. M. Chimaeras of myc oncoprotein and steroid receptors cause hormone-dependent transformation of cells. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):66–68. doi: 10.1038/340066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Rusconi S., Miesfeld R., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that are constitutive activators of transcriptional enhancement. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):365–368. doi: 10.1038/325365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Walter P., Kumar V., Krust A., Bornert J. M., Argos P., Chambon P. Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):134–139. doi: 10.1038/320134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groyer A., Schweizer-Groyer G., Cadepond F., Mariller M., Baulieu E. E. Antiglucocorticosteroid effects suggest why steroid hormone is required for receptors to bind DNA in vivo but not in vitro. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):624–626. doi: 10.1038/328624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKALA M. T., ZAKRZEWSKI S. F., NICHOL C. A. Relation of folic acid reductase to amethopterin resistance in cultured mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:952–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Weinberger C., Ong E. S., Cerelli G., Oro A., Lebo R., Thompson E. B., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Primary structure and expression of a functional human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):635–641. doi: 10.1038/318635a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. I., Kaufman R. J. Highly inducible expression from vectors containing multiple GRE's in CHO cells overexpressing the glucocorticoid receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4589–4604. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Bertino J. R., Schimke R. T. Quantitation of dihydrofolate reductase in individual parental and methotrexate-resistant murine cells. Use of a fluorescence activated cell sorter. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5852–5860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Amplification and expression of sequences cotransfected with a modular dihydrofolate reductase complementary dna gene. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 25;159(4):601–621. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J. Vectors used for expression in mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:487–511. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85041-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Palmiter R. D. Glucocorticoid regulation of metallothionein-I mRNA synthesis in cultured mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2621–2624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel D. B., Bodwell J. E., Munck A. Glucocorticoid receptors lacking hormone-binding activity are bound in nuclei of ATP-depleted cells. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):478–480. doi: 10.1038/324478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Rusconi S., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Okret S., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Genetic complementation of a glucocorticoid receptor deficiency by expression of cloned receptor cDNA. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moguilewsky M., Philibert D. RU 38486: potent antiglucocorticoid activity correlated with strong binding to the cytosolic glucocorticoid receptor followed by an impaired activation. J Steroid Biochem. 1984 Jan;20(1):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(84)90216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura H., Littlefield J. W. Purification, properties, and synthesis of dihydrofolate reductase from wild type and methotrexate-resistant hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):179–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann E., Schaefer-Ridder M., Wang Y., Hofschneider P. H. Gene transfer into mouse lyoma cells by electroporation in high electric fields. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):841–845. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oprian D. D., Molday R. S., Kaufman R. J., Khorana H. G. Expression of a synthetic bovine rhodopsin gene in monkey kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8874–8878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Salser S. J., Yamamoto K. R. A movable and regulable inactivation function within the steroid binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Yamamoto K. R. Two signals mediate hormone-dependent nuclear localization of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3333–3340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusconi S., Yamamoto K. R. Functional dissection of the hormone and DNA binding activities of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1309–1315. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02369.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Kaufman R. J., Alt F. W., Kellems R. F. Gene amplification and drug resistance in cultured murine cells. Science. 1978 Dec 8;202(4372):1051–1055. doi: 10.1126/science.715457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simental J. A., Sar M., Lane M. V., French F. S., Wilson E. M. Transcriptional activation and nuclear targeting signals of the human androgen receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):510–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Superti-Furga G., Bergers G., Picard D., Busslinger M. Hormone-dependent transcriptional regulation and cellular transformation by Fos-steroid receptor fusion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5114–5118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]