Key Points
PU-H71, a novel purine scaffold inhibitor, shows potent therapeutic efficacy in JAK-mutant ALL cells and mouse models.
HSP90 inhibition retains therapeutic efficacy in ruxolitinib-persistent JAK-mutant ALL cells.
Abstract
The development of the dual Janus kinase 1/2 (JAK1/2) inhibitor ruxolitinib for the treatment of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) has led to studies of ruxolitinib in other clinical contexts, including JAK-mutated acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). However, the limited ability of JAK inhibition to induce molecular or clinicopathological responses in MPNs suggests a need for development of better therapies for JAK kinase-dependent malignancies. Here, we demonstrate that heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) inhibition using a purine-scaffold HSP90 inhibitor in early clinical development is an effective therapeutic approach in JAK-dependent ALL and can overcome persistence to JAK-inhibitor therapy in ALL cells.
Introduction
Somatic mutations in Janus kinases (JAKs), including JAK2V617F, were first identified in myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs).1,2 Subsequent studies identified somatic mutations in JAK1, JAK2, and JAK3 in ∼10% of pediatric high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).3,4 In aggregate, 3.4% of B-cell ALL (B-ALL) and 18.4% of T-cell ALL (T-ALL) cases harbor JAK1 mutations.5 Mutations and rearrangements that activate JAKs are seen in Ph-like B-ALL, in the presence and absence of CRLF2 rearrangements.3,6-8 Of note, the overall survival of Ph-like ALL is significantly lower than that seen in non-Ph-like ALL, both in pediatric patients and in young adults.9,10 The JAK1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib was approved for MPN patients based on its ability to reduce spleen size and improve constitutional symptoms, likely due to inhibition of cytokine production from malignant and nonmalignant cells.11 However, JAK-inhibitor therapy does not reduce the proportion of JAK2-mutant cells in MPN patients, underscoring the need for better therapies for JAK-mutant malignancies.
We and others have previously shown that heat shock protein 90 (HSP90), a molecular chaperone, represents a therapeutic target in JAK-dependent malignancies.12-14 The HSP90 inhibitor AUY922 has demonstrated preclinical efficacy in CRLF2-rearranged, JAK2-mutant ALL.15 However, the efficacy of HSP90 inhibition in JAK-inhibitor persistent ALL cells, and in ALL cells with mutated JAK1, has not been investigated. We therefore assessed the efficacy of PU-H71, a novel purine-scaffold HSP90 inhibitor completing phase 1 trials, in JAK-mutant ALL that are sensitive and resistant to JAK kinase inhibitors.
Study design
Patient samples
Patient samples were obtained from the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Institutional review board approval was obtained from the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) Institutional Review Board; all patients provided informed consent.
Animal studies
MOHITO transplantation experiments were performed as described.16 At first signs of disease, mice were randomized to begin treatment with PU-H71 or vehicle. For human xenograft studies, NSG mice were transplanted with 800 000 T-ALL cells. When human chimerism reached 10%, mice were sacrificed, and bone marrow was collected and transplanted to secondary recipients for drug treatment experiments. Therapy was initiated when human chimerism was >1%.
Results and discussion
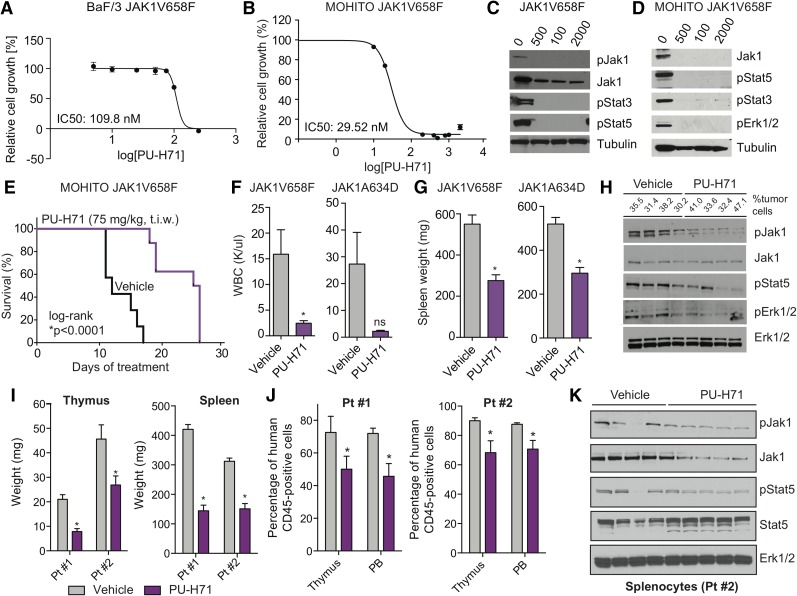
We first assessed the ability of PU-H71 to inhibit proliferation in BaF/3 cells expressing the ALL-associated JAK1V658F and JAK2R683G mutations and in BaF/3 cells that express the JAK2R683G mutation and overexpress wild-type CRLF2. In each case, PU-H71 dose-dependently inhibited the proliferation of JAK-mutant cells in vitro (Figure 1A; supplemental Figure 1A, see supplemental Data available on the Blood Web site). Furthermore, PU-H71 dose-dependently inhibited the proliferation of murine T-ALL cell line MOHITO cells16 expressing 2 ALL-associated JAK1 mutations, JAK1V658F and JAK1A634D (Figure 1B; supplemental Figure 1B). Consistent with the impact on proliferation, PU-H71 dose-dependently inhibited signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 and 5 (Stat3 and Stat5) phosphorylation and attenuated phosphorylated and total Jak protein levels (Figure 1C-D; supplemental Figure 1C-D). These data show PU-H71 treatment results in degradation of JAKs and inhibition of JAK-STAT signaling in JAK-mutant ALL.
Figure 1.
JAK-mutant ALL cell lines and diseased mice are sensitive to HSP90 inhibition. (A-B) BaF/3 cells (A) and MOHITO cells (B) expressing the ALL-associated JAK1V658F mutation are highly sensitive to growth inhibition by PU-H71. In each case, IC50 values are indicated. Relative cell growth compared with DMSO-treated control is shown. Inhibitor concentrations are plotted in logarithmic scale. (C-D) Western blots reveal a dose-dependent inhibition of JAK1, JAK2, and signaling intermediates in the JAK-STAT pathway after treatment with PU-H71–isogenic BaF/3 (C) and MOHITO (D) cell lines. (E) Cytokine-independent MOHITO cells expressing the activating JAK1V658F mutation were injected (tail vein) into lethally irradiated syngeneic mice. Leukemic mice treated with PU-H71 (75 mg/kg, 3 times per week [t.i.w.], i.p.) survived significantly longer compared with vehicle control mice (vehicle, n = 7; PU-H71, n = 8; *P < .0001, log-rank test). (F-G) Treatment of MOHITO JAK1V658F- and JAK1A634D-transplanted mice treated with PU-H71 significantly reduced WBC (K/μL) (F) and spleen size (G) compared with vehicle-treated controls (*P < .05, Student t test, n = 7 per group). (H) Protein analysis of whole-cell lysates prepared from splenocytes of PU-H71 (single dose, 75 mg/kg, 16 hours prior to tissue harvest) and vehicle-treated JAK1V658F-diseased mice showing that HSP90 inhibition causes degradation of phosphorylated JAK1 in vivo and concomitant inhibition of downstream signaling proteins Stat5 and Erk1/2. Tubulin is shown as loading control. Tumor burden (percentage of GFP-positive cells) in the spleen at time of tissue harvest is shown. (I) Thymus (*P < .05, Student t test) and spleen (*P < .05, Student t test) size was significantly smaller in PU-H71–treated mice compared with vehicle control; n = 7-12 in each group. (J) PU-H71–treated mice had lower numbers of leukemic human CD45-positive cells in the thymus and PB; n = 7-13 in each group. Data from 2 patient-derived xenograft models are shown. (K) Protein analysis of whole-cell lysates from splenocytes of vehicle- and PU-H71–treated mice (Pt #2) showing that HSP90 inhibition causes degradation of total and phosphorylated Jak1 in vivo and inhibition of downstream signaling target Stat5. Erk1/2 is shown as independent loading control. DMSO, dimethylsulfoxide; Erk, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; GFP, green fluorescent protein; IC50, 50% inhibitory concentration; i.p., intraperitoneally; ns, not significant; p, phosphorylated form; PB, peripheral blood; Pt, patient; WBC, white blood cell count.
We next investigated whether HSP90 is a potential therapeutic target in JAK-dependent T-ALL. To test the efficacy of HSP90 inhibition in vivo, we injected mice with JAK1-mutant MOHITO cells. Transplantation of JAK1V658F-positive MOHITO cells caused a lethal disease in vehicle-treated mice with a median survival of 23 days (Figure 1E). PU-H71 treatment (75 mg/kg, t.i.w.) significantly improved survival compared with vehicle-treated mice (23 days vs 36.5 days, P < .0001). White blood cell counts and spleen size were markedly reduced in PU-H71–treated MOHITO mice compared with vehicle treatment (Figure 1F-G). Furthermore, administration of a single dose of PU-H71 16 hours prior to sacrifice reduced Jak1 phosphorylation levels in MOHITO-diseased mouse splenocytes and inhibited Jak1 downstream targets demonstrating in vivo target inhibition (Figure 1H).
We then assessed whether PU-H71 can show therapeutic efficacy in human xenograft models of JAK1-mutant T-ALL (supplemental Table 1). We injected primary JAK1-mutant T-ALL cells into NSG mice and randomized engrafted mice to receive treatment with PU-H71 or vehicle. Thymus and spleen size were significantly reduced by PU-H71 treatment in comparison with control mice (Figure 1I). The percentage of human CD45-positive leukemic cells was significantly reduced in the thymus and peripheral blood of PU-H71–treated mice (Figure 1J). We also observed a trend toward improved survival of PU-H71–treated mice compared with control mice (P = .07 [log-rank test], supplemental Figure 2). PU-H71–treated splenocytes from leukemic mice had reduced Jak1 protein expression and reduced phosphorylation of the Jak1 downstream target Stat5 (Figure 1K). These studies suggest that HSP90 inhibition with PU-H71 can show significant therapeutic efficacy in JAK1-mutated ALL.
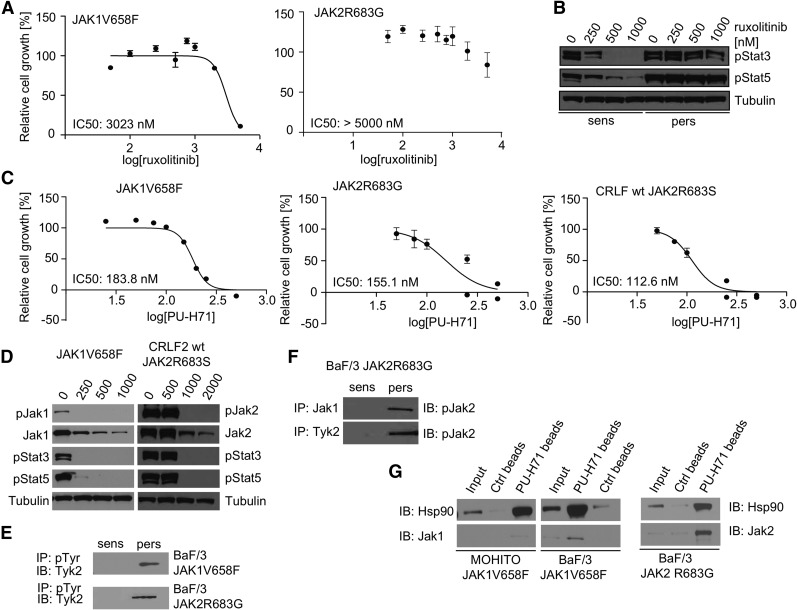
MPN cells are able to become insensitive to ruxolitinib and other JAK kinase inhibitors through transactivation of JAK2 by other tyrosine kinases.17 JAK-inhibitor persistent MPN cells remain dependent on JAK2,18 suggesting that therapeutic strategies resulting in JAK2 degradation should remain effective in cells that survive JAK-inhibitor therapy. To investigate whether JAK-mutant ALL cells can use a similar mechanism of JAK-inhibitor persistence, we cultured BaF/3 cell lines with the different ALL-associated mutations with ruxolitinib for 4 to 6 weeks. In each case, JAK-mutant cells could survive and proliferate at inhibitor concentrations that potently inhibited proliferation in parental cells, consistent with inhibitor persistence (Figure 2A; supplemental Figure 3A-B). JAK-inhibitor persistent cells were sixfold to 30-fold less sensitive to ruxolitinib compared with parental cells and exhibited constitutive Stat pathway activation at inhibitor doses sufficient to inhibit signaling in parental cells (Figure 2B; supplemental Figure 4A).
Figure 2.
Pharmacologic loss of mutated JAKs can overcome persistence to ruxolitinib. (A) Proliferation of JAK-inhibitor persistent BaF/3 cell lines (JAK1V658F and JAK2R683G) with ruxolitinib. Cell growth relative to DMSO-treated control is shown. Data from wells plated in triplicates (s.d.) are shown and are representative of 3 independent experiments. (B) Western blot analysis revealing retained phosphorylation of JAK downstream targets Stat3 and Stat5 in persistent cells (BaF/3 JAK2R683G) treated with increasing concentrations of ruxolitinib. (C) PU-H71 inhibits potently the proliferation of ruxolitinib-persistent cells. Cell growth relative to DMSO-treated control is shown. Data from wells plated in triplicates (s.d.) are shown and are representative of 3 independent experiments. In each case, IC50 values are displayed. (D) Treatment with HSP90 inhibitor PU-H71 strongly reduces constitutive activation of signaling pathways downstream of mutant JAKs and causes degradation of total and phosphorylated JAK2 in ruxolitinib-persistent cells. Protein analysis of whole-cell lysates from BaF/3 JAK1V658F and CRLF2 wt/JAK2R683S cell lines is shown. Tubulin is shown as loading control. (E) Western blot analysis revealing that activation of Tyk2 is restricted to JAK-inhibitor persistent BaF/3 cell lines. (F) Immune precipitation of Jak1 and Tyk2 from JAK2R683G-expressing BaF/3 cells demonstrated that both tyrosine kinases only directly interact with phosphorylated Jak2 in persistent cells. (G) Immune precipitation of Hsp90 and Jak1 from ruxolitinib-persistent JAK1V658F-mutant cell lines (MOHITO, left panel; BaF/3, right panel) resulted in coprecipitation of the kinase and the chaperone protein with PU-H71–coated beads. Ctrl, control; DMSO, dimethylsulfoxide; IB, immunoblot; IP, immunoprecipitation; log, logarithmic; p, phosphorylated form; pers, ruxolitinib-persistent cells; s.d., standard deviation; sens, ruxolitinib-naive cells; wt, wild type.
PU-H71 therapy potently inhibited the proliferation of persistent cells, suggesting abrogation of JAK-inhibitor persistence (Figure 2C). Signaling analysis showed that PU-H71 treatment inhibited Jak1/Jak2, Stat3, and Stat5 phosphorylation and decreased total Jak1/Jak2 levels in a dose-dependent manner in persistent cells similar to inhibitor naive cells (Figure 2D; supplemental Figure 4B). To investigate whether JAK-inhibitor persistence in ALL cells was due to JAK kinase transactivation, as previously shown for MPN cells, we assessed the activation status of Tyk2 in JAK1/JAK2-mutant cell lines, and found that Tyk2 was activated in persistent cells, but not in naive cells (Figure 2E). Immunoprecipitation studies in JAK2R683G-expressing BaF/3 cells demonstrated that Jak1 and Tyk2 associate with phosphorylated Jak2 in persistent cells, but not in parental cells (Figure 2F). This finding shows that in ALL-associated JAK-mutant cell lines, JAK2 transactivation and persistent JAK-STAT activation induces JAK-inhibitor persistence, which can be reversed by PU-H71. We next investigated whether PU-H71 directly interacts with mutant JAK proteins in ALL cells. We performed immunoprecipitation with PU-H71–bound agarose beads, and showed that PU-H71 could bind mutant Jak1 and Jak2, as well as Hsp90, in persistent ALL cells (Figure 2G). These data demonstrate that PU-H71 is able to bind and degrade mutant JAK1 and JAK2 in JAK-inhibitor naive and persistent cells, and provides a rationale for targeting JAKs with PU-H71 in ALL cells that persist after JAK-inhibitor therapy.
In summary, we demonstrate the purine scaffold HSP90 inhibitor PU-H71 shows preclinical efficacy in JAK1- and JAK2-dependent cell lines and in murine models of ALL. JAK-mutant ALL cells were sensitive to PU-H71 therapy, and PU-H71 exposure resulted in dose-dependent JAK kinase degradation and inhibition of downstream signaling pathways. Furthermore, Hsp90 inhibition reduced disease burden and improved survival of T-cell leukemic mice. Finally, ruxolitinib persistence in JAK1- and JAK2-mutant ALL cells can be reversed with PU-H71. Our data suggest that HSP90 is a valid target in JAK1- and JAK2-mutant ALL, and that clinical studies of PU-H71, alone and in combination with JAK inhibitors and other ALL therapies, are warranted in JAK-mutant, relapsed/high-risk ALL.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank members of the Levine laboratory for helpful comments and discussion.
This work was supported by grants from the William Lawrence and Blanche Hughes Foundation (N.K. and R.L.L.) and from the William and Alice Goodwin Experimental Therapeutics Center and the Kleberg Foundation (S.A. and R.L.L.). Technical services provided by the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) Core Facilities were supported in part by MSKCC Support Grant/Core Grant P30 CA008748.
M.K. is a fellow of the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society and was previously supported by an EMBO Long-Term Fellowship. A.A.F. and R.L.L. are Leukemia & Lymphoma Society Scholars.
Footnotes
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Authorship
Contribution: N.K., M.K., and R.L.L. conceived the project, designed experiments, and wrote the manuscript with input from all other authors; N.K., N.B., E. Papalexi, P.K., L.D., A.K., L.L., M.S.M., and M.K. performed experiments; N.K., S.M., N.B., P.K., A.K., S.A., J.T.-F., A.A.F., L.L., M.K., and R.L.L. analyzed data; S.O.O., G.C., M.S.T., E. Paietta, J.M.R., and C.G.M. provided patient samples and xenograft models; and K.W., J.H., D.L., P.S., and V.M. performed mutational analysis of xenografts.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: R.L.L. is a consultant and receives research support from Novartis Pharmaceuticals. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center holds the intellectual rights to PU-H71. Samus Therapeutics, of which G.C. has partial ownership, has licensed PU-H71. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Maria Kleppe, Human Oncology and Pathogenesis Program, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, 1275 York Ave, Box 20, New York, NY 10065; e-mail: kleppem@mskcc.org; and Ross L. Levine, Human Oncology and Pathogenesis Program, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, 1275 York Ave, Box 20, New York, NY 10065; e-mail: leviner@mskcc.org.
References
- 1.Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, et al. A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(17):1779–1790. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa051113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, et al. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell. 2005;7(4):387–397. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2005.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mullighan CG, Collins-Underwood JR, Phillips LA, et al. Rearrangement of CRLF2 in B-progenitor- and Down syndrome-associated acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Genet. 2009;41(11):1243–1246. doi: 10.1038/ng.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mullighan CG, Zhang J, Harvey RC, et al. JAK mutations in high-risk childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(23):9414–9418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811761106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Flex E, Petrangeli V, Stella L, et al. Somatically acquired JAK1 mutations in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Exp Med. 2008;205(4):751–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.20072182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Harvey RC, Mullighan CG, Chen IM, et al. Rearrangement of CRLF2 is associated with mutation of JAK kinases, alteration of IKZF1, Hispanic/Latino ethnicity, and a poor outcome in pediatric B-progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2010;115(26):5312–5321. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-245944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Russell LJ, Capasso M, Vater I, et al. Deregulated expression of cytokine receptor gene, CRLF2, is involved in lymphoid transformation in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2009;114(13):2688–2698. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-208397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yoda A, Yoda Y, Chiaretti S, et al. Functional screening identifies CRLF2 in precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(1):252–257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911726107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Roberts KG, Li Y, Payne-Turner D, et al. Targetable kinase-activating lesions in Ph-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(11):1005–1015. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1403088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mullighan CG, Su X, Zhang J, et al. Children’s Oncology Group. Deletion of IKZF1 and prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(5):470–480. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0808253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kleppe M, Kwak M, Koppikar P, et al. JAK-STAT pathway activation in malignant and nonmalignant cells contributes to MPN pathogenesis and therapeutic response. Cancer Discov. 2015;5(3):316–331. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hertlein E, Wagner AJ, Jones J, et al. 17-DMAG targets the nuclear factor-kappaB family of proteins to induce apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: clinical implications of HSP90 inhibition. Blood. 2010;116(1):45–53. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-01-263756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kamal A, Thao L, Sensintaffar J, et al. A high-affinity conformation of Hsp90 confers tumour selectivity on Hsp90 inhibitors. Nature. 2003;425(6956):407–410. doi: 10.1038/nature01913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Schoof N, von Bonin F, Trümper L, Kube D. HSP90 is essential for Jak-STAT signaling in classical Hodgkin lymphoma cells. Cell Commun Signal. 2009;7:17. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-7-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Weigert O, Lane AA, Bird L, et al. Genetic resistance to JAK2 enzymatic inhibitors is overcome by HSP90 inhibition. J Exp Med. 2012;209(2):259–273. doi: 10.1084/jem.20111694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kleppe M, Mentens N, Tousseyn T, Wlodarska I, Cools J. MOHITO, a novel mouse cytokine-dependent T-cell line, enables studies of oncogenic signaling in the T-cell context. Haematologica. 2011;96(5):779–783. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2010.035931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Koppikar P, Bhagwat N, Kilpivaara O, et al. Heterodimeric JAK-STAT activation as a mechanism of persistence to JAK2 inhibitor therapy. Nature. 2012;489(7414):155–159. doi: 10.1038/nature11303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bhagwat N, Koppikar P, Keller M, et al. Improved targeting of JAK2 leads to increased therapeutic efficacy in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood. 2014;123(13):2075–2083. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-01-547760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]