Abstract
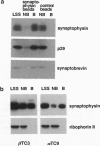
A variety of peptide-secreting endocrine cells contain a population of recycling microvesicles that share several major membrane polypeptides with neuronal synaptic vesicles (SVs). The function of these synaptic-like microvesicles (SLMVs) remains to be elucidated. It was previously suggested that SLMVs of pancreatic beta cells may store and secrete gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA, the major nonpeptide inhibitory neurotransmitter of the central nervous system, is stored in and secreted from SVs. GABA uptake into SVs is mediated by a transporter that is driven by a vacuolar proton ATPase. GABA is also present at high concentration in the endocrine pancreas where it is selectively localized in insulin-secreting beta cells, the core cells of pancreatic islets. GABA is not present in peripheral islet cells (mantle cells), represented primarily by glucagon-secreting alpha cells. In this study, an immunoisolation procedure was used to purify SLMVs from cell lines derived from mouse beta cells and alpha cells. SLMVs obtained from the beta-cell line, but not those obtained from the alpha-cell line, displayed a GABA-transport activity dependent upon a proton electrochemical gradient generated by a vacuolar proton ATPase. These data support the hypotheses that (i) SLMVs have a secretory function similar to that of SVs and (ii) beta-cell SLMVs are involved in the secretion of GABA, which in turn may have a paracrine function on mantle cells of the islet.
Full text
PDF
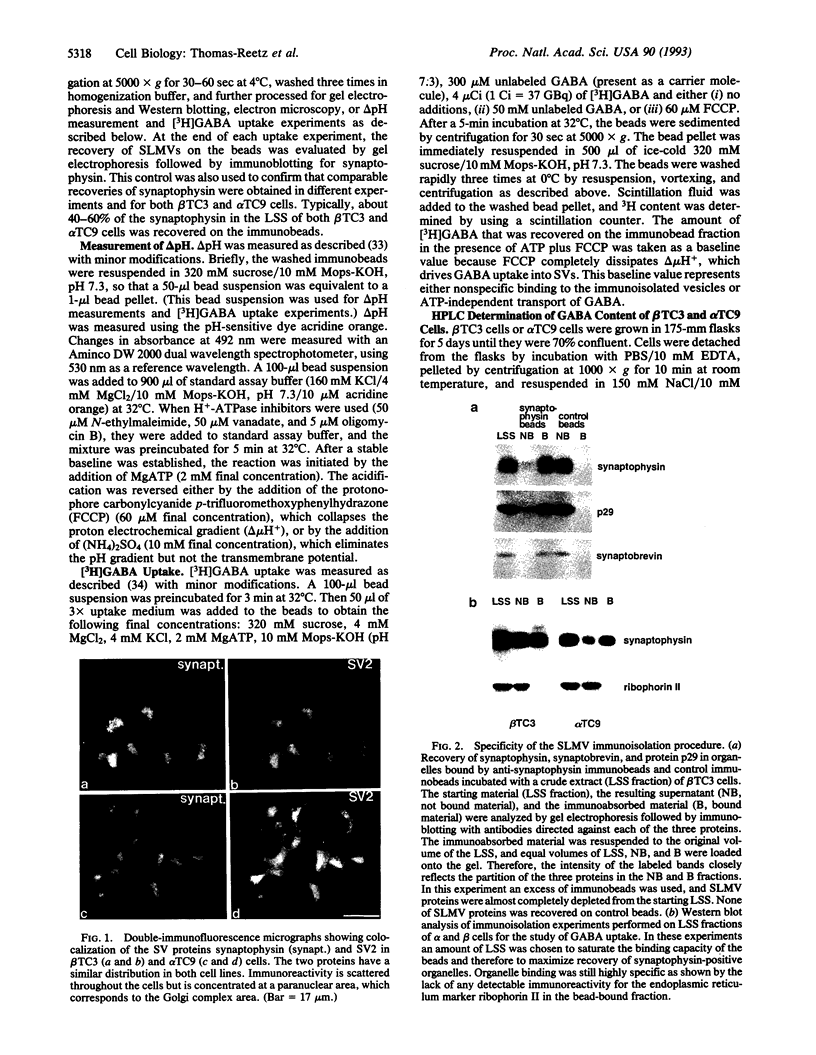
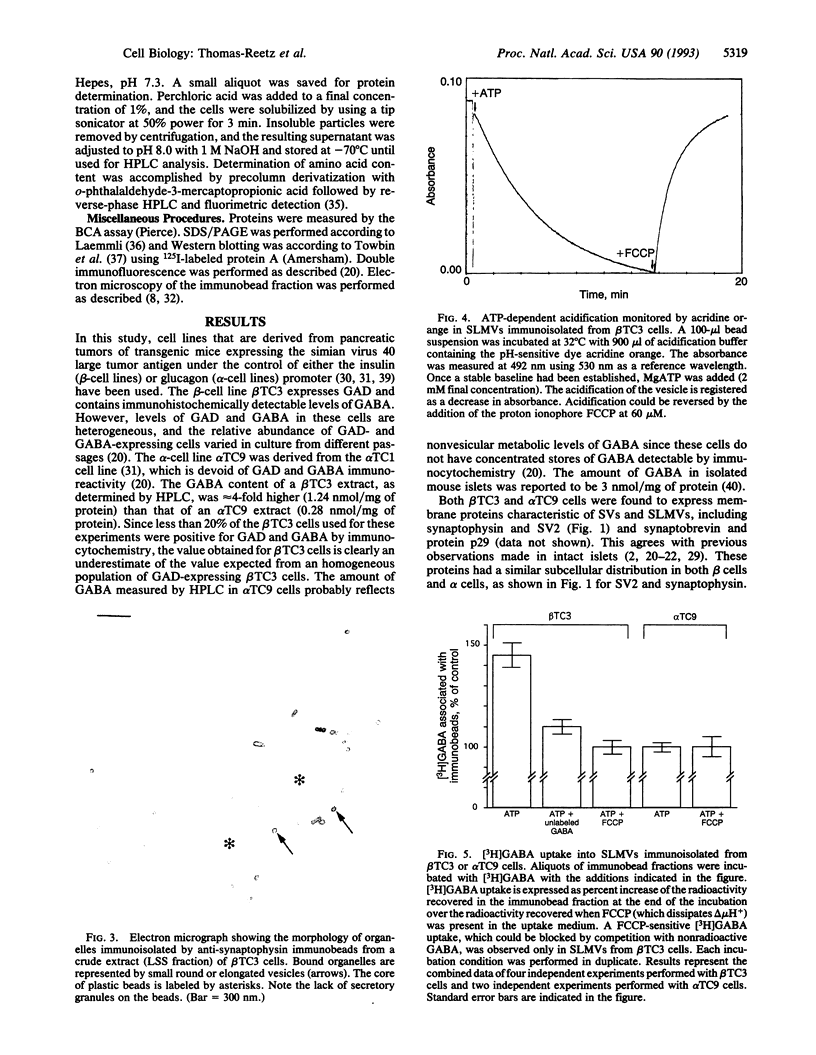


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Wiedenmann B. The amphicrine pancreatic cell line, AR42J, secretes GABA and amylase by separate regulated pathways. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 7;314(1):41–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81457-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumert M., Maycox P. R., Navone F., De Camilli P., Jahn R. Synaptobrevin: an integral membrane protein of 18,000 daltons present in small synaptic vesicles of rat brain. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):379–384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumert M., Takei K., Hartinger J., Burger P. M., Fischer von Mollard G., Maycox P. R., De Camilli P., Jahn R. P29: a novel tyrosine-phosphorylated membrane protein present in small clear vesicles of neurons and endocrine cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1285–1294. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briel G., Gylfe E., Hellman B., Neuhoff V. Microdetermination of free amino acids in pancreatic islets isolated from obese-hyperglycemic mice. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972 Feb;84(2):247–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb05175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger P. M., Hell J., Mehl E., Krasel C., Lottspeich F., Jahn R. GABA and glycine in synaptic vesicles: storage and transport characteristics. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger P. M., Mehl E., Cameron P. L., Maycox P. R., Baumert M., Lottspeich F., De Camilli P., Jahn R. Synaptic vesicles immunoisolated from rat cerebral cortex contain high levels of glutamate. Neuron. 1989 Dec;3(6):715–720. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90240-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron P. L., Südhof T. C., Jahn R., De Camilli P. Colocalization of synaptophysin with transferrin receptors: implications for synaptic vesicle biogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):151–164. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clift-O'Grady L., Linstedt A. D., Lowe A. W., Grote E., Kelly R. B. Biogenesis of synaptic vesicle-like structures in a pheochromocytoma cell line PC-12. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1693–1703. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Jahn R. Pathways to regulated exocytosis in neurons. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:625–645. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durkin T. A., Anderson G. M., Cohen D. J. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of neurotransmitter amino acids in brain. J Chromatogr. 1988 Jun 24;428(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)83885-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Linde S., Kofod H., Spector D., Delannoy M., Grant S., Hanahan D., Baekkeskov S. Beta-cell lines derived from transgenic mice expressing a hybrid insulin gene-oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9037–9041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdö S. L., Wolff J. R. gamma-Aminobutyric acid outside the mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1990 Feb;54(2):363–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewert M., de Blas A. L., Möhler H., Seeburg P. H. A prominent epitope on GABAA receptors is recognized by two different monoclonal antibodies. Brain Res. 1992 Jan 8;569(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90368-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garry D. J., Coulter H. D., McIntee T. J., Wu J. Y., Sorenson R. L. Immunoreactive GABA transaminase within the pancreatic islet is localized in mitochondria of the B-cell. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Aug;35(8):831–836. doi: 10.1177/35.8.3298424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilon P., Bertrand G., Loubatières-Mariani M. M., Remacle C., Henquin J. C. The influence of gamma-aminobutyric acid on hormone release by the mouse and rat endocrine pancreas. Endocrinology. 1991 Nov;129(5):2521–2529. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-5-2521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi K., Leiter E. H. Comparison of cytokine effects on mouse pancreatic alpha-cell and beta-cell lines. Viability, secretory function, and MHC antigen expression. Diabetes. 1990 Apr;39(4):415–425. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.4.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hell J. W., Maycox P. R., Stadler H., Jahn R. Uptake of GABA by rat brain synaptic vesicles isolated by a new procedure. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3023–3029. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03166.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häring P., Stähli C., Schoch P., Takács B., Staehelin T., Möhler H. Monoclonal antibodies reveal structural homogeneity of gamma-aminobutyric acid/benzodiazepine receptors in different brain areas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4837–4841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Cameron P. L., Stukenbrok H., Jahn R., De Camilli P., Südhof T. C. Synaptophysin is targeted to similar microvesicles in CHO and PC12 cells. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2863–2872. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner B. I., Schuldiner S. Mechanism of transport and storage of neurotransmitters. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1987;22(1):1–38. doi: 10.3109/10409238709082546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maycox P. R., Deckwerth T., Hell J. W., Jahn R. Glutamate uptake by brain synaptic vesicles. Energy dependence of transport and functional reconstitution in proteoliposomes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15423–15428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navone F., Jahn R., Di Gioia G., Stukenbrok H., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Protein p38: an integral membrane protein specific for small vesicles of neurons and neuroendocrine cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2511–2527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers A. C., Efrat S., Mojsov S., Spector D., Habener J. F., Hanahan D. Proglucagon processing similar to normal islets in pancreatic alpha-like cell line derived from transgenic mouse tumor. Diabetes. 1990 Apr;39(4):406–414. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.4.406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reetz A., Solimena M., Matteoli M., Folli F., Takei K., De Camilli P. GABA and pancreatic beta-cells: colocalization of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and GABA with synaptic-like microvesicles suggests their role in GABA storage and secretion. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1275–1284. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08069.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins M. S., Grouse L. H., Sorenson R. L., Elde R. P. Effect of muscimol on glucose-stimulated somatostatin and insulin release from the isolated, perfused rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1981 Feb;30(2):168–171. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.2.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Régnier-Vigouroux A., Tooze S. A., Huttner W. B. Newly synthesized synaptophysin is transported to synaptic-like microvesicles via constitutive secretory vesicles and the plasma membrane. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3589–3601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04925.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solimena M., Folli F., Denis-Donini S., Comi G. C., Pozza G., De Camilli P., Vicari A. M. Autoantibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase in a patient with stiff-man syndrome, epilepsy, and type I diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1988 Apr 21;318(16):1012–1020. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198804213181602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S. R., Hökfelt T., Wu J. Y., Elde R. P., Morgan L. M., Kimmel J. R. Immunohistochemical studies of the GABA system in the pancreas. Neuroendocrinology. 1983;36(3):197–204. doi: 10.1159/000123456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Rehm H., Knierim M., Becker C. M. Fractionation of synaptophysin-containing vesicles from rat brain and cultured PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Nov 21;240(1-2):71–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Blas A. L., Vitorica J., Friedrich P. Localization of the GABAA receptor in the rat brain with a monoclonal antibody to the 57,000 Mr peptide of the GABAA receptor/benzodiazepine receptor/Cl- channel complex. J Neurosci. 1988 Feb;8(2):602–614. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-02-00602.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]