Abstract
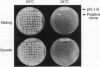
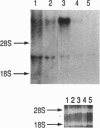
The STE5 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae was cloned using a screening procedure designed to isolate genes of the S. cerevisiae pheromone response pathway. We screened a yeast genomic high-copy-number plasmid library for genes that allow mating of cdc25ts mutants at the restrictive temperature without affecting the cell-cycle-arrest phenotype. One of the genes cloned was identified by genetic analysis as STE5. STE5 encodes a predicted open reading frame of 916 amino acids and exhibits significant homology to Far1 protein. RNA blot analysis reveals that STE5 gene transcription is regulated by the mating type of the cell and depends on an intact pheromone-response pathway.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinder D., Bouvier S., Jenness D. D. Constitutive mutants in the yeast pheromone response: ordered function of the gene products. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):479–486. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Falco S. C., Stewart S. E., Brennan M., Scherer S., Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Sterile host yeasts (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broek D., Toda T., Michaeli T., Levin L., Birchmeier C., Zoller M., Powers S., Wigler M. The S. cerevisiae CDC25 gene product regulates the RAS/adenylate cyclase pathway. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):789–799. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns B. R., Ramer S. W., Kornberg R. D. Order of action of components in the yeast pheromone response pathway revealed with a dominant allele of the STE11 kinase and the multiple phosphorylation of the STE7 kinase. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1305–1318. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F., Herskowitz I. Identification of a gene necessary for cell cycle arrest by a negative growth factor of yeast: FAR1 is an inhibitor of a G1 cyclin, CLN2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):999–1011. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90503-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J., Becker J. M., Enari E., Levitzki A. The activation of adenylate cyclase by guanyl nucleotides in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is controlled by the CDC25 start gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3857–3861. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J., Simchen G. Clones from two different genomic regions complement the cdc25 start mutation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1986;10(9):643–646. doi: 10.1007/BF00410911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan J. W., Kirkman C., Fields S. The yeast STE12 protein binds to the DNA sequence mediating pheromone induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5703–5707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Brill J. A., Fink G. R. FUS3 represses CLN1 and CLN2 and in concert with KSS1 promotes signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9392–9396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelberg D., Simchen G., Levitzki A. In vitro reconstitution of cdc25 regulated S. cerevisiae adenylyl cyclase and its kinetic properties. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):641–651. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08156.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Chaleff D. T., Sprague G. F., Jr Yeast STE7, STE11, and STE12 genes are required for expression of cell-type-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):551–556. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner A., Nasmyth K., Ammerer G. Signal transduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires tyrosine and threonine phosphorylation of FUS3 and KSS1. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1280–1292. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz R. D., Sugino A. New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90185-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goutte C., Johnson A. D. a1 protein alters the DNA binding specificity of alpha 2 repressor. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):875–882. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90429-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., McCaffrey G., Sprague G. F., Jr Pheromone response elements are necessary and sufficient for basal and pheromone-induced transcription of the FUS1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):2952–2961. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.2952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae unresponsive to cell division control by polypeptide mating hormone. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):811–822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness D. D., Goldman B. S., Hartwell L. H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants unresponsive to alpha-factor pheromone: alpha-factor binding and extragenic suppression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1311–1319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S., Vignais M. L., Broach J. R. The CDC25 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae promotes exchange of guanine nucleotides bound to ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2641–2646. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronstad J. W., Holly J. A., MacKay V. L. A yeast operator overlaps an upstream activation site. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90491-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J. Pheromone response in yeast. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1097–1129. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay V., Manney T. R. Mutations affecting sexual conjugation and related processes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Genetic analysis of nonmating mutants. Genetics. 1974 Feb;76(2):273–288. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh L., Neiman A. M., Herskowitz I. Signal transduction during pheromone response in yeast. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:699–728. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Ishikawa T. Control of cell division in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants defective in adenylate cyclase and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Jun;146(1):151–161. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Ishikawa T. Identification of the structural gene and nonsense alleles for adenylate cyclase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):277–282. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.277-282.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. M., MacKay V. L., Nasmyth K. A. Identification and comparison of two sequence elements that confer cell-type specific transcription in yeast. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):598–603. doi: 10.1038/314598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima I., Nakafuku M., Nakayama N., Brenner C., Miyajima A., Kaibuchi K., Arai K., Kaziro Y., Matsumoto K. GPA1, a haploid-specific essential gene, encodes a yeast homolog of mammalian G protein which may be involved in mating factor signal transduction. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1011–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama N., Kaziro Y., Arai K., Matsumoto K. Role of STE genes in the mating factor signaling pathway mediated by GPA1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3777–3783. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto S., Nakayama N., Arai K., Matsumoto K. Regulation of the yeast pheromone response pathway by G protein subunits. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):691–696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08161.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. V., Dutchik J. E., Graham M. Y., Brodeur G. M., Helms C., Frank M., MacCollin M., Scheinman R., Frank T. Random-clone strategy for genomic restriction mapping in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7826–7830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman R., Eilam Y., Padan E., Simchen G., Levitzki A. Rapid intracellular alkalinization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae MATa cells in response to alpha-factor requires the CDC25 gene product. Cell Signal. 1989;1(6):577–586. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid B. J., Hartwell L. H. Regulation of mating in the cell cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):355–365. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. C., Gibbs J. B., Marshall M. S., Sigal I. S., Tatchell K. CDC25: a component of the RAS-adenylate cyclase pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1218–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.3547648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F., Wakem P. Mapping yeast genes. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:38–57. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague G. F., Jr Signal transduction in yeast mating: receptors, transcription factors, and the kinase connection. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):393–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. J., Rhodes N., Errede B., Sprague G. F., Jr Constitutive mutants of the protein kinase STE11 activate the yeast pheromone response pathway in the absence of the G protein. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1293–1304. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Hougan L., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y., Bell L., Saari G. C., Grant F. J., O'Hara P., MacKay V. L. The STE4 and STE18 genes of yeast encode potential beta and gamma subunits of the mating factor receptor-coupled G protein. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90249-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]