Abstract
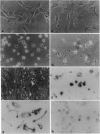
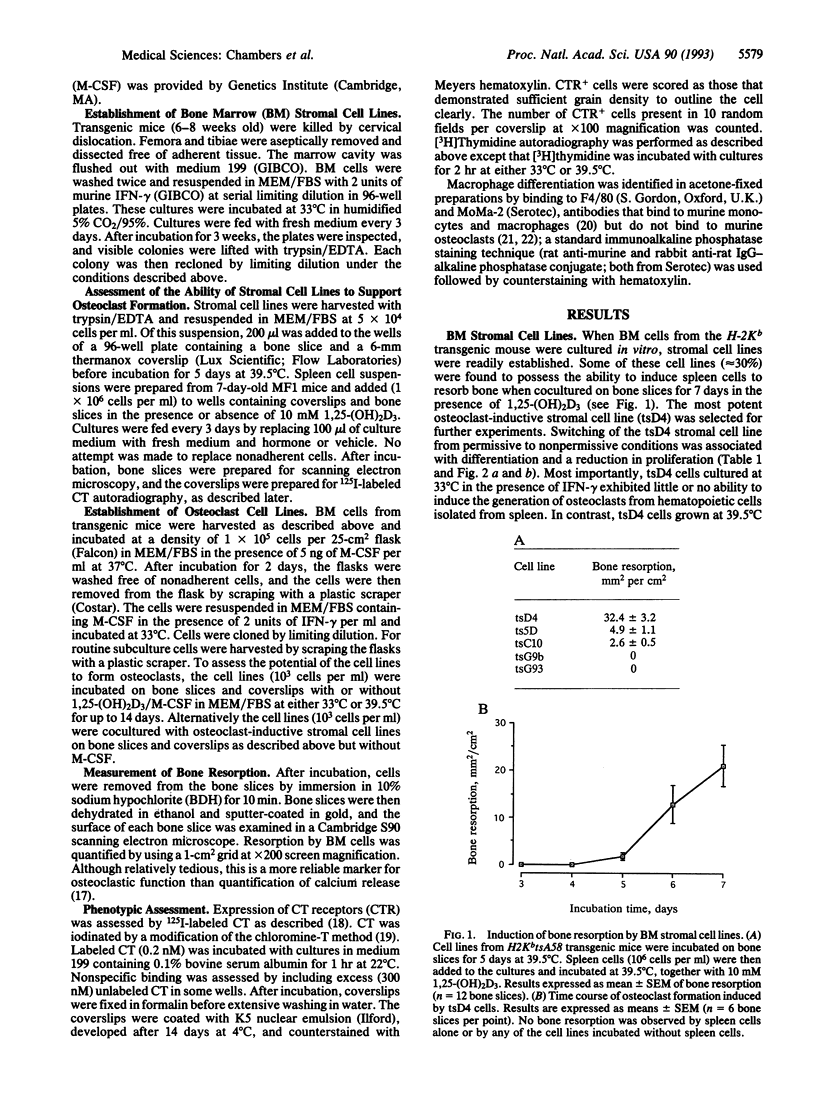
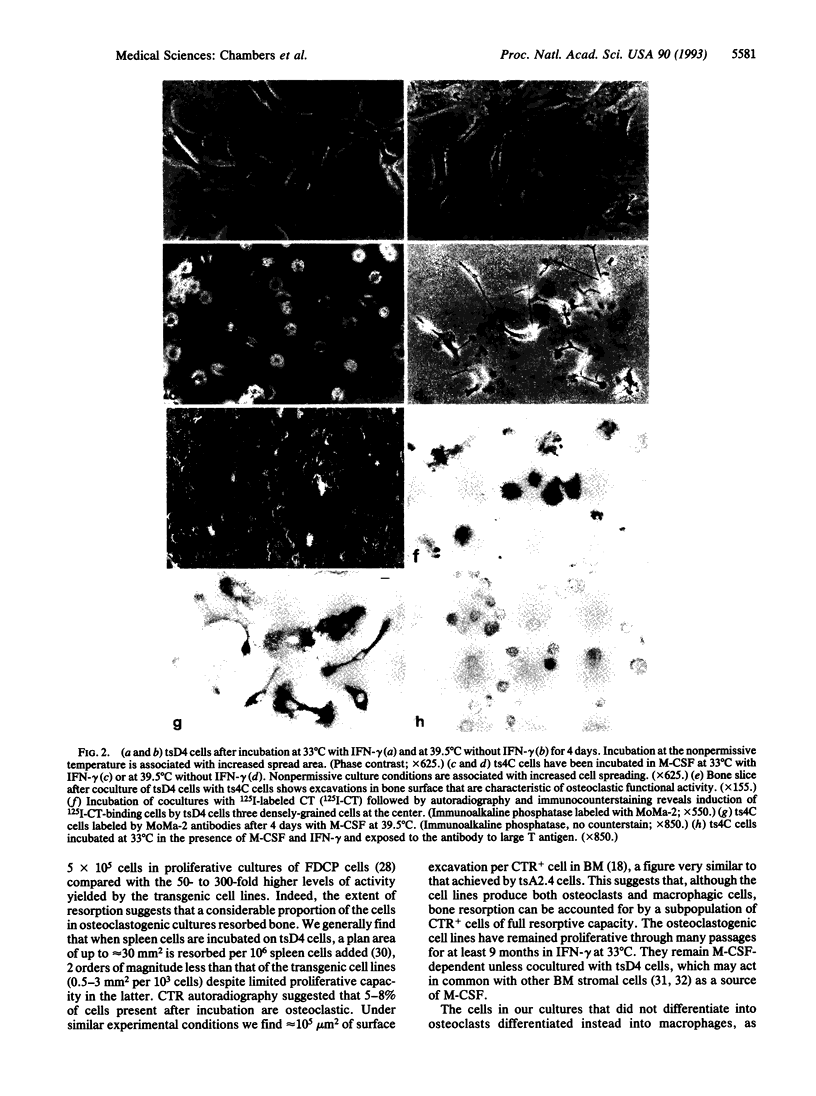
The development of osteoclastic cell lines would greatly facilitate analysis of the cellular and molecular biology of bone resorption. Several cell lines have previously been reported to be capable of osteoclastic differentiation. However, such cell lines form at best only occasional excavations, suggesting that osteoclastic differentiation is either incomplete or that osteoclasts represent a very small proportion of the cells present. We have used the recently developed H-2KbtsA58 transgenic mouse, in which the interferon-inducible major mouse histocompatibility complex H-2Kb promoter drives the temperature-sensitive (ts) immortalizing gene of simian virus 40 (tsA58), to develop cell lines from bone marrow with high efficiency. Bone marrow cells were incubated with gamma interferon at 33 degrees C, then cloned, and expanded. The cell lines were characterized at 39.5 degrees C in the absence of gamma interferon. First, stromal cell lines were established that induced osteclast formation (resorption of bone slices) when cocultured with hemopoietic spleen cells. Some of the stromal cell lines so generated were able to resorb approximately 30 mm2/cm2 of bone surface. We then established cell lines of hemopoietic origin, several of which possess osteoclastic potential. When these osteoclast-precursor cell lines were cocultured with stromal cell lines, extensive bone resorption was observed. Osteoclast formation did not occur if the precursor cell lines were incubated on bone slices without stromal cells; osteoclast formation was also dependent upon the presence of 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. These cell lines represent a model for osteoclast formation and a valuable resource for identification of the mechanisms and factors that regulate osteoclast differentiation and function.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abboud S. L., Pinzani M. Peptide growth factors stimulate macrophage colony-stimulating factor in murine stromal cells. Blood. 1991 Jul 1;78(1):103–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benayahu D., Horowitz M., Zipori D., Wientroub S. Hemopoietic functions of marrow-derived osteogenic cells. Calcif Tissue Int. 1992 Sep;51(3):195–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00334547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billecocq A., Emanuel J. R., Levenson R., Baron R. 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 regulates the expression of carbonic anhydrase II in nonerythroid avian bone marrow cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6470–6474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Horton M. A. Failure of cells of the mononuclear phagocyte series to resorb bone. Calcif Tissue Int. 1984 Sep;36(5):556–558. doi: 10.1007/BF02405365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Revell P. A., Fuller K., Athanasou N. A. Resorption of bone by isolated rabbit osteoclasts. J Cell Sci. 1984 Mar;66:383–399. doi: 10.1242/jcs.66.1.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. A., Chambers T. J. Effect of prostaglandins E1, E2, and F2 alpha on osteoclast formation in mouse bone marrow cultures. J Bone Miner Res. 1991 Feb;6(2):157–164. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650060209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederiksen K., Jat P. S., Valtz N., Levy D., McKay R. Immortalization of precursor cells from the mammalian CNS. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller K., Chambers T. J. Generation of osteoclasts in cultures of rabbit bone marrow and spleen cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Sep;132(3):441–452. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041320306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattei V., Bernabei P. A., Pinto A., Bezzini R., Ringressi A., Formigli L., Tanini A., Attadia V., Brandi M. L. Phorbol ester induced osteoclast-like differentiation of a novel human leukemic cell line (FLG 29.1). J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):437–447. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattersley G., Chambers T. J. Calcitonin receptors as markers for osteoclastic differentiation: correlation between generation of bone-resorptive cells and cells that express calcitonin receptors in mouse bone marrow cultures. Endocrinology. 1989 Sep;125(3):1606–1612. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-3-1606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattersley G., Chambers T. J. Generation of osteoclasts from hemopoietic cells and a multipotential cell line in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Sep;140(3):478–482. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattersley G., Owens J., Flanagan A. M., Chambers T. J. Macrophage colony stimulating factor (M-CSF) is essential for osteoclast formation in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 31;177(1):526–531. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92015-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume D. A., Loutit J. F., Gordon S. The mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localization of antigen F4/80: macrophages of bone and associated connective tissue. J Cell Sci. 1984 Mar;66:189–194. doi: 10.1242/jcs.66.1.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jat P. S., Noble M. D., Ataliotis P., Tanaka Y., Yannoutsos N., Larsen L., Kioussis D. Direct derivation of conditionally immortal cell lines from an H-2Kb-tsA58 transgenic mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jat P. S., Sharp P. A. Large T antigens of simian virus 40 and polyomavirus efficiently establish primary fibroblasts. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):746–750. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.746-750.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerby J. A., Hattersley G., Collins D. A., Chambers T. J. Derivation of osteoclasts from hematopoietic colony-forming cells in culture. J Bone Miner Res. 1992 Mar;7(3):353–362. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650070316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama H., Yamasaki A., Nose M., Niida S., Ohgame Y., Abe M., Kumegawa M., Suda T. Congenital osteoclast deficiency in osteopetrotic (op/op) mice is cured by injections of macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):269–272. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraal G., Rep M., Janse M. Macrophages in T and B cell compartments and other tissue macrophages recognized by monoclonal antibody MOMA-2. An immunohistochemical study. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Dec;26(6):653–661. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSheehy P. M., Chambers T. J. Osteoblastic cells mediate osteoclastic responsiveness to parathyroid hormone. Endocrinology. 1986 Feb;118(2):824–828. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-2-824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble M., Groves A. K., Ataliotis P., Jat P. S. From chance to choice in the generation of neural cell lines. Brain Pathol. 1992 Jan;2(1):39–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Yamana H., Yoshiki S., Roodman G. D., Mundy G. R., Jones S. J., Boyde A., Suda T. Osteoclast-like cell formation and its regulation by osteotropic hormones in mouse bone marrow cultures. Endocrinology. 1988 Apr;122(4):1373–1382. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-4-1373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tushinski R. J., Oliver I. T., Guilbert L. J., Tynan P. W., Warner J. R., Stanley E. R. Survival of mononuclear phagocytes depends on a lineage-specific growth factor that the differentiated cells selectively destroy. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90376-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udagawa N., Takahashi N., Akatsu T., Sasaki T., Yamaguchi A., Kodama H., Martin T. J., Suda T. The bone marrow-derived stromal cell lines MC3T3-G2/PA6 and ST2 support osteoclast-like cell differentiation in cocultures with mouse spleen cells. Endocrinology. 1989 Oct;125(4):1805–1813. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-4-1805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead R. H., VanEeden P. E., Noble M. D., Ataliotis P., Jat P. S. Establishment of conditionally immortalized epithelial cell lines from both colon and small intestine of adult H-2Kb-tsA58 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):587–591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor-Jedrzejczak W., Bartocci A., Ferrante A. W., Jr, Ahmed-Ansari A., Sell K. W., Pollard J. W., Stanley E. R. Total absence of colony-stimulating factor 1 in the macrophage-deficient osteopetrotic (op/op) mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4828–4832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda T., Alsina M. M., Garcia J. L., Mundy G. R. Differentiation of HL-60 cells into cells with the osteoclast phenotype. Endocrinology. 1991 Aug;129(2):683–689. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-2-683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Hayashi S., Kunisada T., Ogawa M., Nishikawa S., Okamura H., Sudo T., Shultz L. D., Nishikawa S. The murine mutation osteopetrosis is in the coding region of the macrophage colony stimulating factor gene. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):442–444. doi: 10.1038/345442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]